[说明]
一般的树结构常采用孩子-兄弟表示法表示,即用二叉链表作树的存储结构,链表中结点的两个链域分别指向该结点的第一个孩子结点和下一个兄弟结点。例如,图 5-1(a) 所示的树的孩子-兄弟表示如图 5-1(b)示。
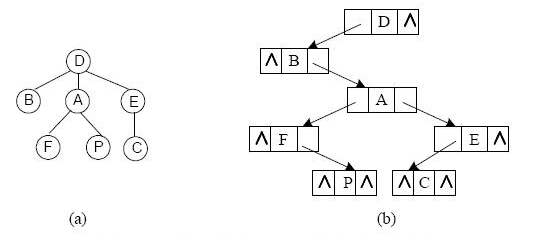
图 5-1 树及其孩子-兄弟表示示意图
函数 LevelTraverse()的功能是对给定树进行层序遍历。例如,对图 5-1 所示的树进 行层序遍历时,结点的访问次序为:D B A E F P C 。
对树进行层序遍历时使用了队列结构,实现队列基本操作的函数原型如下表所示:
|
函数原型 |
说明 |
|
void InitQueue(Queue *Q) |
初始化队列 |
|
Bool IsEmpty(Queue Q) |
判断队列是否为空,若是则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE |
|
void EnQueue(Queue *Q,TreeNode p) |
元素入队列 |
|
void DeQueue(Queue *Q,TreeNode *p) |
元素出队列 |
Bool、Status 类型定义如下:
typedef enum {FALSE = 0,TRUE = 1} Bool;
typedef enum {OVERFLOW = -2,UNDERFLOW = -1,ERROR = 0,OK = 1} Status;
树的二叉链表结点定义如下:
typedef struct Node {
char data;
struct Node *firstchild,*nextbrother;
}Node,*TreeNode;
[函数]
Status LevelTraverse(TreeNode root)
{ /*层序遍历树,树采用孩子-兄弟表示法,root 是树根结点的指针*/
Queue tempQ;
TreeNode ptr,brotherptr;
if (!root)
return ERROR;
InitQueue(&tempQ);
EnQueue(&tempQ,root) ;
brotherptr = root -> nextbrother;
while (brotherptr){ EnQueue(&tempQ,brotherptr);
brotherptr=brotherptr->nextbrother;
} /*end-while*/
while ( !IsEmpty(tempQ) ) {
DeQueue(&temp,&ptr);
printf("%c\t",ptr->data);
if (!ptr->firstchild) continue;
EnQueue(&tempQ,ptr->firstchild);
brotherptr = ptr->firstchild->nextbrother;
while (brotherptr){ EnQueue(&tempQ,brotherptr);
brotherptr=brotherptr->nextbrother;
} /*end-while*/
} /*end-while*/
return OK;
}/*LevelTraverse*/




