spring security简介与使用
spring security
spring security使用目的:验证,授权,攻击防护。原理:创建大量的filter和interceptor来进行请求的验证和拦截,以此来达到安全的效果。
新建一个springboot项目
创建一个springboot项目,添加一个
/helloController
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
}
这样,这个/hello是可以默认访问,返回一个hello字符串。
添加spring security
向pom.xml中添加security依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
这样在启动的时候会在控制台显示随机生成的密码。
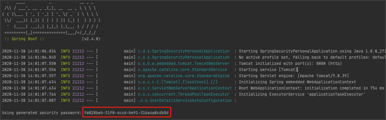
这时访问http://localhost:8080/hello会重定向到http://localhost:8080/login,这个页面是spring默认的。
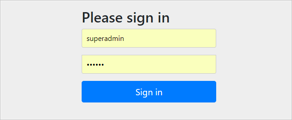
登录
使用默认用户和随机生成的密码登录
spring security 默认的用户名是user,spring security启动的时候会生成默认密码(在启动日志中可以看到)。
我们填入user 和 上图显示的fa028beb-31f0-4ccd-be91-31ba4a0cdb8d,那么就会正常的访问/hello。
使用yaml文件定义的用户名、密码登录
在application.yaml中定义用户名密码:
spring:
security:
user:
name: root
password: root
使用root/root登录,可以正常访问/hello。
使用代码中指定的用户名、密码登录
- 使用configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder) 添加认证。
- 使用configure(httpSecurity) 添加权限
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth
.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("admin") // 添加用户admin
.password("{noop}admin") // 不设置密码加密
.roles("ADMIN", "USER")// 添加角色为admin,user
.and()
.withUser("user") // 添加用户user
.password("{noop}user")
.roles("USER")
.and()
.withUser("tmp") // 添加用户tmp
.password("{noop}tmp")
.roles(); // 没有角色
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/product/**").hasRole("USER") //添加/product/** 下的所有请求只能由user角色才能访问
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") //添加/admin/** 下的所有请求只能由admin角色才能访问
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 没有定义的请求,所有的角色都可以访问(tmp也可以)。
.and()
.formLogin().and()
.httpBasic();
}
}
添加AdminController、ProductController
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/admin")
public class AdminController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "admin hello";
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/product")
public class ProductController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "product hello";
}
}
通过上面的设置,访问http://localhost:8080/admin/hello只能由admin访问,http://localhost:8080/product/hello admin和user都可以访问,http://localhost:8080/hello 所有用户(包括tmp)都可以访问。
使用数据库的用户名、密码登录
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
添加数据库配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
配置spring-security认证和授权
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)// 设置自定义的userDetailsService
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/product/**").hasRole("USER")
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated() //
.and()
.formLogin()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout");
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();// 使用不使用加密算法保持密码
// return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
如果需要使用BCryptPasswordEncoder,可以先在测试环境中加密后放到数据库中:
@Test
void encode() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
String password = bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("user");
String password2 = bCryptPasswordEncoder.encode("admin");
System.out.println(password);
System.out.println(password2);
}
配置自定义UserDetailsService来进行验证
@Component("userDetailsService")
public class CustomUserDetailsService implements UserDetailsService {
@Autowired
UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String login) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
// 1. 查询用户
User userFromDatabase = userRepository.findOneByLogin(login);
if (userFromDatabase == null) {
//log.warn("User: {} not found", login);
throw new UsernameNotFoundException("User " + login + " was not found in db");
//这里找不到必须抛异常
}
// 2. 设置角色
Collection<GrantedAuthority> grantedAuthorities = new ArrayList<>();
GrantedAuthority grantedAuthority = new SimpleGrantedAuthority(userFromDatabase.getRole());
grantedAuthorities.add(grantedAuthority);
return new org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User(login,
userFromDatabase.getPassword(), grantedAuthorities);
}
}
配置JPA中的UserRepository
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findOneByLogin(String login);
}
添加数据库数据

CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(28) NOT NULL,
`login` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`role` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8mb4_general_ci DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_general_ci;
INSERT INTO `demo`.`user`(`id`, `login`, `password`, `role`) VALUES (1, 'user', 'user', 'ROLE_USER');
INSERT INTO `demo`.`user`(`id`, `login`, `password`, `role`) VALUES (2, 'admin', 'admin', 'ROLE_ADMIN');
默认角色前缀必须是
ROLE_,因为spring-security会在授权的时候自动使用match中的角色加上ROLE_后进行比较。
获取登录信息
@RequestMapping("/info")
public String info(){
String userDetails = null;
Object principal = SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();
if(principal instanceof UserDetails) {
userDetails = ((UserDetails)principal).getUsername();
}else {
userDetails = principal.toString();
}
return userDetails;
}
使用SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal();获取当前的登录信息。
Spring Security 核心组件
SecurityContext
SecurityContext是安全的上下文,所有的数据都是保存到SecurityContext中。
可以通过SecurityContext获取的对象有:
- Authentication
SecurityContextHolder
SecurityContextHolder用来获取SecurityContext中保存的数据的工具。通过使用静态方法获取SecurityContext的相对应的数据。
SecurityContext context = SecurityContextHolder.getContext();
Authentication
Authentication表示当前的认证情况,可以获取的对象有:
UserDetails:获取用户信息,是否锁定等额外信息。
Credentials:获取密码。
isAuthenticated:获取是否已经认证过。
Principal:获取用户,如果没有认证,那么就是用户名,如果认证了,返回UserDetails。
UserDetails
public interface UserDetails extends Serializable {
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities();
String getPassword();
String getUsername();
boolean isAccountNonExpired();
boolean isAccountNonLocked();
boolean isCredentialsNonExpired();
boolean isEnabled();
}
UserDetailsService
UserDetailsService可以通过loadUserByUsername获取UserDetails对象。该接口供spring security进行用户验证。
通常使用自定义一个CustomUserDetailsService来实现UserDetailsService接口,通过自定义查询UserDetails。
AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager用来进行验证,如果验证失败会抛出相对应的异常。
PasswordEncoder
密码加密器。通常是自定义指定。
BCryptPasswordEncoder:哈希算法加密
NoOpPasswordEncoder:不使用加密
spring security session 无状态支持权限控制(前后分离)
spring security会在默认的情况下将认证信息放到HttpSession中。
但是对于我们的前后端分离的情况,如app,小程序,web前后分离等,httpSession就没有用武之地了。这时我们可以通过
configure(httpSecurity)设置spring security是否使用httpSession。
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// code...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
//设置无状态,所有的值如下所示。
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
// code...
}
// code...
}
共有四种值,其中默认的是ifRequired。
- always – a session will always be created if one doesn’t already exist,没有session就创建。
- ifRequired – a session will be created only if required (default),如果需要就创建(默认)。
- never – the framework will never create a session itself but it will use one if it already exists
- stateless – no session will be created or used by Spring Security 不创建不使用session
由于前后端不通过保存session和cookie来进行判断,所以为了保证spring security能够记录登录状态,所以需要传递一个值,让这个值能够自我验证来源,同时能够得到数据信息。选型我们选择JWT。对于java客户端我们选择使用jjwt。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-api</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-impl</artifactId>
<version>0.11.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt-jackson</artifactId> <!-- or jjwt-gson if Gson is preferred -->
<version>0.11.2</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
创建工具类JWTProvider
JWTProvider需要至少提供两个方法,一个用来创建我们的token,另一个根据token获取Authentication。
provider需要保证Key密钥是唯一的,使用init()构建,否则会抛出异常。
@Component
@Slf4j
public class JWTProvider {
private Key key; // 私钥
private long tokenValidityInMilliseconds; // 有效时间
private long tokenValidityInMillisecondsForRememberMe; // 记住我有效时间
@Autowired
private JJWTProperties jjwtProperties; // jwt配置参数
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
byte[] keyBytes;
String secret = jjwtProperties.getSecret();
if (StringUtils.hasText(secret)) {
log.warn("Warning: the JWT key used is not Base64-encoded. " +
"We recommend using the `jhipster.security.authentication.jwt.base64-secret` key for optimum security.");
keyBytes = secret.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} else {
log.debug("Using a Base64-encoded JWT secret key");
keyBytes = Decoders.BASE64.decode(jjwtProperties.getBase64Secret());
}
this.key = Keys.hmacShaKeyFor(keyBytes); // 使用mac-sha算法的密钥
this.tokenValidityInMilliseconds =
1000 * jjwtProperties.getTokenValidityInSeconds();
this.tokenValidityInMillisecondsForRememberMe =
1000 * jjwtProperties.getTokenValidityInSecondsForRememberMe();
}
public String createToken(Authentication authentication, boolean rememberMe) {
long now = (new Date()).getTime();
Date validity;
if (rememberMe) {
validity = new Date(now + this.tokenValidityInMillisecondsForRememberMe);
} else {
validity = new Date(now + this.tokenValidityInMilliseconds);
}
User user = userRepository.findOneByLogin(authentication.getName());
Map<String ,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sub",authentication.getName());
map.put("user",user);
return Jwts.builder()
.setClaims(map) // 添加body
.signWith(key, SignatureAlgorithm.HS512) // 指定摘要算法
.setExpiration(validity) // 设置有效时间
.compact();
}
public Authentication getAuthentication(String token) {
Claims claims = Jwts.parserBuilder()
.setSigningKey(key)
.build()
.parseClaimsJws(token).getBody(); // 根据token获取body
User principal;
Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities;
principal = userRepository.findOneByLogin(claims.getSubject());
authorities = principal.getAuthorities();
return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, token, authorities);
}
}
注意这里我们创建的User需要实现UserDetails对象,这样我们可以根据
principal.getAuthorities()获取到权限,如果不实现UserDetails,那么需要自定义authorities并添加到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken中。
@Data
@Entity
@Table(name="user")
public class User implements UserDetails {
@Id
@Column
private Long id;
@Column
private String login;
@Column
private String password;
@Column
private String role;
@Override
// 获取权限,这里就用简单的方法
// 在spring security中,Authorities既可以是ROLE也可以是Authorities
public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() {
return Collections.singleton(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role));
}
@Override
public String getUsername() {
return login;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isAccountNonLocked() {
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired() {
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled() {
return true;
}
}
创建登录成功,登出成功处理器
登录成功后向前台发送jwt。
认证成功,返回jwt:
public class MyAuthenticationSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler{
void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException{
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(jwtProvider.createToken(authentication, true));
}
}
登出成功:
public class MyLogoutSuccessHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {
void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest var1, HttpServletResponse var2, Authentication var3) throws IOException, ServletException{
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("logout success");
writer.flush();
}
}
设置登录、登出、取消csrf防护
登出无法对token进行失效操作,可以使用数据库保存token,然后在登出时删除该token。
@Configuration
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// code...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
// code...
// 添加登录处理器
.formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/login").successHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(jwtProvider.createToken(authentication, true));
})
// 取消csrf防护
.and().csrf().disable()
// code...
// 添加登出处理器
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout").logoutSuccessHandler((HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("logout success");
writer.flush();
})
// code...
}
// code...
}
使用JWT集成spring-security
添加Filter供spring-security解析token,并向securityContext中添加我们的用户信息。
在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class之前我们需要执行根据token添加authentication。关键方法是从jwt中获取authentication,然后添加到securityContext中。
在SecurityConfiguration中需要设置Filter添加的位置。
创建自定义Filter,用于jwt获取authentication:
@Slf4j
public class JWTFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
private final static String HEADER_AUTH_NAME = "auth";
private JWTProvider jwtProvider;
public JWTFilter(JWTProvider jwtProvider) {
this.jwtProvider = jwtProvider;
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
String authToken = httpServletRequest.getHeader(HEADER_AUTH_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(authToken)) {
// 从自定义tokenProvider中解析用户
Authentication authentication = this.jwtProvider.getAuthentication(authToken);
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
// 调用后续的Filter,如果上面的代码逻辑未能复原“session”,SecurityContext中没有想过信息,后面的流程会检测出"需要登录"
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
向HttpSecurity添加Filter和设置Filter位置:
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
// code...
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
//设置添加Filter和位置
.and().addFilterBefore(new JWTFilter(jwtProvider), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
// code...
}
// code...
}
MySecurityConfiguration代码
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class MySecurityConfiguration extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Autowired
private JWTProvider jwtProvider;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService)// 设置自定义的userDetailsService
.passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder());
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)//设置无状态
.and()
.authorizeRequests() // 配置请求权限
.antMatchers("/product/**").hasRole("USER") // 需要角色
.antMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated() // 所有的请求都需要登录
.and()
// 配置登录url,和登录成功处理器
.formLogin().loginProcessingUrl("/login").successHandler((request, response, authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println(jwtProvider.createToken(authentication, true));
})
// 取消csrf防护
.and().csrf().disable()
.httpBasic()
// 配置登出url,和登出成功处理器
.and().logout().logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessHandler((HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication) -> {
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
writer.println("logout success");
writer.flush();
})
// 在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter之前执行我们添加的JWTFilter
.and().addFilterBefore(new JWTFilter(jwtProvider), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return NoOpPasswordEncoder.getInstance();
}
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) {
// 添加不做权限的URL
web.ignoring()
.antMatchers("/swagger-resources/**")
.antMatchers("/swagger-ui.html")
.antMatchers("/webjars/**")
.antMatchers("/v2/**")
.antMatchers("/h2-console/**");
}
}
使用注解对方法进行权限管理
需要在
MySecurityConfiguration上添加@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)注解,prePostEnabled默认为false,需要设置为true后才能全局的注解权限控制。
prePostEnabled设置为true后,可以使用四个注解:
添加实体类School:
@Data
public class School implements Serializable {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
}
-
@PreAuthorize
在访问之前就进行权限判断
@RestController public class AnnoController { @Autowired private JWTProvider jwtProvider; @RequestMapping("/annotation") // @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')") public String info(){ return "拥有admin权限"; } }hasRole和hasAuthority都会对UserDetails中的getAuthorities进行判断区别是hasRole会对字段加上
ROLE_后再进行判断,上例中使用了hasRole('ADMIN'),那么就会使用ROLE_ADMIN进行判断,如果是hasAuthority('ADMIN'),那么就使用ADMIN进行判断。 -
@PostAuthorize
在请求之后进行判断,如果返回值不满足条件,会抛出异常,但是方法本身是已经执行过了的。
@RequestMapping("/postAuthorize") @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PostAuthorize("returnObject.id%2==0") public School postAuthorize(Long id) { School school = new School(); school.setId(id); return school; }returnObject是内置对象,引用的是方法的返回值。
如果
returnObject.id%2==0为 true,那么返回方法值。如果为false,会返回403 Forbidden。 -
@PreFilter
在方法执行之前,用于过滤集合中的值。
@RequestMapping("/preFilter") @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PreFilter("filterObject%2==0") public List<Long> preFilter(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids) { return ids; }filterObject是内置对象,引用的是集合中的泛型类,如果有多个集合,需要指定filterTarget。@PreFilter(filterTarget="ids", value="filterObject%2==0") public List<Long> preFilter(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids,@RequestParam("ids") List<User> users,) { return ids; }filterObject%2==0会对集合中的值会进行过滤,为true的值会保留。第一个例子返回的值在执行前过滤返回2,4。

-
@PostFilter
会对返回的集合进行过滤。
@RequestMapping("/postFilter") @PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')") @PostFilter("filterObject.id%2==0") public List<School> postFilter() { List<School> schools = new ArrayList<School>(); School school; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { school = new School(); school.setId((long)i); schools.add(school); } return schools; }上面的方法返回结果为:id为0,2,4,6,8的School对象。

