WSGI python
应用程序端:
应用程序应该是一个可调用对象
Python中应该是函数,类,实现了call方法的类的实例
可调用对象应该接收两个参数
函数实现:
def application(environ,start_response):
pass
类实现
class Application:
def __init__(self,environ,start_response):
pass
class Application:
def __call__(self,environ,start_response):
pass
可调用对象的实现,都必须返回一个可迭代对象
response_str=b'uiopp\n'
def application(environ,start_response):
return [response_str]
class application:
def __init__(self,envrion,start_response):
pass
def __iter__(self):
yield response_str
class application:
def __call__(self,envrion,start_response):
return [response_str]
参数
environ & start_response这两个参数名可以是任何合法名,默认是environ & start_response
environ是包含HTTP请求信息的dict对象
| name | implication |
| REQUEST_METHOD | 请求方法,GET POST |
| PATH_INFO | URL路径 |
| QUERY_STRING | 查询字符串 |
| SERVER_NAME,SERVER_PORT | server_name & port |
| HTTP_HOST | address & port |
| SERVER_PROTOCOL | protocol |
| HTTP_USER_AGENT | UserAgent |
start_response是一个可调用对象,有三个参数
start_response(status,response_headers,exc_info=None)
status状态码
response_headers是一个元素为二元组的列表,例如[('Content-Type'),('text/plain;charset=utf-8')]
exc_info在错误处理的时候使用
start_response应该在返回可迭代对象之前调用,因为它返回的是Response _Header,返回的可迭代对象是Response Body
Server
服务器程序需要调用符合上述定义的可调用对象,传入environ,start_response,拿到返回的可迭代对象,返回客户端
wsgiref
wsgiref是一个WSGI参考实现库
wsgiref.simple_server实现了一个简单的WSGI HTTP Server
wsgiref.simple_server.make_server(host,port,app,server_class=WSGIServer,handler_class=WSGIRequestHandler)启动一个WSGI Server
wsgiref.simple_server.demo_app(environ,start_response) 函数,小巧完整的WSGI application实现
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server,demo_app
ip='127.0.0.1'
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,demo_app)
server.serve_forever()
environ
环境数据有很多,都是存在字典中,字典存取没有对象的属性使用方便,使用第三方库webob,可以把环境数据解析,封装成对象
webob.Request对象
将环境参数解析封装成request对象
GET方法,发送的数据是URL中Query string,在Request Header中
request.GET 就是一个字典MultiDict,里面封装着Query string
POST方法,提交的数据于 Request Body中,但是也可以同时使用Query String
request.POST可以获取Request Body中的数据,也是字典MultiDict
不关心什么方法提交,只关系数据,可以使用request.params,里面是所有提交数据的封装
request=webob.Request(environ)
print(request.method)
print(request.path)
print(request.query_string)
print(request.GET) # GET方法所有数据
print(request.POST) # POST方法所有数据
print('params = {}'.format(request.params)) # 所有数据,参数
MultiDict:允许一个key存放若干值
from webob.multidict import MultiDict
md=MultiDict()
md.add(1,'uiop')
md.add(1,'vbnm')
md.add('a',1)
md.add('a',2)
md.add('b','3')
md['b']='4'
for pair in md.items():
print(pair)
print(md.getall(1))
# print(md.getone('a'))
print(md.get('a'))
print(md.get('c')) # None
webob.Response对象
import webob
res=webob.Response()
print(res.status)
print(res.headerlist)
start_response(res.status,res.headerlist)
html='<h1>uiop</h1>'.encode('utf8')
return [html]
如果application是一个类的实例,可以实现__call__方法
from webob import Response,Request,dec
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
def application(environ:dict,start_response):
request=Request(environ)
print(request.method)
print(request.path)
print(request.GET)
print(request.POST)
print('params = {}'.format(request.params))
print(request.query_string)
# response=Response('<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>')
response=Response() # [('Content-Type','text/html;charset=utf8'),('Content-length','0)]
response.status_code=250 # default 200
print(response.content_type)
html='<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>'.encode('utf8')
response.body=html
return response(environ,start_response)
ip='127.0.0.1'
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,application)
server.serve_forever()
server.server.close()
wsgify装饰器装饰的函数应该具有一个参数,这个参数是webob.Request类型,是对字典environ对象化后的实例,返回值必须是一个webob.Response类型
所有在函数中,要创建一个webob.Response类型的实例
from webob.dec import wsgify
import webob
@wsgify
def app(request:webob.Request) -> webob.Response:
response=webob.Response('<h1>uiop</h1>')
return response
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
import webob
from webob.dec import wsgify
def application(environ:dict,start_response):
request=webob.Request(environ)
print(request.method,request.path,request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = {}'.format(request.params))
response=webob.Response() # [('Content-Type','text/html;charset=utf8'),('Content-lenght','0')]
response.status_code=301
print(response.content_type)
html='<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>'
response.body=html
return response(environ,start_response)
@wsgify
def app(request:webob.Request) -> webob.Response:
print(request.method,request.path)
print(request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = %s' % request.params)
response=webob.Response('<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>')
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
ip=''
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,app)
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
import webob
from webob.dec import wsgify
def application(environ:dict,start_response):
request=webob.Request(environ)
print(request.method,request.path,request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = {}'.format(request.params))
response=webob.Response() # [('Content-Type','text/html;charset=utf8'),('Content-lenght','0')]
response.status_code=301
print(response.content_type)
html='<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>'
response.body=html
return response(environ,start_response)
@wsgify
def app(request:webob.Request) -> webob.Response:
print(request.method,request.path)
print(request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = %s' % request.params)
response=webob.Response()
if request.path == '/':
response.body='path = /'.encode()
elif request.path == '/uiop':
response.body='path = /uiop'.encode()
else:
response.status_code=404
response.body='Not Found'.encode()
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
ip=''
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,app)
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
增加路由
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
import webob
from webob.dec import wsgify
def application(environ:dict,start_response):
request=webob.Request(environ)
print(request.method,request.path,request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = {}'.format(request.params))
response=webob.Response() # [('Content-Type','text/html;charset=utf8'),('Content-lenght','0')]
response.status_code=301
print(response.content_type)
html='<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>'
response.body=html
return response(environ,start_response)
def index(request:webob.Request):
response=webob.Response()
response.body='path = /'.encode()
return response
def uiop(request:webob.Request):
response=webob.Response()
response.body='path = {}'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
def not_found(request:webob.Request):
response=webob.Response()
response.status_code=404
response.body='path = {} not Found'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
@wsgify
def app(request:webob.Request) -> webob.Response:
print(request.method,request.path)
print(request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = %s' % request.params)
if request.path == '/':
return index(request)
elif request.path == '/uiop':
return uiop(request)
else:
return not_found(request)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ip=''
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,app)
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
注册路由表
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
import webob
from webob.dec import wsgify
def application(environ:dict,start_response):
request=webob.Request(environ)
print(request.method,request.path,request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = {}'.format(request.params))
response=webob.Response() # [('Content-Type','text/html;charset=utf8'),('Content-lenght','0')]
response.status_code=301
print(response.content_type)
html='<h1>uiopvbnm</h1>'
response.body=html
return response(environ,start_response)
def index(request:webob.Request):
response=webob.Response()
response.body='path = /'.encode()
return response
def uiop(request:webob.Request):
response=webob.Response()
response.body='path = {}'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
def not_found(request:webob.Request):
response=webob.Response()
response.status_code=404
response.body='path = {} not Found'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
ROUTING={} # routing table
def register(path,handler):
ROUTING[path]=handler
register('/',index)
register('/uiop',uiop)
@wsgify
def app(request:webob.Request) -> webob.Response:
print(request.method,request.path)
print(request.query_string,request.GET,request.POST)
print('params = %s' % request.params)
return ROUTING.get(request.path,not_found)(request)
if __name__ == '__main__':
ip=''
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,app)
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
pass
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from webob import Response,Request
from webob.dec import wsgify
@wsgify
def app(request:Request) -> Response:
print(request.method, request.path, request.query_string, request.GET, request.POST)
print('params = {}'.format(request.params))
response=Response()
if request.path == '/':
response.status_code=200
response.content_type= 'text/html'
response.charset= 'utf8'
response.body= '<h1>uivb</h1>'.encode()
elif request.path == '/python':
response.content_type= 'text/plain'
response.charset= 'gb2312'
response.body= 'uopjip'.encode()
else:
response.status_code=404
response.body='not found'.encode()
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
ip=''
port=9999
server=make_server(ip,port,app)
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
静态和动态web服务器都需要路径和资源或处理程序的映射,最终返回HTML文本
静态web服务器,解决路径和文件之间的映射
动态web服务器,解决路径和应用程序之间的映射
所有web框架都是如此,都有路由配置
路由字典的实现
路由硬编码
路由逻辑写死到代码中
好的办法,写到配置文件,动态加载
字典,path => function
routetable = {
'/':index,
'/python':python
}
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from webob import Request, Response, exc
from webob.dec import wsgify
class Application:
ROUTING = {}
@classmethod
def register(cls, path):
def wrapper(fn):
cls.ROUTING[path] = fn
return fn
return wrapper
@wsgify
def __call__(self, request: Request):
try:
return self.ROUTING[request.path](request)
except Exception:
raise exc.HTTPNotFound('Not FoundD!!!!!!')
@Application.register('/')
def index(request: Request) -> Response:
response = Response()
response.status_code = 200
response.content_type = 'text/html'
response.charset = 'utf8'
response.body = 'uiop'.encode()
return response
@Application.register('/vbnm')
def vbnm(request: Request) -> Response:
response = Response()
response.status_code = 301
response.content_type = 'text/plain'
response.charset = 'gb2312'
response.body = 'vbnm'.encode()
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
server = make_server('', 9999, Application())
try:
server.serve_forever()
except:
pass
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
Application是WSGI中的应用程序,但是这个应用程序已经变成了一个路由程序,处理逻辑已经移到应用程序外了,而这部分就是以后需要编写的部分
路由正则匹配
__call__方法中实现模式和Path比较
compile
match 从头匹配一次
search 匹配一次
fullmatch 完全匹配
findall 从头找到所有匹配
'/(?P<biz>.*)/(?P<url>.*)'
'/(?P<biz>.*?)/(?P<url>.*)'
@Application.register('^/$') only /
@Application.register('/python$')
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from webob import Request,Response,exc
from webob.dec import wsgify
import re
class Application:
GET='GET'
POST='POST'
HEAD='HEAD'
ROUTING=[]
@classmethod
def register(cls,method,pattern):
def wrapper(handler):
cls.ROUTING.append((method,re.compile(pattern),handler))
return handler
return wrapper
@classmethod
def get(cls,pattern):
return cls.register('GET',pattern)
@classmethod
def post(cls,pattern):
return cls.register('POST',pattern)
@classmethod
def head(cls,pattern):
return cls.register('HEAD',pattern)
@wsgify
def __call__(self,request:Request) -> Response:
for method,pattern,handler in self.ROUTING:
if pattern.match(request.path): # 先判断path,path匹配后再判断method
if request.method.upper() != method:
raise exc.HTTPBadRequest('method is illegal!!')
return handler(request)
raise exc.HTTPNotFound('not Found!!!!!!!!')
# @Application.register('^/$')
@Application.register(Application.GET,'^/$')
@Application.get('^/$')
def index(request:Request) -> Response:
response=Response()
response.status_code=200
response.content_type='text/html'
response.charset='utf8'
response.body='path = {}'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
# @Application.register('^/uiop')
# @Application.register(Application.GET,'^/uiop')
@Application.post('^/uiop')
def uiop(request:Request) -> Response:
response=Response()
response.status_code=301
response.content_type='text/plain'
response.charset='gb2312'
response.body='request.path = {}'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(Application.ROUTING)
server=make_server('',9999,Application())
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt as e:
print(e.args)
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
如果一个URL可以设定多种请求方法?
- method没有写,相当于所有方法都支持
@Application.register('^/$') # method=None - 如果一个handler需要关联多个请求方法method
@Application.register(('GET','POST','HEAD'),'^/$') @Application.register(['GET','POST','HEAD'],'^/$') @Application.register({'GET','POST','HEAD'},'^/$') - 调整参数位置,把method放到后面变成可变参数
def register(cls,pattern,*method): passmethod空元组表示匹配所有方法,非空,匹配指定方法
@Application.register('^/$','GET','POST','HEAD') @Application.register('^/$')
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from webob import Request,Response,exc
from webob.dec import wsgify
import re
class Application:
GET='GET'
POST='POST'
HEAD='HEAD'
ROUTING=[]
@classmethod
def register(cls,pattern,*methods):
def wrapper(handler):
cls.ROUTING.append((methods,re.compile(pattern),handler))
return handler
return wrapper
@classmethod
def get(cls,pattern):
return cls.register(pattern,'GET')
@classmethod
def post(cls,pattern):
return cls.register(pattern,'POST')
@classmethod
def head(cls,pattern):
return cls.register(pattern,'HEAD')
@wsgify
def __call__(self,request:Request) -> Response:
for methods,pattern,handler in self.ROUTING:
print(methods,request.method)
if pattern.match(request.path):
if request.method.upper() in methods or not methods:
return handler(request)
else:
raise exc.HTTPBadRequest('request {} is illegal'.format(request.method))
raise exc.HTTPNotFound('request.path = {} not Found'.format(request.path))
@Application.get('^/$')
@Application.post('^/$')
def index(request:Request) -> Response:
response=Response()
response.status_code=200
response.content_type='text/html'
response.charset='utf8'
response.body='path = {}'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
@Application.register('^/uiop')
# @Application.post('^/uiop')
def uiop(request:Request) -> Response:
response=Response()
response.status_code=301
response.content_type='text/plain'
response.charset='gb2312'
response.body='request.path = {}'.format(request.path).encode()
return response
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(Application.ROUTING)
server=make_server('',9999,Application())
try:
server.serve_forever()
except KeyboardInterrupt as e:
print(e.args)
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()
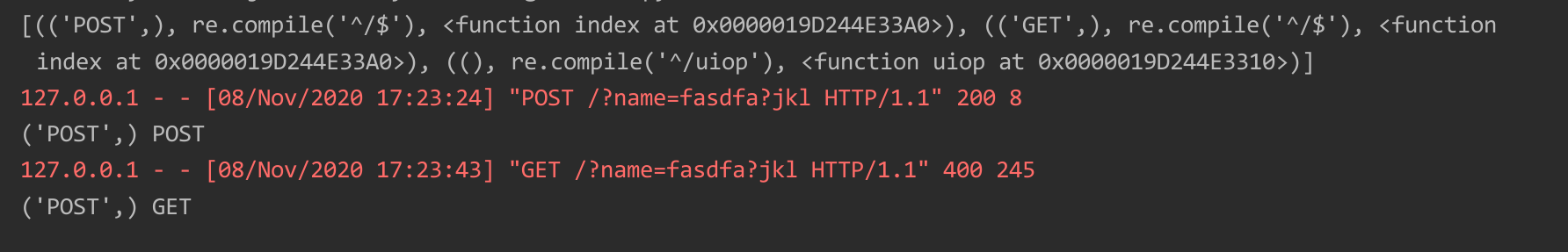
上述代码存在一定问题,如果分别注册的话,存在多个元组,路径相同的情况下,GET如果位于POST后面,则会报错
路由匹配从 URL => handler 变成 URL + method => handler
路由功能的实现
分组捕获
什么时候捕获?
在框架回调__call__方法时,送入request,拿到request.path和regex的模式匹配后,就可以提取分组了
如何处理分组?
应用程序就是handler对应的不同函数,其参数request时一样的,将捕获的数据动态的增加到request对象上
@wsgify
def __call__(self,request:Request) -> Response:
for methods,pattern,handler in self.ROUTING:
print(methods,request.method)
matcher=pattern.match(request.path)
if matcher:
if request.method.upper() in methods or not methods:
request.args=matcher.group() # 所有分组组成的元组(including named)
reqeust.kwargs=matcher.groupdict() # 所有分组组成的dict
return handler(request)
else:
raise exc.HTTPBadRequest('request {} is illegal'.format(request.method))
raise exc.HTTPNotFound('request.path = {} not Found'.format(request.path))
用动态增加属性,为request增加了args,kwargs属性,在handler中使用的时候,就可以直接从属性中,将args,kwargs拿出来使用
路由分组:
路由分组就是按照前缀分别映射
需求
Path为/product/1234
需要将产品ID提取出来
这个Path可以看作时一级路由分组
product=Router('/product') # 匹配前缀product
product.get('/(?P<id>\d+)') # 匹配Path为/product/id
常见的一级目录
/admin 后台管理
/product 产品
这些目录都是 / 根目录下的第一级,称为前缀prefix
前缀要求必须以 / 开头,但不能以分隔符结尾
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | 下面的定义已经不能描述prefix和URL的关系@Application.get('^/$')def index(request:Request) -> Response: pass@Application.route('^/python$')def show_python(request:Request) -> Request: pass |
如何建立prefix & URL 间的隶属关系
一个Prefix下可以有若干URL,这些URL都属于此Prefix
建立一个类Router,里面保存Prefix,同时保存URL和handler关系
以前,所有注册方法都是Application的类方法,也就是所有映射信息都保存在一个类属性ROUTETABLE中,但是现在不同前缀就是不同的Router实例,所有注册方法,都成了实例的方法,
路由表属于实例
Application中现在需要保存所有的注册Router对象就行了,__call__方法依然时回调入口,在其中遍历所有Router实例,找到路径匹配的Router实例,让Router实例返回Response对象
from wsgiref.simple_server import make_server
from webob import Request,Response,exc
from webob.dec import wsgify
import re
class Router:
def __init__(self,prefix:str=""):
self.__prefix=prefix.rstrip('/\\') # prefix such as /product
self.__routetable=[] # 三元组
@property
def prefix(self):
return self.__prefix
def router(self,pattern,*methods):
def wrapper(handler):
self.__routetable.append((methods,re.compile(pattern),handler)) # pre-compile
return handler
return wrapper
def get(self,pattern):
return self.router(pattern,'GET')
def post(self,pattern):
return self.router(pattern,'POST')
def head(self,pattern):
return self.router(pattern,'HEAD')
def match(self,request:Request) -> Response:
print(r'{} {}'.format(self,self.prefix))
if not request.path.startswith(self.__prefix) or (self.__prefix == '' and request.path != ''):
print('ccccccccccccccccccccccccc')
return None
for methods,pattern,handler in self.__routetable:
print(request.path,22222222222222222)
print(request.path.replace(self.prefix,'',1))
matcher=pattern.match(request.path.replace(self.__prefix,'',1))
print(matcher)
if matcher:
if not methods or request.method.upper() in methods:
request.args=matcher.group()
request.kwargs=matcher.groupdict()
print(request.args,request.kwargs)
return handler(request)
else:
raise exc.HTTPMethodNotAllowed('{} is not allowed'.format(request.method))
return exc.HTTPNotFound('{} not Found'.format(request.path))
class Application:
ROUTERS=[]
@classmethod
def register(cls,router:Router):
cls.ROUTERS.append(router)
@wsgify
def __call__(self,request:Request) -> Response:
print(request.path)
for router in self.ROUTERS:
response=router.match(request)
if response:
return response
raise exc.HTTPBadRequest('{} is illegal'.format(request.path))
# 创建router
ii=Router()
uu=Router('/python')
# register
Application.register(ii)
Application.register(uu)
@ii.get('^/$')
def index(request:Request) -> Response:
response=Response()
response.status_code=301
response.content_type='text/html'
response.charset='utf8'
response.body='<a href="http://baidu.com">vbnm</a>'.encode()
return response
@uu.router('/(\w+)') # 支持所有method,匹配/uiop
def uiop(request:Request) -> Response:
response=Response()
response.content_type='text/plain'
response.charset='gb2312'
response.body='<h3>uiop</h3>'.encode()
return response
print(ii._Router__routetable,ii.prefix,ii)
print(uu._Router__routetable,uu.prefix,uu)
if __name__ == '__main__':
server=make_server('',9999,Application())
try:
server.serve_forever()
except:
pass
finally:
server.shutdown()
server.server_close()





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律