前面我们讲过GO.db这个包,现在接着延伸topGO包,该包是用来协助GO富集分析
1)安装
if("topGO" %in% rownames(installed.packages()) == FALSE) {source("http://bioconductor.org/biocLite.R");biocLite("topGO")}
suppressMessages(library(topGO))
ls("package:topGO")
2)使用方法
该包主要有三个使用步骤:
2.1、Data preparation:准备数据集,用于构建 topGOdata.对象。
2.1.1、包括gene标识符(List of genes identifiers)及相应的分值gene scores(例如p值等)
2.1.2、差异表达基因list或经一定标准按照分值筛选的基因集用于后续分析(list of differentially expressed genes or a criteria for selecting genes
based on their scores);
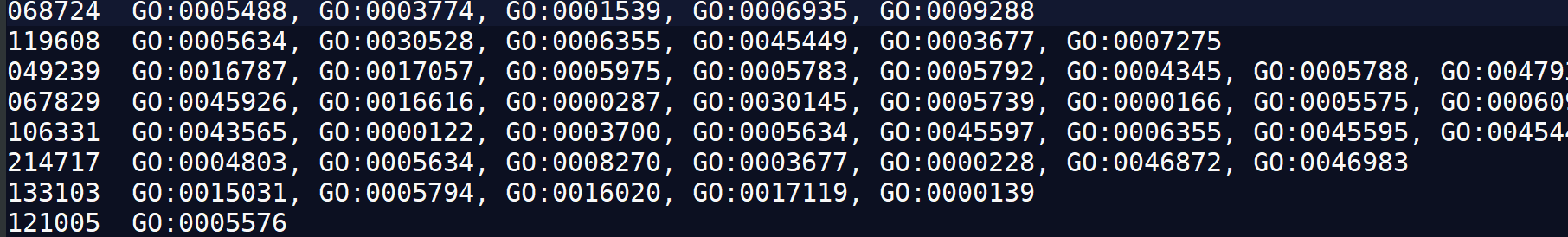
2.1.3、identifier和GO term间的map,即GOterm表:(gene-to-GO annotations ) ####例如测试文件中的geneid2go.map
2.1.4、GO的层级结构,由GO.db提供,目前这个包只支持GO.db提供的结构
goterm表示例(gene-to-GO annotations ):
2.2、Running enrichment tests:进行富集分析,用任何可行的混合统计测试和方法来处理 GO拓扑结构(GO topology)
2.3、Analysis results:用 summary functions 和 visualisation tools对第二步进行统计和可视化
3)简单示例(guide)
3.1.1、准备输入文件
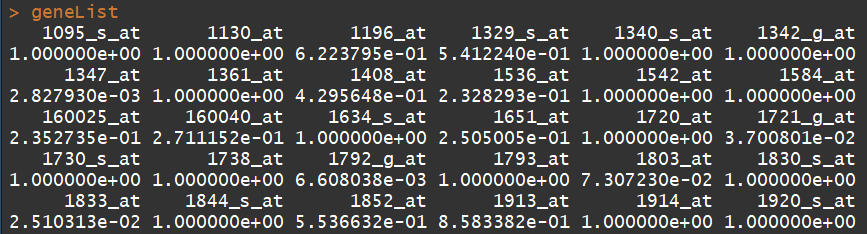
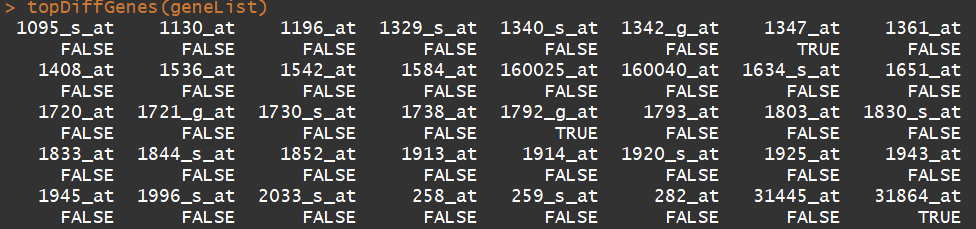
library(ALL) data(ALL) data(geneList) ##文件1:基因list, affyLib <- paste(annotation(ALL), "db", sep = ".") #####"hgu95av2.db" library(package = affyLib, character.only = TRUE) ########GO term表 sum(topDiffGenes(geneList) ###选择差异基因集,
3.1.2、构建 topGOdata对象(核心步骤):
sampleGOdata <- new("topGOdata",
description = "Simple session", ##topGOdata的描述,可选
ontology = "BP", ##可指定要分析的GO term的类型,即BP、CC之类
allGenes = geneList, ##基因identifier的原始列表
geneSel = topDiffGenes, ##geneSelectionFun联合作用,筛选出后续参与分析的基因
nodeSize = 10, ##富集的GO term辖下基因的最小数目,这里选择10.即最少10个
annot = annFUN.db, ##提取gene-to-GO mappings 的对应关系
affyLib = affyLib)
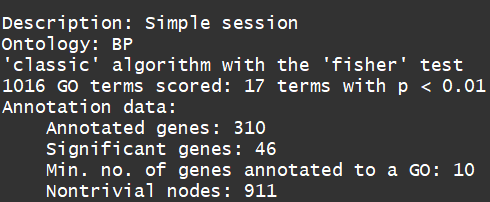
sampleGOdata

3.2 Performing the enrichment tests
有了topGOdata对象,接下来就可以用来进行富集分析。这里用两种检验方法:Fisher’s exact test (基于 gene counts)和Kolmogorov-Smirnov like test (computes enrichment based on gene scores)。
其中用runTest函数来进行这些检验,该函数含有3个参数:第一个是topGOdata对象、第二个是algorithm(用于指定处理 GO graph structured的方法)、第三个是statistic(用于指定检验方法)
resultFisher <- runTest(sampleGOdata, algorithm = "classic", statistic = "fisher") ##Fisher’s exact test
resultKS <- runTest(sampleGOdata, algorithm = "classic", statistic = "ks") #Kolmogorov-Smirnov test,classic method
resultKS.elim <- runTest(sampleGOdata, algorithm = "elim", statistic = "ks")#Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, elim method
3.3 Analysis of results
当富集检验结束后,我们就可以分析并解析结果。
runTest()这个函数用来分析显著富集的 GO terms及其相应的p值。
allRes <- GenTable(sampleGOdata, ##之前构建的topGOdata实例
classicFisher = resultFisher, ##生成GO graphde的方法
classicKS = resultKS, ##生成GO graphde的方法
elimKS = resultKS.elim, ##生成GO graphde的方法
orderBy = "elimKS",
ranksOf = "classicFisher",
topNodes = 10) ##这里显示前10个显著结果
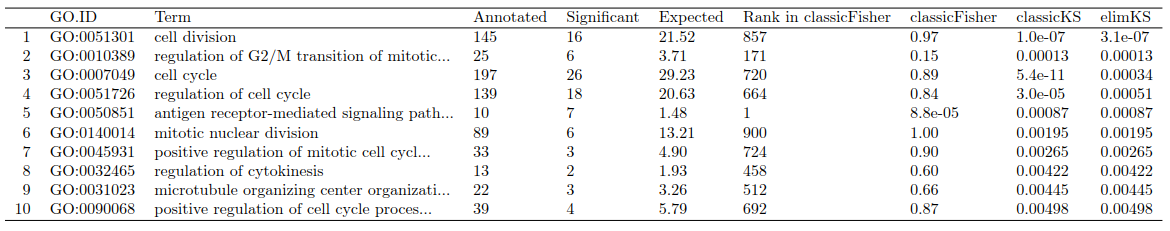
用 score()函数来测评topGO结果对象中 GO term的 p-values ,并用散点图来说明。
pValue.classic <- score(resultKS)
pValue.elim <- score(resultKS.elim)[names(pValue.classic)]
gstat <- termStat(sampleGOdata, names(pValue.classic))
gSize <- gstat$Annotated / max(gstat$Annotated) * 4
plot(pValue.classic, pValue.elim, xlab = "p-value classic", ylab = "p-value elim",pch = 19, cex = gSize)
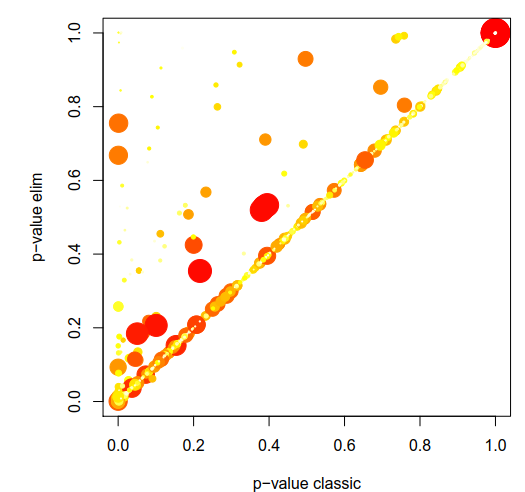
差看显著富集的GO terms在 GO graph中的分布.
showSigOfNodes(sampleGOdata, score(resultKS.elim), firstSigNodes = 5, useInfo = 'all')
4)实战
4.1 原始数据集的准备(上面的4个文件)
library(topGO) library(ALL) ##准备数据集 data(ALL) ##文件1:原始数据集 BPterms <- ls(GOBPTerm) MFterms <- ls(GOMFTerm) CCterms <- ls(GOCCTerm) head(BPterms) head(MFterms) head(CCterms) library(genefilter) ##对原始数据进行过滤 selProbes <- genefilter(ALL, filterfun(pOverA(0.20, log2(100)), function(x) (IQR(x) > 0.25)))#数据清洗 eset <- ALL[selProbes, ] ##数据清洗:这里去掉及其低表达的基因,及探针在每个样品中表达变化不大的的基因
myInterestingGenes <- sample(geneNames, length(geneNames) / 10) #文件二:经一定标准对p值等筛选获取感兴趣基因集用于后续分析
geneList <- factor(as.integer(geneNames %in% myInterestingGenes))
names(geneList) <- geneNames
str(geneList)
geneID2GO <- readMappings(file = system.file("examples/geneid2go.map", package = "topGO"))##文件三:goterm的map文件
str(head(geneID2GO))
GO2geneID <- inverseList(geneID2GO) ###额外知识:用inverseList()函数实现gene-to-GOs与 GO-to-genes 之间的转换
str(head(GO2geneID)) ##


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号