Java: Stream
- 数据收集
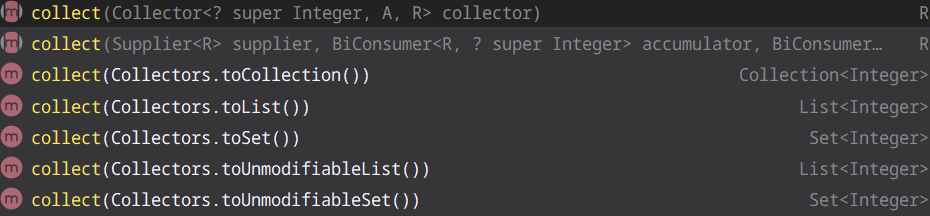
import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class B{ public static void main(String[] args){ List<Integer> l1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).toList(); System.out.println("l1.getClass() = " + l1.getClass()); List<Integer> l2 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("l2.getClass() = " + l2.getClass()); ArrayList<Integer> l3 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(() -> { return new ArrayList<Integer>(); })); System.out.println("l3.getClass() = " + l3.getClass()); Collection<Integer> l4 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(new Supplier<Collection<Integer>>(){ @Override public Collection<Integer> get(){ return new ArrayList<Integer>(); } })); System.out.println("l4.getClass() = " + l4.getClass()); LinkedList<Integer> l5 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedList::new)); System.out.println("l5.getClass() = " + l5.getClass()); } }
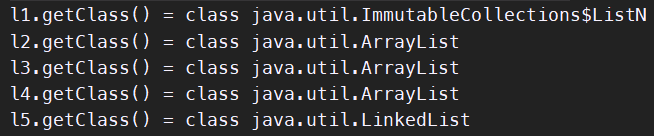
import java.util.*; import java.util.function.Supplier; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class B{ public static void main(String[] args){ Set<Integer> s1 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toSet()); System.out.println("s1.getClass() = " + s1.getClass()); HashSet<Integer> s2 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(() -> { return new HashSet<>(); })); System.out.println("s2.getClass() = " + s2.getClass()); HashSet<Integer> s3 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new)); System.out.println("s3.getClass() = " + s3.getClass()); Collection<Integer> s4 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).collect(Collectors.toCollection(new Supplier<Collection<Integer>>(){ @Override public Collection<Integer> get(){ return new HashSet<>(); } })); System.out.println("s4.getClass() = " + s4.getClass()); } }
- toArray
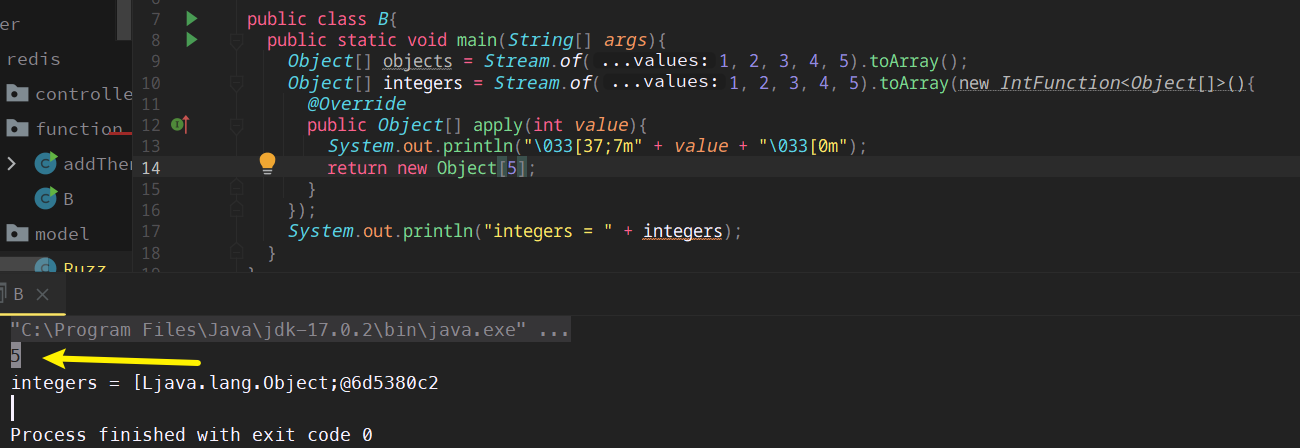
public class B{ public static void main(String[] args){ Object[] objects = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).toArray(); Integer[] integers = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5).toArray(new IntFunction<Integer[]>(){ @Override public Integer[] apply(int value){ // value为数组大小 System.out.println("\033[37;7m" + value + "\033[0m"); return new Integer[5]; } }); System.out.println("integers = " + Arrays.toString(integers)); } }
- Aggregate
package io.veer.redis.function; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class addThen{ public static void main(String[] args){ Jot[] jots = new Jot[]{ new Jot("aa", 11), new Jot("bb", 22), new Jot("bb", 33), new Jot("cc", 44) }; Optional<Jot> maxAge = Stream.of(jots ).collect(Collectors.maxBy((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge())); System.out.println("maxAge.get() = " + maxAge.get()); Optional<Jot> minAge = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.minBy((o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge())); System.out.println("minAge.get() = " + minAge.get()); Integer sumAge = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.summingInt(jot -> jot.getAge())); System.out.println("sumAge = " + sumAge); Double avgAge = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Jot::getAge)); System.out.println("avgAge = " + avgAge); Long count = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.counting()); System.out.println("count = " + count); } } class Jot{ String name; Integer age; public Jot(String name, Integer age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public Integer getAge(){ return age; } public void setAge(Integer age){ this.age = age; } @Override public String toString(){ final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Jot{"); sb.append("name='").append(name).append('\''); sb.append(", age=").append(age); sb.append('}'); return sb.toString(); } }
- Group
package io.veer.redis.function; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class addThen{ public static void main(String[] args){ Jot[] jots = new Jot[]{ new Jot("aa", 11), new Jot("bb", 22), new Jot("bb", 33), new Jot("cc", 44), new Jot("dd", 44) }; Map<String, List<Jot>> map = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Jot::getName)); map.forEach((k, v) -> { System.out.println("k = " + k); System.out.println("v = " + v); }); Map<String, List<Jot>> ageMap = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(jot -> jot.getAge() >= 33 ? "young" : "old")); ageMap.forEach((k, v) -> { System.out.println("k = " + k); System.out.println("v = " + v); }); Map<String, Map<String, List<Jot>>> mapMap = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Jot::getName, Collectors.groupingBy(jot -> jot.getAge() > 33 ? "young" : "old"))); mapMap.forEach((k, v) -> { System.out.println("k = " + k); v.forEach((kk, vv) -> { System.out.println("\tkk = " + kk); System.out.println("\tvv = " + vv); }); }); } } class Jot{ String name; Integer age; public Jot(String name, Integer age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public Integer getAge(){ return age; } public void setAge(Integer age){ this.age = age; } @Override public String toString(){ final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Jot{"); sb.append("name='").append(name).append('\''); sb.append(", age=").append(age); sb.append('}'); return sb.toString(); } }
- Partition
public class addThen{ public static void main(String[] args){ Jot[] jots = new Jot[]{ new Jot("aa", 11), new Jot("bb", 22), new Jot("bb", 33), new Jot("cc", 44), new Jot("dd", 44) }; Map<Boolean, List<Jot>> map = Stream.of(jots).collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(jot -> jot.getAge() > 33)); map.forEach((k,v)->{ System.out.println("k = " + k); System.out.println("v = " + v); }); } }
- Join
public class addThen{ public static void main(String[] args){ Jot[] jots = new Jot[]{ new Jot("aa", 11), new Jot("bb", 22), new Jot("bb", 33), new Jot("cc", 44), new Jot("dd", 44) }; String s = Stream.of(jots).map(Jot::getName).collect(Collectors.joining()); System.out.println("s = " + s); // aabbbbccdd String ss = Stream.of(jots).map(Jot::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("-")); System.out.println("ss = " + ss); // aa-bb-bb-cc-dd String sss = Stream.of(jots).map(Jot::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("-", "@", "%")); System.out.println("sss = " + sss); // @aa-bb-bb-cc-dd% } }
- parallel
public class addThen{ public static void main(String[] args){ Jot[] jots = new Jot[]{ new Jot("aa", 11), new Jot("bb", 22), new Jot("bb", 33), new Jot("cc", 44), new Jot("dd", 44) }; Stream.of(jots).forEach(jot -> { System.out.println("\033[37;7m" + Thread.currentThread() + "\033[0m"); }); Stream.of(jots).parallel().filter(s->{ System.out.println("Thread.currentThread() = " + Thread.currentThread()); return true; }).count(); LinkedList<Integer> integers = new LinkedList<>(); Stream<Integer> integerStream = integers.parallelStream(); integers.add(5); integers.add(55); integerStream.forEach(b->{ System.out.println("\033[37;7m" + Thread.currentThread()+ "\033[0m"); System.out.println("b = " + b); }); } }
- 效率对比
public class addThen{ private static final long count = 999999999; public static void main(String[] args){ Jot[] jots = new Jot[]{ new Jot("aa", 11), new Jot("bb", 22), new Jot("bb", 33), new Jot("cc", 44), new Jot("dd", 44) }; System.out.println("\033[37;7m" + "For loop" + "\033[0m"); b1(); System.out.println("\033[37;7m" + "Stream serialization" + "\033[0m"); b2(); System.out.println("\033[37;7m" + "Stream parallel" + "\033[0m"); b3(); } private static void b1(){ long commence = System.currentTimeMillis(); long res = 0; for(int i = 0; i < count; i++){ res += i; } long closure = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("res = " + res); System.out.printf("elapsed: %d\n", (closure - commence)); } private static void b2(){ long commence=System.currentTimeMillis(); long res = LongStream.range(0,count).reduce(0, Long::sum); long closure=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("res = " + res); System.out.printf("elapsed: %d\n", (closure - commence)); } private static void b3(){ long commence=System.currentTimeMillis(); long res = LongStream.range(0,count).parallel().reduce(0, Long::sum); long closure=System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("res = " + res); System.out.printf("elapsed: %d\n", (closure - commence)); } }
- 多线程安全问题
public class addThen{ public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<Object> l1 = new ArrayList<>(); for(int i = 0; i < 1000; i++){ l1.add(i); } System.out.println("l1.size() = " + l1.size()); ArrayList<Object> l2 = new ArrayList<>(); IntStream.range(0, 1000).parallel().forEach(l2::add); System.out.println("l2.size() = " + l2.size()); ArrayList<Integer> l3 = new ArrayList<>(); IntStream.range(0, 1000).parallel().forEach(value -> { synchronized(addThen.class){ l3.add(value); } }); System.out.println("l3.size() = " + l3.size()); List<Integer> l4 = IntStream.rangeClosed(1, 1000).parallel().boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("l4.size() = " + l4.size()); } }
分类:
Java





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
2020-05-25 利用chattr限制sudo修改root密码
2020-05-25 九九乘法表-bash
2020-05-25 通过ping探测主机在线状态
2020-05-25 利用RANDOM生成10个随机数字,输出这个10数字,并显示其中的最大者和最小者