Python: asyncio
改造老旧教程案例:
asyncio.gather
import asyncio async def b(): print(5) await asyncio.sleep(2) print(55) return 5 async def p(): print(4) await asyncio.sleep(1) print(44) return 55 async def main(): tasks = [b(), p()] res = await asyncio.gather(*tasks) print(res) asyncio.run(main())
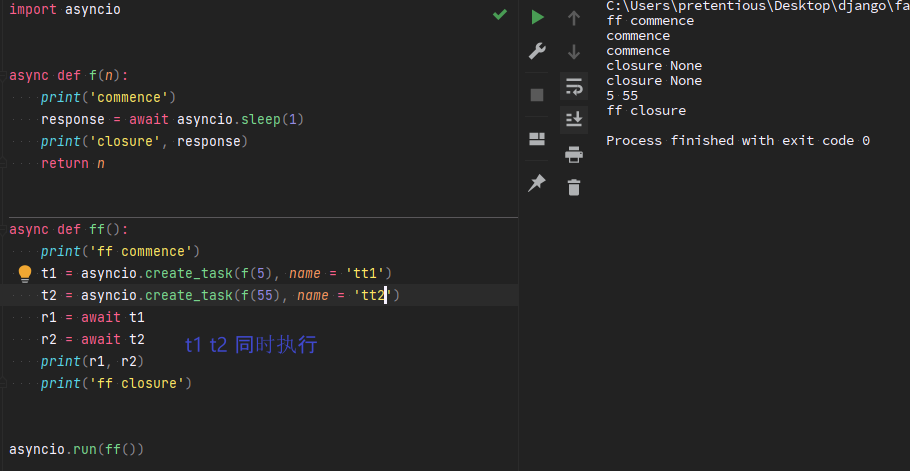
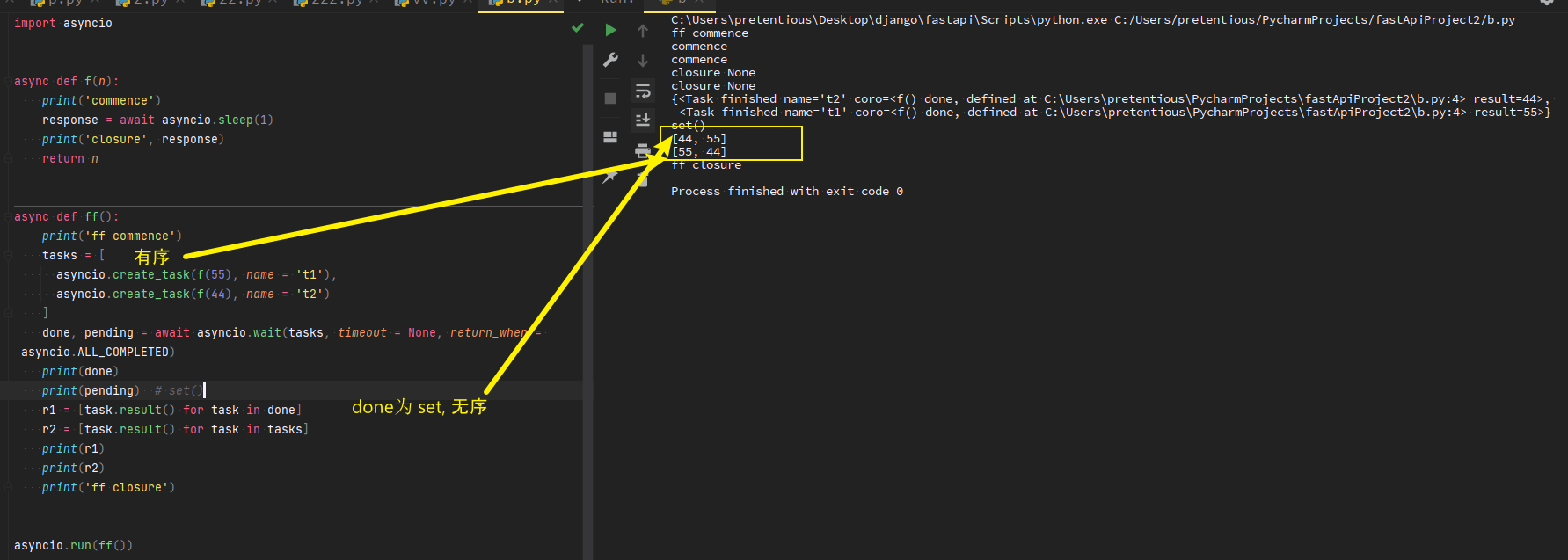
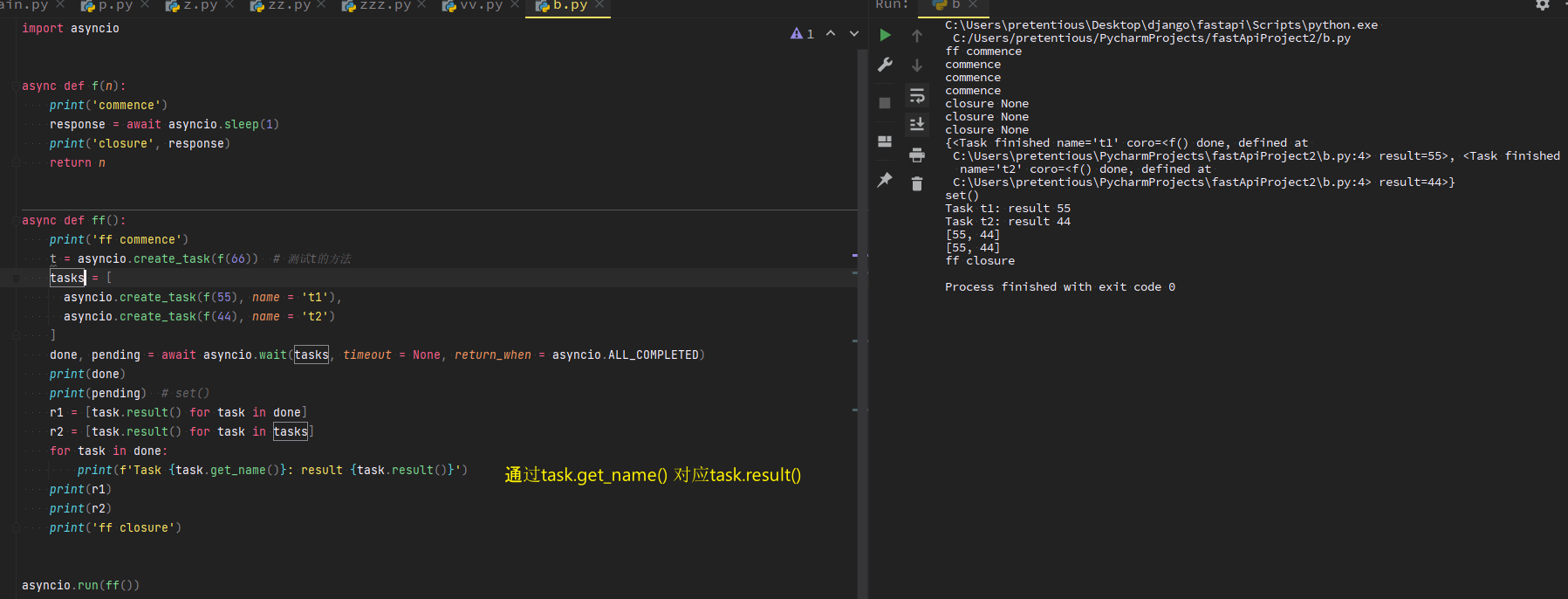
asyncio.create_task
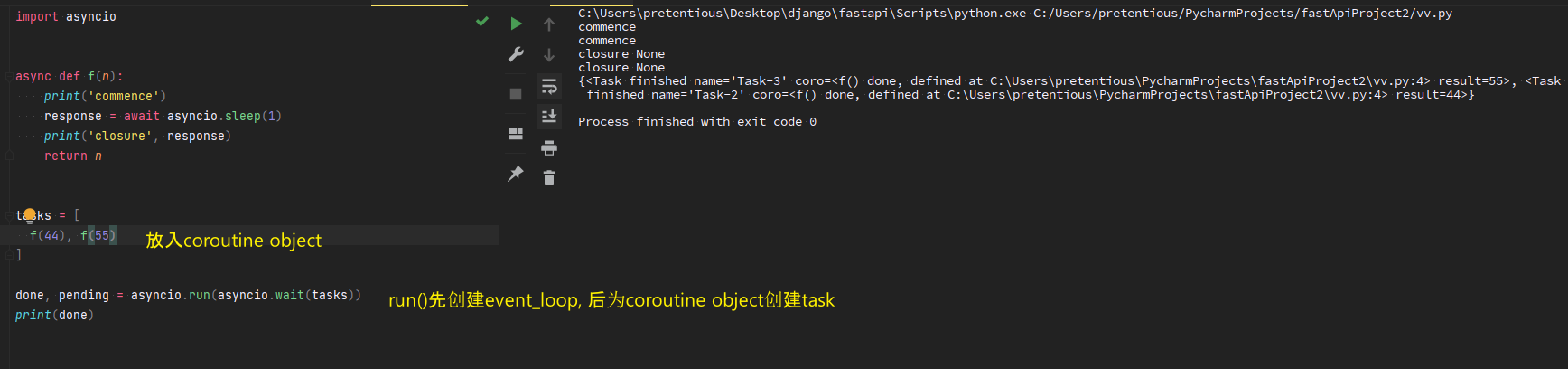
import asyncio async def b(): print(5) await asyncio.sleep(2) print(55) return 5 async def p(): print(4) await asyncio.sleep(1) print(44) return 55 async def main(): task1 = asyncio.create_task(b(), name = 'B') task2 = asyncio.create_task(p(), name = 'P') tasks = [task1, task2] done, pending = await asyncio.wait(tasks, timeout = None, return_when = asyncio.ALL_COMPLETED) print(type(done)) for task in done: print(task) print(task.result()) print(pending) print(tasks) asyncio.run(main())
new API:
import asyncio, random, datetime async def wait_and_echo(content): wait = random.randint(1, 5) print(f'print {content} after {wait} seconds') await asyncio.sleep(wait) print(f'{content} printed at {datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%H:%M:%S")}') async def main(): await asyncio.gather(*[wait_and_echo(x) for x in range(10)]) asyncio.run(main())
Step by Step:
import asyncio from datetime import datetime async def say_after(delay, content): await asyncio.sleep(delay) print(content) async def main(): print(f'started at {datetime.now().strftime("%T")}') await say_after(1, 'first') await say_after(2, 'second') print(f'finished at {datetime.now().strftime("%T")}') asyncio.run(main())

Use asyncio.create_task()
import asyncio from datetime import datetime async def say_after(delay, content): await asyncio.sleep(delay) print(content) async def main(): # asyncio.create_task() function to run coroutines concurrently as asyncio Tasks task1 = asyncio.create_task(say_after(1, 'first')) task2 = asyncio.create_task(say_after(2, 'second')) print(f'started at {datetime.now().strftime("%T")}') await task1 await task2 print(f'finished at {datetime.now().strftime("%T")}') asyncio.run(main())

Awaitables
We say that an object is an awaitable object if it can be used in an await expression. Many asyncio APIs are designed to accept awaitables.
There are three main types of awaitable objects: coroutines, Tasks, and Futures.
import asyncio async def factorial(name, number): f = 1 for i in range(2, number + 1): print(f'Task {name}: Compute factorial({number}), currently i={i}') await asyncio.sleep(1) f *= i print(f'Task {name}: factorial({number}) = {f}') return f async def main(): # Schedule three calls *concurrently* res = await asyncio.gather(*[ factorial('A', 2), factorial('B', 3), factorial('C', 4) ]) print(res) asyncio.run(main())
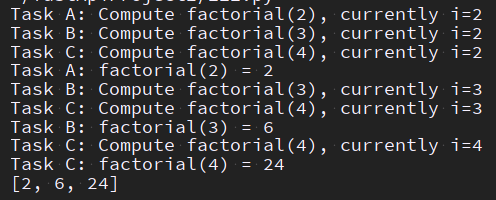


Task:


import asyncio async def main(): loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() # asyncio.ProactorEventLoop # <ProactorEventLoop running=True closed=False debug=False> <class 'asyncio.windows_events.ProactorEventLoop'> print(loop, type(loop)) future = loop.create_future() # asyncio.Future print(future) await future asyncio.run(main())
import asyncio async def main(): # 获取当前事件循环 loop = asyncio.get_running_loop() # asyncio.ProactorEventLoop # <ProactorEventLoop running=True closed=False debug=False> <class 'asyncio.windows_events.ProactorEventLoop'> print(loop, type(loop)) future = loop.create_future() # asyncio.Future await loop.create_task(set_result(future)) data = await future print(data) async def set_result(future: asyncio.Future): await asyncio.sleep(2) future.set_result(55) print(future.result()) asyncio.run(main())








【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律