JavaScript:
以下测不出效果, 因为程序逻辑是在function two中执行
<script> function one () { console.info('one') } function two () { setTimeout(() => { console.info('two') }, 1) } function three () { console.info('three') } function run () { one() two() three() } run() </script>
假设run需要拿到two的执行结果, 进行操作
<script> function one () { return 'one' } function two () { setTimeout(() => { return 'two' }, 1) } function three () { return 'three' } function run () { console.log(one()) console.log(two()) console.log(three()) } run() </script>
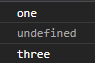
利用async await Promise将程序改造成同步
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <script> function one () { return 'one' } function two () { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { resolve('resolve two') // return 'two' }, 2000) }) } function three () { return 'three' } async function run () { console.log(one()) console.log(await two()) console.log(three()) } run() </script> </body> </html>
分类:
JavaScript





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律