1)介绍
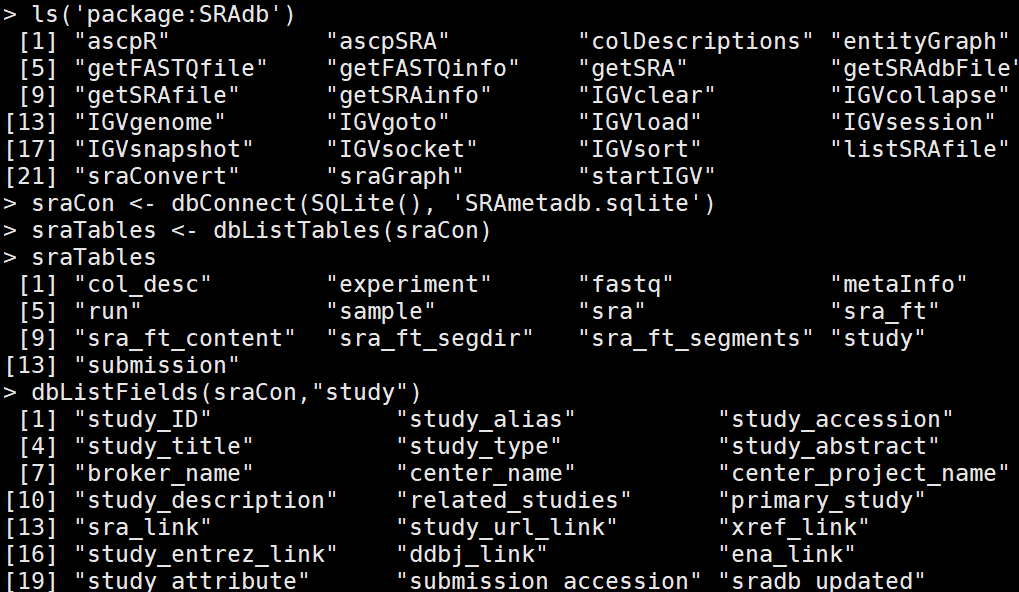
我们用SRAdb library来对SRA数据进行处理。 SRAdb 可以更方便更快的接入 metadata associated with submission, 包括study, sample, experiment, and run. SRAdb 包通过 NCBI SRA数据库中的metadata信息 作用. 首先dbConnect ()接入 R system 中的local database systems, 所有的搜索就在本地文件的基础上进行。
the queries we tried with the dbGetQuery function are passed in the form of SQL queries, which is a Select From Where framework. This part actually requires the
RSQLite package, which is installed when installing the SRAdb package, as a dependency. The getSRA function can actually do a full text search in the SRA data again via RSQLite and fetch the data in the selected fields for the query.
2)下载
source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R")
biocLite("SRAdb")
library(SRAdb)
3)了解SRA database
#sqlFile <- getSRAdbFile() #在线获取,太大了,不要这样做。
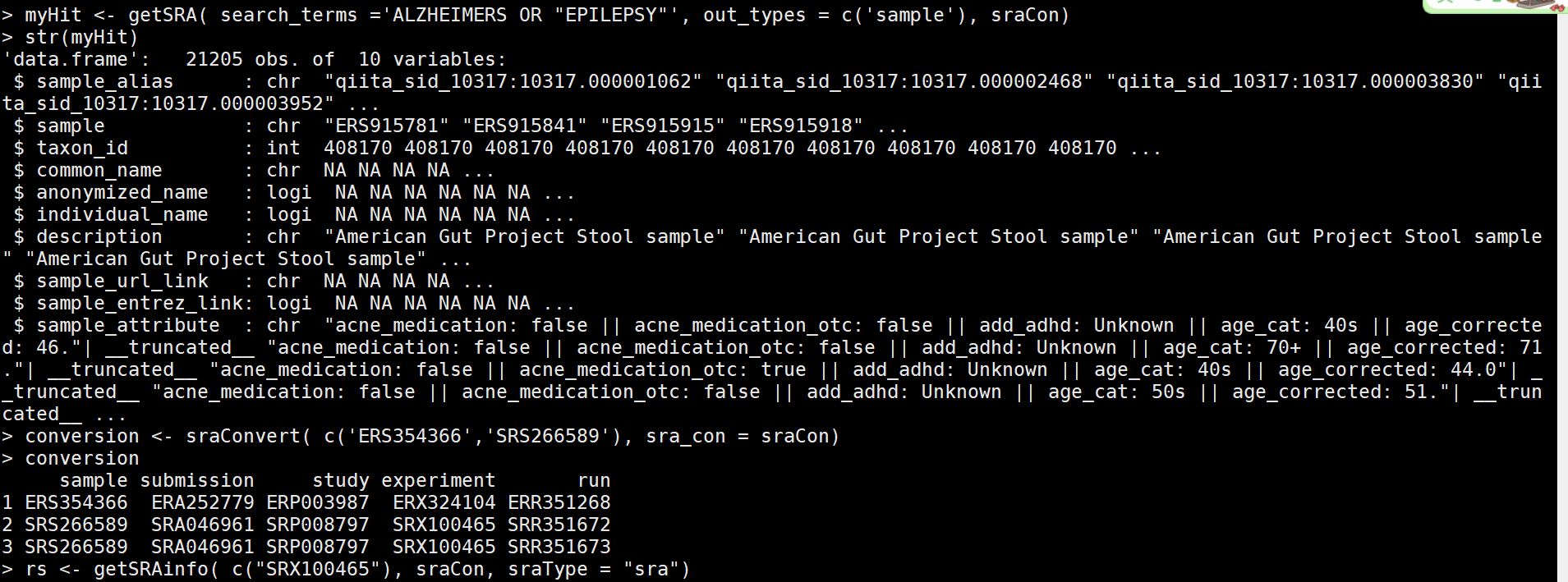
sraCon <- dbConnect(SQLite(), 'SRAmetadb.sqlite') #于是我下载了这个文件,压缩文件2个G(解压后36个G),然后读取了这个文件,相当于下载nr库到本地。 sraTables <- dbListTables(sraCon) # investigate the content of the database dbListFields(sraCon,"study") #########关键词keyword: embryo myHit <- dbGetQuery(sraCon, paste("select study_accession,study_title from study where","study_description like'%embryo'",sep=" ")) # myHit <- getSRA( search_terms = "brain", out_types = c('run','study'), sraCon) #free text收索 myHit <- getSRA( search_terms ='Alzheimers OR "EPILEPSY"', out_types = c('sample'), sraCon) #逻辑收索
4)从SRA database下载数据
myHit <- getSRA( search_terms ='ALZHEIMERS OR "EPILEPSY"', out_types = c('sample'), sraCon) #关键词收索
conversion <- sraConvert( c('ERS354366','SRS266589'), sra_con = sraCon) #选择其中的2个,查看信息
conversion
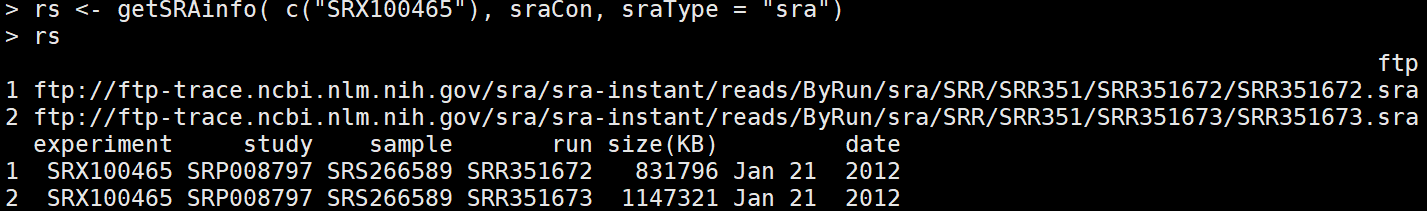
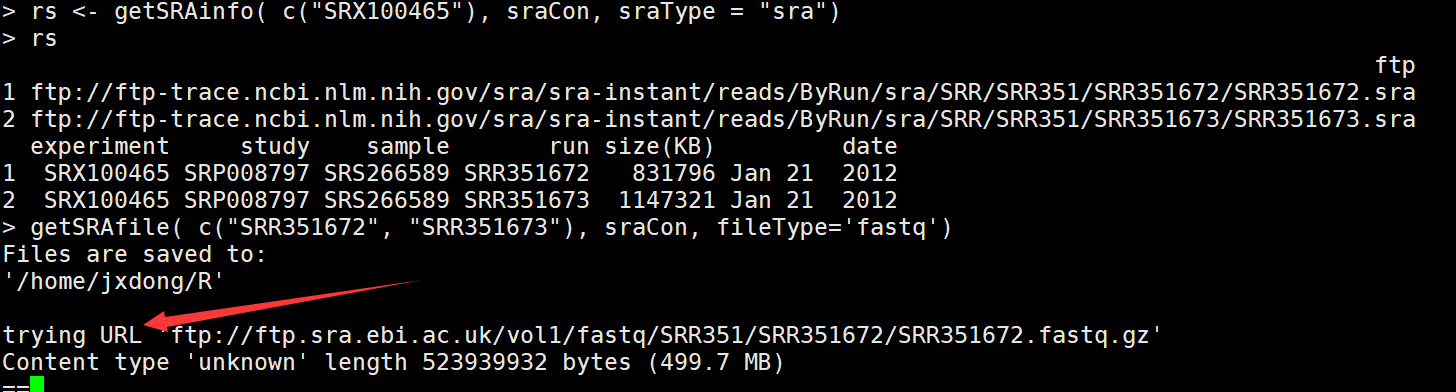
rs <- getSRAinfo( c("SRX100465"), sraCon, sraType = "sra") #选择其中一个看相应的信息,会显示出ftp地址
getSRAfile( c("SRR351672", "SRR351673"), sraCon, fileType='fastq') ##下载感兴趣的run
5)下载完fq文件后,用R进行读取
install.packages("R.utils")
library(R.utils) #下载数据用
download.file(url="ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/SRA000/SRA000241/SRX000122/SRR000648.fastq.bz2", destfile = "SRR000648.fastq.bz2")
bunzip2(list.files(pattern = ".fastq.bz2$")) #解压
biocLite("ShortRead")
library(ShortRead) #读取fq文件
MyFastq <- readFastq(getwd(), pattern=".fastq") #小心运行,要至少8G内存
readLines("SRR000648.fastq", 4) # first four lines of the file
6)下载并读取比对数据(bam)
download.file(url="http://genome.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/help/examples/bamExample.bam", destfile = "bamExample.bam") library(Rsamtools) bam <- scanBam("bamExample.bam") #读取bam names(bam[[1]]) #查看bam的信息 countBam("bamExample.bam") #统计bam信息 what <- c("rname", "strand", "pos", "qwidth", "seq") #只读取其中的几列 param <- ScanBamParam(what=what) bam2 <- scanBam("bamExample.bam", param=param) names(bam2[[1]]) bam_df <- do.call("DataFrame", bam[[1]]) # Read the data as a DataFrame object head(bam_df) table(bam_df$rname == '21' & bam_df$flag == 16) #提取符合指定要求的sequences,即flag=16为reverse strands

7)对原始raw NGS data 的预处理
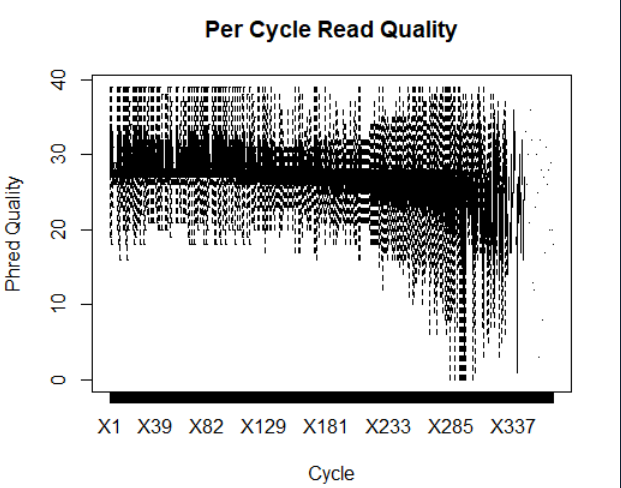
prefetch SRR000648 prefetch SRR000657 fastq-dump --split-3 -O ./ SRR000657 fastq-dump --split-3 -O ./ SRR000648 library(ShortRead) myFiles <- list.files(getwd(), "fastq", full=TRUE) myFQ <- lapply(myFiles, readFastq) myQual <- FastqQuality(quality(quality(myFQ[[1]]))) #读取质量 readM <- as(myQual, "matrix") #将质控转化为矩阵 boxplot(data.frame(readM), outline = FALSE, main="Per Cycle Read Quality", xlab="Cycle", ylab="Phred Quality") #画箱型图