Java知识点
java知识点
基础知识:
八种基本数据类型
short:16位
int:32位
byte:8位
char:16位
long:64位
boolean:8位
float:32位
double:64位(unicode字符集)
Java修饰符
访问控制修饰符
public:同类、同一包、子类、其他包
protected:同类、同一包、子类
default:同类、同一包
private:同类
非访问修饰符
static:
final:
abstract:
synchronized、transient、volatile:
备忘
-
&与&&
- 两者都表示逻辑与,前者可以作位运算符使用,表示按位与,后者有短路的作用,比如A&&B,若A为False,则不会执行B。
-
Java中跳出多层循环
一是标签:
ok:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println("i=" + i + ",j=" + j);
if (j == 5) break ok;
}
}
二是状态标识:
int[][] arr = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6, 7}, {9}};
boolean found = false;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length && !found; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i + ", j = " + j);
if (arr[i][j] == 5) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
}
-
switch能否作用于byte,long,String?
- 范围小于等于int的可以,如byte,short,char,long不行,String在Java1.7后可以,属于是语法糖。
-
Java中+=的特殊性
- 比如short a = 1; a = a + 1;不行,但是short a = 1; a += 1;行。
-
Java移位
- 左移<<,右移>>,右移>>>(无符号);对于计算来说,移位的速度比乘除要快
Integer.toBinaryString(-8)
//11111111111111111111111111111000
Integer.toBinaryString((-8)>>>1)
// 1111111111111111111111111111100
Integer.toBinaryString((-8)>>1)
//11111111111111111111111111111100
Integer.toBinaryString((-8)<<1)
//11111111111111111111111111110000
- 如何实现超大数计算(超过最大的long)?
(1) Java.math.BigInteger类
(2) 手动实现的一种思路:将输入数据转化为byte[],按照小学数学列式计算的方法逐位计算,加法的实现如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class calculation {
private char sign = '0';
private byte[] data;
public calculation(){
this.data = "0".getBytes();
}
public calculation(String value) throws Exception{
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("^-?\\d+$");
if(value == null || value.length() <= 0){
value = "0";
}
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(value);
if (!matcher.find()){
throw new Exception("the value is not a number string :" + value);
}
char firstChar = value.charAt(0);
if(firstChar == '-'){
if(value.length() >= 2){
sign = firstChar;
value = value.substring(1);
value = getTemp(value);
}
} else{
value = getTemp(value);
}
this.data = value.getBytes();
}
/**
*
* @param value
* @return
*/
private String getTemp(String value){
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[^0]{1}");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(value);
if(matcher.find()){
value = value.substring(matcher.start());
} else{
value = "0";
}
return value;
}
/**
*
* @param other
* @return
*/
public calculation add(calculation other){
calculation result = new calculation();
int thisLength = this.data.length;
int otherLength = other.data.length;
int shorterLength = thisLength > otherLength ? otherLength : thisLength;
ArrayList<Byte> resultData = new ArrayList<Byte>();
int flag = 0;
int i = thisLength - 1;
int j = otherLength - 1;
int k = shorterLength;
if(other.sign == this.sign){
while(k > 0){
Integer temp = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{this.data[i]})) + Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{other.data[i]})) + flag;
flag = temp / 10;
resultData.add(0, ((temp % 10) + "").getBytes()[0]);
k--;
i--;
j--;
}
if(i == -1){
while (j >=0){
Integer temp = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{other.data[j]})) + flag;
flag = temp / 10;
resultData.add(0, ((temp % 10) + "").getBytes()[0]);
j--;
}
} else if(j == -1){
while(i >= 0){
Integer temp = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{this.data[i]})) + flag;
flag = temp / 10;
resultData.add(0, ((temp % 10) + "").getBytes()[0]);
i--;
}
}
if(flag != 0){
for (byte by : (flag + "").getBytes()) {
resultData.add(0, by);
}
}
result.sign = other.sign;
} else{
if(thisLength > otherLength){
result.sign = this.sign;
resultData = subtract(this.data, other.data);
}else if(thisLength < otherLength){
result.sign = other.sign;
resultData = subtract(other.data, this.data);
}else{
Integer thisInt = 0;
Integer otherInt = 0;
for(int n = 0; n< thisLength; n++){
thisInt = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{this.data[n]}));
otherInt = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{other.data[n]}));
if(!thisInt.equals(otherInt)){
break;
}
}
if(thisInt > otherInt){
result.sign = this.sign;
resultData = subtract(this.data, other.data);
}else{
result.sign = other.sign;
resultData = subtract(other.data, this.data);
}
}
}
result.data = new byte[resultData.size()];
for(int m = 0; m < resultData.size(); m++){
result.data[m] = resultData.get(m);
}
return result;
}
/**
*
* @param larger
* @param smaller
* @return
*/
private ArrayList<Byte> subtract(byte[] larger, byte[] smaller){
ArrayList<Byte> resultData = new ArrayList<Byte>();
int flag = 0;
int i = smaller.length - 1;
int j = larger.length - 1;
int k = smaller.length;
while(k > 0){
Integer temp = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{larger[j]})) + flag - Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{smaller[i]}));
if(temp < 0){
flag = -1;
temp += 10;
}else{
flag = 0;
}
resultData.add(0, (temp + "").getBytes()[0]);
j--;
i--;
k--;
}
while(j >= 0){
Integer temp = Integer.valueOf(new String(new byte[]{larger[j]})) + flag;
if(temp < 0){
flag = -1;
temp += 10;
}else{
flag = 0;
}
resultData.add(0, (temp + "").getBytes()[0]);
j--;
}
return resultData;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
String str = new String(this.data);
str = getTemp(str);
if(sign == '-' && str !="0"){
str = sign + str;
}
return str;
}
}
-
final、finally、finalize
- final:修饰变量:变量引用不能变,但值可以变;修饰方法:方法不能被重载;修饰类:类不能被继承;final修饰的变量必须在构造函数结束之前赋值
- finally:一种异常处理机制,在异常处理的最后阶段执行
- finalize:是一种方法,定义在Object中,在类被内存回收之前做一些清理工作
-
==与equal
- ==是操作符,比较引用是否一致,equal是方法,具体定义根据类而定,一般比较的是值
-
静态变量与实例变量
- 前者定义在对象创建之前,类定义之时,后者定义在对象创建之时;前者唯一,后者不唯一
-
static方法能否调用非static变量
- 不行,逻辑矛盾
-
math.round()
- 四舍五入;math.round(0.5)=1;math.round(-0.5)=0
-
抽象类、接口
-
抽象类特点:
(1) 抽象类本身不能实例化
(2) 抽象类可以不含抽象方法,抽象类子类不一定要覆写其抽象方法(若子类也为抽象类则不用)
(3) 抽象类可以用public和protected修饰,默认为public -
接口特点:
(1) 接口变量(public static final)修饰与方法(public abstract)修饰是固定的,所以按默认来就行
(2) 非抽象类必须被实现接口中所有方法 -
区别:一类继承一个抽象类,但可以有多个接口;抽象类更接近一个类,可以有静态方法
-
-
覆盖和重载(override and overload)
- override:抛出的异常必须为父类方法抛出异常的子类;覆盖方法的其他标志应该完全一致
- overload:重载只能是参数不同,只是返回值不同不行,异常类型无影响
-
Java native
- native修饰方法表示使用其它语言实现。可在Java文件中将其声明,使用javac -h . <Java文件>生成定义了native方法的.h头文件,再去编写对应的c/cpp文件实现.h文件中的方法,最后生成动态链接库DLL文件,在Java文件中加载后就可以使用了。
public class App {
public native void sayhi(String str);
static{
System.load(System.getProperty("user.dir")+"\\lib\\sayhi.dll");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new App().sayhi("hihihi");
}
}
生成sayhi.h:
javac -h App.java
sayhi.h:
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include "jni.h"
/* Header for class App */
#ifndef _Included_App
#define _Included_App
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: App
* Method: sayhi
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)V
*/
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_App_sayhi
(JNIEnv *, jobject, jstring);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
sayhi.cpp:
#include "JAVA_DLL.h"
#include <stdio.h>
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_App_sayhi(JNIEnv *env, jobject jo, jstring str){
const char *c_str1 = NULL;
c_str1 = env->GetStringUTFChars(str, 0);
if (str==NULL){
return;
}
printf("JAVA use C++ to print:\n");
printf(c_str1);
return;
}
生成DLL:
gcc -m64 -Wl,--add-stdcall-alias -I%JAVA_HOME%\\include -I%JAVA_HOME%\\include\\win32 -shared -o sayhi.dll sayhi.cpp
-
Java内部类
- 方法外:static和非static两种,实例化的方法不一样,static类似于外部类,但不能定义static变量和方法,因为没有意义;非static比较常规
- 方法内:不能定义static类,因为没有意义,也不能有修饰符
-
String、StringBuffer
- String:final,不可变对象,频繁操作会创建多个对象,内存不友好
- StringBuffer:可变对象,内存友好
-
运行时异常、一般异常、error、exception
- 运行时异常:由虚拟机接管抛出;一般异常:定义方法时必须声明
- error:难以处理,通常导致程序停止运行;exception:不一定会导致程序停止运行,一般是程序设计上的问题
常见的运行时异常:
ArithmeticException——由于除数为0引起的异常;
ArrayStoreException——由于数组存储空间不够引起的异常;
ClassCastException—一当把一个对象归为某个类,但实际上此对象并不是由这个类创建的,也不是其子类创建的,则会引起异常;
IllegalMonitorStateException——监控器状态出错引起的异常;
NegativeArraySizeException—一数组长度是负数,则产生异常;
NullPointerException—一程序试图访问一个空的数组中的元素或访问空的对象中的 方法或变量时产生异常; OutofMemoryException——用new语句创建对象时,如系统无法为其分配内存空 间则产生异常;
SecurityException——由于访问了不应访问的指针,使安全性出问题而引起异常;
IndexOutOfBoundsExcention——由于数组下标越界或字符串访问越界引起异常;
IOException——由于文件未找到、未打开或者I/O操作不能进行而引起异常;
ClassNotFoundException——未找到指定名字的类或接口引起异常;
CloneNotSupportedException——一程序中的一个对象引用Object类的clone方法,但 此对象并没有连接Cloneable接口,从而引起异常;
InterruptedException—一当一个线程处于等待状态时,另一个线程中断此线程,从 而引起异常,有关线程的内容,将在下一章讲述;
NoSuchMethodException一所调用的方法未找到,引起异常;
Illega1AccessExcePtion—一试图访问一个非public方法;
StringIndexOutOfBoundsException——访问字符串序号越界,引起异常;
ArrayIdexOutOfBoundsException—一访问数组元素下标越界,引起异常;
NumberFormatException——字符的UTF代码数据格式有错引起异常;
IllegalThreadException—一线程调用某个方法而所处状态不适当,引起异常;
FileNotFoundException——未找到指定文件引起异常;
EOFException——未完成输入操作即遇文件结束引起异常。
- Thread
- 多线程创建办法:
(1) 继承重写Thread的Run方法;
(1) 使用Runnable接口实现Run方法;
(3) 线程池 - 线程池:
(1) 类:Executors、ThreadPoolExecutor
(2) 接口:Executor、ExecutorService
(3) 创建方法:newCachedThreadPool、newFixedThreadPool、newScheduledThreadPool、newSingleThreadExecutor、ThreadPoolExecutor(推荐) - ThreadPoolExecutor方法参数:
(1) corePoolSize:指定了线程池中的线程数量,它的数量决定了添加的任务是开辟新的线程去执行,还是放到workQueue任务队列中去;
(2) maximumPoolSize:指定了线程池中的最大线程数量,这个参数会根据你使用的workQueue任务队列的类型,决定线程池会开辟的最大线程数量
(3) keepAliveTime:当线程池中的空闲线程数量超过corePoolSize时,多余的线程会在多长时间内被销毁;
(4) unit:keepAliveTime的单位
(5) workQueue:任务队列,被添加到线程池中,但尚未被执行的任务;它一般分为直接提交队列(SynchronousQueue)、有界任务队列(ArrayBlockingQueue)、无界任务队列(LinkedBlockingQueue)、优先任务队列(PriorityBlockingQueue)几种;
(6) threadFactory:线程工厂,用于创建线程,一般用默认即可;
(7) handler:拒绝策略,当任务太多来不及处理时,如何拒绝任务,包括AbortPolicy(默认;直接抛出异常)、CallerRunsPolicy(常用)、DiscardOldestPolicy(删除最老的任务)、DiscardPolicy(删除无法处理的任务) - wait和nitify和synchronized:
- 多线程创建办法:
pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,
10,
1000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(5),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()
);
Runnable thread1Runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized(App.class){
System.out.println("通知释放");
App.class.notify();
}
}
};
Runnable thread2Runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized(App.class){
try {
System.out.println("开始阻塞");
App.class.wait();
System.out.println("已释放");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
pool.execute(thread2Runnable);
pool.execute(thread1Runnable);
pool.shutdown();
开始阻塞
通知释放
已释放
- 线程基本状态:就绪、运行、阻塞、挂起、结束
-
synchronized与java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock
- 后者控制更加精细,前者不能手动释放,后者可以
-
Collection、Map
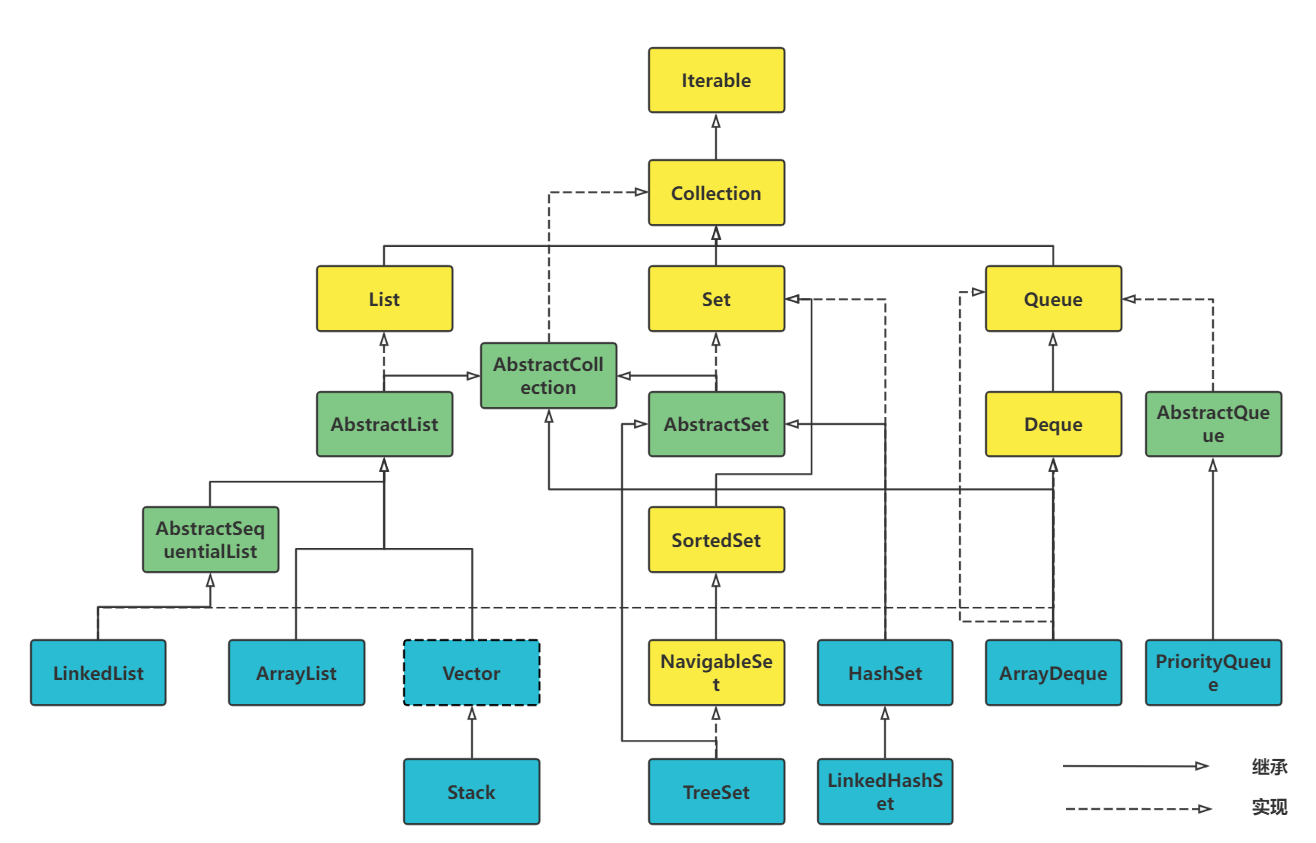
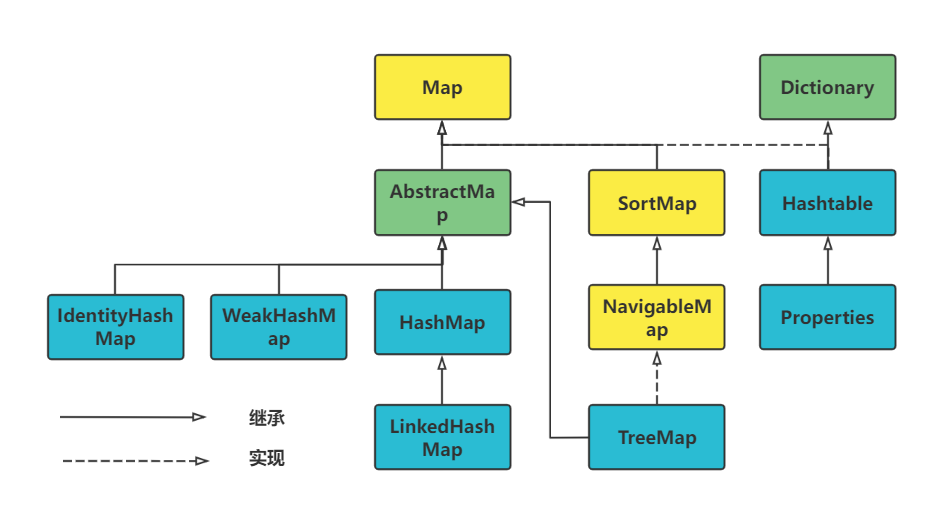
-
迭代器Iterater
List<String> b = new ArrayList<>();
b.add("a");
b.add("b");
b.add("c");
b.add("d");
b.add("e");
System.out.println(b);
Iterator<String> i = b.iterator();
while(i.hasNext()){
System.out.print(i.next());
}
System.out.println("\n---------------------------");
for(Iterator<String> it = b.iterator();it.hasNext();){
System.out.print(it.next());
}
System.out.println("\n---------------------------");
for(String s : b){
System.out.print(s);
}
System.out.println("\n---------------------------");
[a, b, c, d, e]
abcde
---------------------------
abcde
---------------------------
abcde
---------------------------
-
heap和stack
- heap:堆,存放new出来的对象的实例或数组,一般是不确定大小的,且物理地址不连续
- stack:栈,存放基本数据类型或对象的引用,一般大小确定,物理地址连续
-
Java内存区域
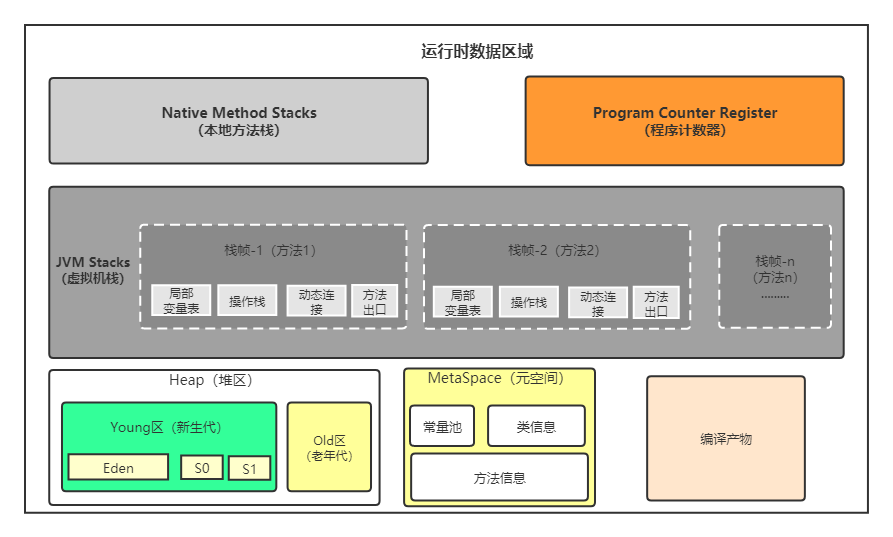
转自知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/297001119 -
I/O流
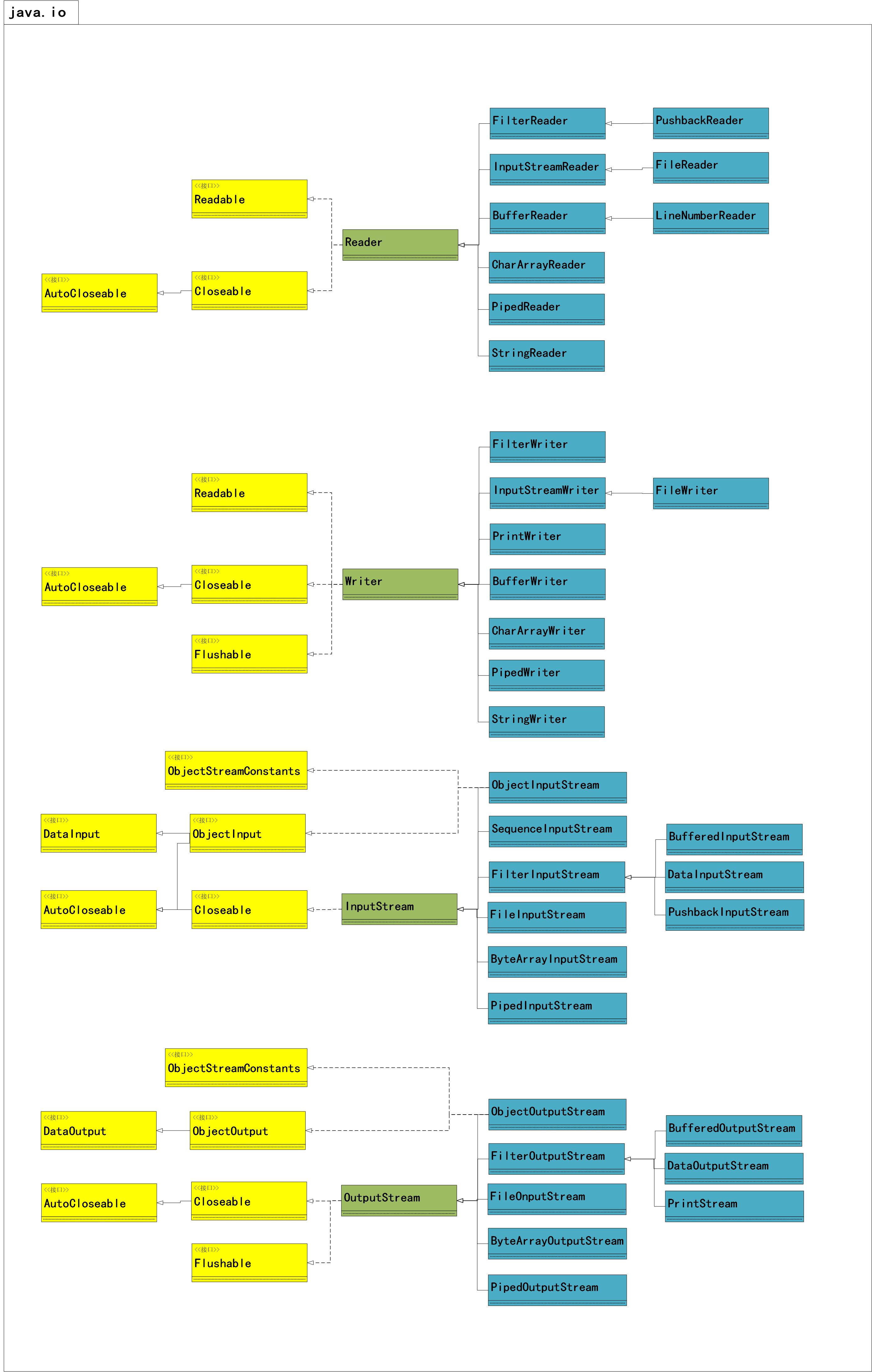
-
GC
- Garbage Collection:
- Mark-Sweep:标记-清除;效率低下、占用空间高
- Copying:复制; 内存缩小为原来的一半
- Mark-Compact:标记-压缩;不直接移动某一特定对象,统一移动
- Generational Collection:分代收集;根据Java堆代的区别,使用合适的收集算法。
(待补充)
- 内存泄漏:长生命周期的对象引用了短生命周期的对象,短生命周期对象的引用无法释放,可能会发生内存泄漏
- Garbage Collection:


