Spring中基于注解的IOC(一):基础介绍
1. Spring中的常用注解
注解配置和xml配置要实现的功能都是一样的,都要降低程序的耦合,只是配置的形式不一样
xml中配置示例:
注解分类:
1.用于创建对象的注解
它们的作用就和在xml中编写一个bean标签是一样的
2.用于注入数据的注解
它们的作用就和在xml中bean标签中写一个property标签是一样的
3.用于改变作用范围的注解
它们的作用就和在xml中bean标签中使用scope属性实现的功能是一样的
4.和生命周期相关的注解
它们的作用就和在bean标签中使用init-method和destroy-method属性是一样的
1.1 用于创建对象的注解
相当于:
(1)@Component
作用:
用于把当前类对象存入Spring容器中,相当于在 xml 中配置一个 bean。
属性:
value:用于指定bean的id,当我们不写时,它的默认值是当前类名且首字母改小写
如果注解中有一个属性,且这个属性是value时,可以省略value=,即一个省略属性的值,就是value的值
示例:
对于注解配置,我们需要修改配置文件xml
查找约束文件
bean.xml
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
IAccountDao.java
package cn.cqu.dao;
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
*模拟保存账户
*/
void saveAccount();
}
AccountDaoImpl.java
package cn.cqu.dao.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*
*
*scope="" init-method="" destroy-method="">
*
*
*/
@Component("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户");
}
}
Client.java
package cn.cqu.ui;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 获取spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象
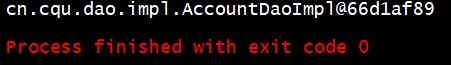
IAccountDao dao = ac.getBean("accountDao",IAccountDao.class);
System.out.println(dao);
}
}
(2)@Controller
一般用于控制层
(3)@Service
一般用于服务层
(4)@Repository
一般用于持久层
以上三个注解它们的作用和属性和@Component是一模一样的
它们三个是spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使我们的三层对象更加清晰
细节:如果注解中有且只有一个属性要赋值时,且名称是 value,value 在赋值是可以不写。
1.2 用于注入数据的注解
相当于:
(1)@Autowired
出现位置:
可以是成员变量上,也可以是方法上
细节:
在使用注解注入时,set方法就不是必须的了
作用:
自动按照类型注入,只要容器中有一个唯一的一个bean对象类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,就可以注入成功
如果IOC容器中没有任何bean的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错
示例代码:
package cn.cqu.dao;
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
*模拟保存账户
*/
void saveAccount();
}
package cn.cqu.dao.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*
*/
@Component("accountDao")
public class AccountDaoImpl {//implements IAccountDao
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户");
}
}
注意此处我们对implements IAccountDao进行了注释,即AccountDaoImpl不是IAccountDao类型了
package cn.cqu.service;
/**
* 账户的service层接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
void saveAccount();
}
package cn.cqu.service.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
package cn.cqu.ui;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 获取spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
as.saveAccount();
}
}
取消上述注释,成功运行
如果有多个类型匹配时,它先按照类型找到满足该类型的几个Object,然后根据变量名和key去匹配,如果在key中找不到与变量名匹配的,就报错
示例代码:
package cn.cqu.dao;
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
*模拟保存账户
*/
void saveAccount();
}
package cn.cqu.dao.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*
*/
@Component("accountDao1")
public class AccountDaoImpl1 implements IAccountDao{
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存了账户1111111");
}
}
package cn.cqu.dao.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*
*/
@Component("accountDao2")
public class AccountDaoImpl2 implements IAccountDao{
public void saveAccount() {
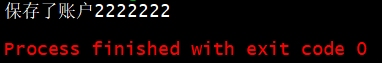
System.out.println("保存了账户2222222");
}
}
package cn.cqu.service;
/**
* 账户的service层接口
*/
public interface IAccountService {
void saveAccount();
}
package cn.cqu.service.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Autowired
private IAccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
}
package cn.cqu.ui;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 获取spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
as.saveAccount();
}
}
注意此时类AccountServiceImpl中仍然是
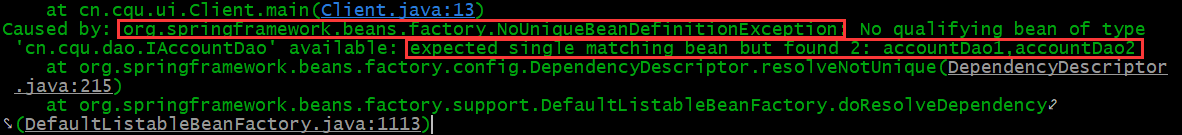
修改为
,运行结果如下
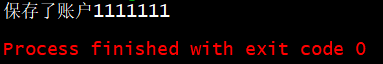
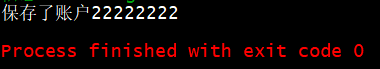
修改为
,运行结果如下
通过以上可以发现当有多个类型需要匹配时,我们需要修改属性变量名,但是通过以下注解@Qualifier与@Autowired我们就可以避免修改变量名
(2)Qualifier
作用:
按照类型注入的基础上再按照名称Qualifier中value值注入
它在给类成员注入时,不能单独使用,但是在给方法参数注入时可以
属性:
value:用于指定注入bean的id
注意:
@Qualifier必须和@Autowired一起使用
示例:
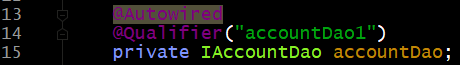
上述代码中,我们仍然使用accountDao,当加入注解@Qualifier
第一种:
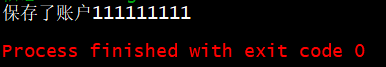
运行结果:
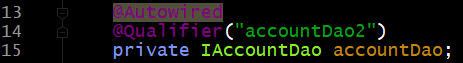
第二种:
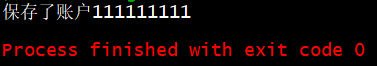
运行结果:

(3)Resource
作用:
直接按照bean的id注入,它可以独立使用
Resource可以直接指定bean的id,作用相当于@Qualifier必须和@Autowired一起使用的作用
属性:
name:用于指定bean的id
示例:
以上三个注解都只能注入其他类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现,
另外,集合类型的注入只能通过XML来实现
(4)@Value
作用:
用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据
属性:
value:用于指定数据的值,它可以使用Spring中的SpEL(即Spring的EL表达式)
SpEL写法:${表达式}
1.3 用于改变作用范围的注解
相当于:
Scope
作用:
用于指定bean的作用范围
属性:
value:指定范围的取值
常用取值:singleton、prototype
当我们不指定,默认情况下也是单例的
示例:
对上述代码中main方法中做如下修改
package cn.cqu.ui;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 获取spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象
IAccountService as01 = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
IAccountService as02 = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
System.out.println(as01==as02);
}
}

当我们使用@Scope注解设置它的value为prototype时
无锡人流医院哪家好 http://www.wxbhnkyy120.com/


1.4 和生命周期相关的注解
相当于:
(1)Predestroy
作用:
用于指定销毁方法
(2)PostConstruct
作用:
用于指定初始化方法
示例代码:
修改上述代码中AccountServiceImpl如下
package cn.cqu.service.impl;
import cn.cqu.dao.IAccountDao;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Service("accountService")
public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService {
@Resource(name="accountDao2")
private IAccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("初始化方法执行了");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("销毁方法执行了");
}
}
修改main如下
package cn.cqu.ui;
import cn.cqu.service.IAccountService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 获取spring的IOC核心容器,并根据id获取对象
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器对象
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据id获取bean对象
IAccountService as = ac.getBean("accountService",IAccountService.class);
as.saveAccount();
ac.close();
}
}
运行结果:

1.5 关于 Spring 注解和 XML 的选择问题
注解的优势:
配置简单,维护方便(我们找到类,就相当于找到了对应的配置)。
XML 的优势:
修改时,不用改源码。不涉及重新编译和部署。
Spring 管理 Bean 方式的比较


