扩展分区和文件系统_Linux数据盘
扩容云盘(ResizeDisk)只是扩大云盘的存储容量,不会扩容ECS实例的文件系统,您需要按照本文步骤扩容文件系统,实现ECS实例存储空间的扩展。
前提条件
- 已创建快照备份数据。
为防止操作失误导致数据丢失,建议您操作前使用快照备份数据。具体操作请参见创建普通快照。
- 已在控制台上扩容云盘。
若尚未扩容,请参见在线扩容云盘(Linux系统)或离线扩容云盘(Linux系统)。
- 远程连接ECS实例。连接方式请参见连接方式概述。
背景信息
本文示例中使用的配置如下:
- ECS实例的操作系统:公共镜像Alibaba Cloud Linux 2.1903 LTS 64位
- 数据盘:高效云盘
- 数据盘设备名:/dev/vdb
若您使用的操作系统和数据盘设备名与本文示例不同,请根据实际情况调整命令或参数配置。
确认分区表格式和文件系统
- 运行以下命令确认数据盘的分区表格式。
fdisk -lu /dev/vdb本示例中,原有的数据盘空间已做分区/dev/vdb1。- 如果
"System"="Linux",说明数据盘使用的是MBR分区表格式。 - 如果
"System"="GPT",说明数据盘使用的是GPT分区表格式。
[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -lu /dev/vdb Disk /dev/vdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x9277b47b Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/vdb1 2048 41943039 20970496 83 Linux - 如果
- 运行以下命令确认已有分区的文件系统类型。
blkid /dev/vdb1本示例中,/dev/vdb1的文件系统类型为ext4。[root@ecshost ~]# blkid /dev/vdb1 /dev/vdb1: UUID="e97bf1e2-fc84-4c11-9652-73********24" TYPE="ext4"说明 未分区并且未创建文件系统的数据盘,以及已分区但未创建文件系统的数据盘,不会返回结果。 - 运行以下命令确认文件系统的状态。
- ext*文件系统:
e2fsck -n /dev/vdb1 - xfs文件系统:
xfs_repair -n /dev/vdb1
注意 本示例中,文件系统状态为clean,表示文件系统状态正常。如果状态不是clean,请排查并修复。[root@ecshost ~]# e2fsck -n /dev/vdb1 Warning! /dev/vdb1 is mounted. Warning: skipping journal recovery because doing a read-only filesystem check. /dev/vdb1: clean, 11/1310720 files, 126322/5242624 blocks - ext*文件系统:
选择扩容分区或文件系统的方式
根据您查询到的分区格式和文件系统情况确定操作选项。
| 扩容场景 | 相关操作 |
|---|---|
| 数据盘已分区并创建文件系统 |
|
| 全新数据盘,未分区,未创建文件系统 | 在控制台扩容数据盘空间后,请参见分区并格式化数据盘或者分区格式化大于2 TiB数据盘。 |
| 数据盘是裸设备,已创建文件系统,未分区 | 在控制台扩容数据盘空间后,请参见选项五:扩容裸设备文件系统。 |
| 数据盘未挂载到实例上 | 挂载数据盘到实例后,参见本文档的操作步骤完成扩容。 |
说明
- 如果一个已有分区采用了MBR分区格式,则不支持扩容到2TiB及以上。为避免造成数据丢失,建议您创建一块大于2TiB的云盘,格式化一个GPT分区,再将MBR分区中的数据拷贝到GPT分区中。具体操作,请参见分区格式化大于2 TiB数据盘。
- 当出现因扩容格式化工具问题导致的扩容失败时,您可以提前升级工具版本,或者卸载工具后重新安装。
选项一:扩展已有MBR分区
说明 为了防止数据丢失,不建议扩容已挂载的分区和文件系统。请先取消挂载(umount)分区,完成扩容并正常使用后,重新挂载(mount)。针对不同的Linux内核版本,推荐以下操作方式:
- 实例内核版本小于3.6:先取消挂载该分区,再修改分区表,最后扩容文件系统。
- 实例内核版本大于等于3.6:先修改对应分区表,再通知内核更新分区表,最后扩容文件系统。
如果新增空间用于扩容已有的MBR分区,按照以下步骤在实例中完成扩容:
- 修改分区表。扩容文件系统。
- 运行以下命令查看分区信息,并记录旧分区的起始和结束的扇区位置。
fdisk -lu /dev/vdb本示例中,分区/dev/vdb1的起始扇区是2048,结束扇区是41943039。
[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -lu /dev/vdb Disk /dev/vdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x9277b47b Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/vdb1 2048 41943039 20970496 83 Linux - 查看数据盘的挂载路径,根据返回的文件路径卸载分区,直至完全卸载已挂载的分区。
[root@ecshost ~]# mount | grep "/dev/vdb" /dev/vdb1 on /mnt type ext4 (rw,relatime,data=ordered) [root@ecshost ~]# umount /dev/vdb1 [root@ecshost ~]# mount | grep "/dev/vdb" - 使用fdisk工具删除旧分区。
警告 删除旧分区如果出错,可能会删除分区内的数据。如有重要数据(例如数据库中的用户数据),请在操作前进行备份,避免因删除旧分区而造成数据丢失。
- 运行
fdisk -u /dev/vdb:分区数据盘。 - 输入p:打印分区表。
- 输入d:删除分区。
- 输入p:确认分区已删除。
- 输入w:保存修改并退出。
[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -u /dev/vdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/vdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x9277b47b Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/vdb1 2048 41943039 20970496 83 Linux Command (m for help): d Selected partition 1 Partition 1 is deleted Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/vdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x9277b47b Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks. - 运行
- 使用fdisk命令新建分区。
- 运行
fdisk -u /dev/vdb:分区数据盘。 - 输入p:打印分区表。
- 输入n:新建分区。
- 输入p:选择分区类型为主分区。
- 输入<分区号>:选择分区号。本示例选取了1。
- 设置新分区的起始位置和结束位置。
警告 新分区的起始位置必须和旧分区的起始位置相同,结束位置必须大于旧分区的结束位置,否则会导致扩容失败。具体问题与解决方案请参见使用fdisk扩容新分区起始位置无法与扩容前保持一致。
- 输入w:保存修改并退出。
本示例中,将/dev/vdb1由20GiB扩容到40GiB。
[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -u /dev/vdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write command. Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/vdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x9277b47b Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System Command (m for help): n Partition type: p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free) e extended Select (default p): p Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1 First sector (2048-83886079, default 2048): Using default value 2048 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-83886079, default 83886079): Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 40 GiB is set Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks. - 运行
- 通知内核更新分区表。
运行
partprobe /dev/vdb或者partx -u /dev/vdb1,通知内核数据盘的分区表已经修改,需要同步更新。 - 运行
lsblk /dev/vdb确保分区表已经增加。 - 运行
e2fsck -f /dev/vdb1再次检查文件系统,确认扩容分区后的文件系统状态为clean。
- 运行以下命令查看分区信息,并记录旧分区的起始和结束的扇区位置。
-
- ext*文件系统(例如ext3和ext4):依次运行以下命令调整ext*文件系统大小并重新挂载分区。
[root@ecshost ~]# resize2fs /dev/vdb1 resize2fs 1.43.5 (04-Aug-2017) Resizing the filesystem on /dev/vdb1 to 7864320 (4k) blocks. The filesystem on /dev/vdb1 is now 7864320 blocks long. [root@ecshost ~]# mount /dev/vdb1 /mnt - xfs文件系统:依次运行以下命令先重新挂载分区,再调整xfs文件系统大小。
说明 新版xfs_growfs根据挂载点识别待扩容设备,例如
xfs_growfs /mnt。您可以运行xfs_growfs --help查看不同版本xfs_growfs的使用方法。[root@ecshost ~]# mount /dev/vdb1 /mnt/ [root@ecshost ~]# xfs_growfs /mnt meta-data=/dev/vdb1 isize=512 agcount=4, agsize=1310720 blks = sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1 = crc=1 finobt=0 spinodes=0 data = bsize=4096 blocks=5242880, imaxpct=25 = sunit=0 swidth=0 blks naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1 log =internal bsize=4096 blocks=2560, version=2 = sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1 realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0 data blocks changed from 5242880 to 7864320
- ext*文件系统(例如ext3和ext4):依次运行以下命令调整ext*文件系统大小并重新挂载分区。
选项二:新增并格式化MBR分区
如果新增空间用于增加新的MBR分区,按照以下步骤在实例中完成扩容:
- 运行
fdisk -u /dev/vdb命令新建分区。本示例中,为新增的20GiB新建分区,作为/dev/vdb2使用。
[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -u /dev/vdb Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2). Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them. Be careful before using the write commad. Command (m for help): p Disk /dev/vdb: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x2b31a2a3 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/vdb1 2048 41943039 20970496 83 Linux Command (m for help): n Partition type: p primary (1 primary, 0 extended, 3 free) e extended Select (default p): p Partition number (2-4, default 2): 2 First sector (41943040-83886079, default 41943040): Using default value 41943040 Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (41943040-83886079, default 83886079): Using default value 83886079 Partition 2 of type Linux and of size 20 GiB is set Command (m for help): w The partition table has been altered! Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table. Syncing disks. - 运行命令
lsblk /dev/vdb查看分区。[root@ecshost ~]# lsblk /dev/vdb NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT vdb 253:16 0 40G 0 disk ├─vdb1 253:17 0 20G 0 part └─vdb2 253:18 0 20G 0 part - 格式化新的分区。
- 创建ext4文件系统:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb2。[root@ecshost ~]# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb2 Filesystem label= OS type: Linux Block size=4096 (log=2) Fragment size=4096 (log=2) Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks 1310720 inodes, 5242880 blocks 262144 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user First data block=0 Maximum filesystem blocks=2153775104 160 block groups 32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group 8192 inodes per group Superblock backups stored on blocks: 32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208, 4096000 Allocating group tables: done Writing inode tables: done Creating journal (32768 blocks): done Writing superblocks and filesystem accounting information: done [root@ecshost ~]# blkid /dev/vdb2 /dev/vdb2: UUID="e3f336dc-d534-4fdd-****-b6ff1a55bdbb" TYPE="ext4" - 创建ext3文件系统:
mkfs.ext3 /dev/vdb2。 - 创建xfs文件系统:
mkfs.xfs -f /dev/vdb2。 - 创建btrfs文件系统:
mkfs.btrfs /dev/vdb2。
- 创建ext4文件系统:
- 运行
mount /dev/vdb2 /mnt挂载分区。 - 运行
df -h查看目前数据盘空间和使用情况。显示新建文件系统的信息,表示挂载成功。[root@ecshost ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/vda1 40G 1.6G 36G 5% / devtmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 3.9G 460K 3.9G 1% /run tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/vdb2 9.8G 37M 9.2G 1% /mnt tmpfs 783M 0 783M 0% /run/user/0
选项三:扩展已有GPT分区
如果新增空间用于扩容已有的GPT分区,按照以下步骤在实例中完成扩容:
- 查看数据盘的挂载路径,根据返回的文件路径卸载分区,直至完全卸载已挂载的分区。
[root@ecshost ~]# mount | grep "/dev/vdb" /dev/vdb1 on /mnt type ext4 (rw,relatime,data=ordered) [root@ecshost ~]# umount /dev/vdb1 [root@ecshost ~]# mount | grep "/dev/vdb" - 使用Parted工具为现有GPT分区分配容量。运行
fsck -f /dev/vdb1确认文件系统一致性。- 运行
parted /dev/vdb命令进入parted分区工具。如需查看parted工具使用说明,运行
help命令。 - 运行
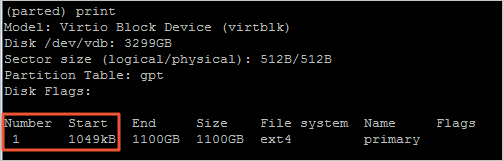
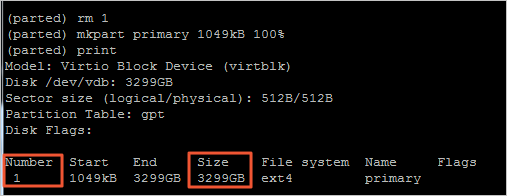
print查看分区信息,并记录现有分区的分区号和起始扇区的值。 - 运行
rm <分区号>命令删除现有分区。本示例中,现有分区的分区号为
1,因此命令为:rm 1 - 运行
mkpart primary <原分区的起始扇区> <容量分配百分比>命令重新创建主分区。本示例中,原分区的起始扇区为
1049kB,且要将扩容后的总容量(即3TiB)全部分配给该分区,因此命令为:mkpart primary 1049kB 100% - 运行
print命令查看新分区是否创建成功。 - 运行
quit退出Parted分区工具。
完整的示例代码如下:[root@ecshost ~]# parted /dev/vdb GNU Parted 3.1 Using /dev/vdb Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands. (parted) print Error: The backup GPT table is not at the end of the disk, as it should be. This might mean that another operating system believes the disk is smaller. Fix, by moving the backup to the end (and removing the old backup)? Fix/Ignore/Cancel? Fix Warning: Not all of the space available to /dev/vdb appears to be used, you can fix the GPT to use all of the space (an extra 4294967296 blocks) or continue with the current setting? Fix/Ignore? Fix Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdb: 3299GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 1049kB 1100GB 1100GB ext4 primary (parted) rm 1 (parted) mkpart primary 1049kB 100% (parted) print Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdb: 3299GB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 1049kB 3299GB 3299GB ext4 primary (parted) quit Information: You may need to update /etc/fstab. - 运行
-
[root@ecshost ~]# fsck -f /dev/vdb1 fsck from util-linux 2.23.2 e2fsck 1.43.5 (04-Aug-2017) Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes Pass 2: Checking directory structure Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity Pass 4: Checking reference counts Pass 5: Checking group summary information /dev/vdb1: 11/67108864 files (0.0% non-contiguous), 4265369/268434944 blocks - 扩展分区对应的文件系统并重新挂载分区。
- ext*文件系统(例如ext3和ext4):依次运行以下命令调整新分区的ext*文件系统大小并重新挂载分区。
[root@ecshost ~]# resize2fs /dev/vdb1 resize2fs 1.43.5 (04-Aug-2017) Resizing the filesystem on /dev/vdb1 to 805305856 (4k) blocks. The filesystem on /dev/vdb1 is now 805305856 blocks long. [root@ecshost ~]# mount /dev/vdb1 /mnt - xfs文件系统:依次运行以下命令先重新挂载分区再调整xfs文件系统大小。
说明 新版xfs_growfs根据挂载点识别待扩容设备,例如
xfs_growfs /mnt。您可以运行xfs_growfs --help查看不同版本xfs_growfs的使用方法。[root@ecshost ~]# mount /dev/vdb1 /mnt/ [root@ecshost ~]# xfs_growfs /mnt
- ext*文件系统(例如ext3和ext4):依次运行以下命令调整新分区的ext*文件系统大小并重新挂载分区。
选项四:新增并格式化GPT分区
如果新增空间用于增加新的分区并希望使用GPT分区格式,按照以下步骤在实例中完成扩容。示例采用一块32 TiB的数据盘,已有一个4.8TiB的分区/dev/vdb1,此次新建了一个/dev/vdb2分区。
- 使用fdisk工具查看数据盘中已有分区的信息。
[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -l Disk /dev/vda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x000b1b45 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/vda1 * 2048 83875364 41936658+ 83 Linux WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion. Disk /dev/vdb: 35184.4 GB, 35184372088832 bytes, 68719476736 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: gpt Disk identifier: BCE92401-F427-45CC-8B0D-B30EDF279C2F # Start End Size Type Name 1 2048 10307921919 4.8T Microsoft basic mnt - 使用parted工具创建新分区并分配容量。为新分区创建文件系统。
- 运行
parted /dev/vdb进入分区工具。 - 运行
print free查看数据盘待分配的容量,记录已有分区的扇区位置和容量。示例中/dev/vdb1的起始位置为1049KB,结束扇区为5278GB,容量为5278GiB。(parted) print free Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdb: 35.2TB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 17.4kB 1049kB 1031kB Free Space 1 1049kB 5278GB 5278GB ext4 mnt 5278GB 35.2TB 29.9TB Free Space - 运行
mkpart <分区名称> <起始扇区> <容量分配百分比>。示例新建了一个名为test的/dev/vdb2分区,起始扇区为上一个分区的结束扇区,并将所有新增空间分配给该分区。
- 运行
print查看容量(Size)是否发生变化。(parted) mkpart test 5278GB 100% (parted) print Model: Virtio Block Device (virtblk) Disk /dev/vdb: 35.2TB Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B Partition Table: gpt Disk Flags: Number Start End Size File system Name Flags 1 1049kB 5278GB 5278GB ext4 mnt 2 5278GB 35.2TB 29.9TB test - 运行
quit退出parted分区工具。
- 运行
-
- 创建ext4文件系统:
mkfs.ext4 /dev/vdb2。 - 创建ext3文件系统:
mkfs.ext3 /dev/vdb2。 - 创建xfs文件系统:
mkfs.xfs -f /dev/vdb2。 - 创建btrfs文件系统:
mkfs.btrfs /dev/vdb2。
[root@ecshost ~]# mkfs -t xfs /dev/vdb2 meta-data=/dev/vdb2 isize=512 agcount=28, agsize=268435455 blks = sectsz=512 attr=2, projid32bit=1 = crc=1 finobt=0, sparse=0 data = bsize=4096 blocks=7301444096, imaxpct=5 = sunit=0 swidth=0 blks naming =version 2 bsize=4096 ascii-ci=0 ftype=1 log =internal log bsize=4096 blocks=521728, version=2 = sectsz=512 sunit=0 blks, lazy-count=1 realtime =none extsz=4096 blocks=0, rtextents=0 - 创建ext4文件系统:
- 运行
fdisk -l查看分区容量变化。[root@ecshost ~]# fdisk -l Disk /dev/vda: 42.9 GB, 42949672960 bytes, 83886080 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: dos Disk identifier: 0x000b1b45 Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System /dev/vda1 * 2048 83875364 41936658+ 83 Linux WARNING: fdisk GPT support is currently new, and therefore in an experimental phase. Use at your own discretion. Disk /dev/vdb: 35184.4 GB, 35184372088832 bytes, 68719476736 sectors Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes Disk label type: gpt Disk identifier: BCE92401-F427-45CC-8B0D-B30EDF279C2F # Start End Size Type Name 1 2048 10307921919 4.8T Microsoft basic mnt 2 10307921920 68719474687 27.2T Microsoft basic test - 运行blkid查看存储设备的文件系统类型。
[root@ecshost ~]# blkid /dev/vda1: UUID="ed95c595-4813-480e-****-85b1347842e8" TYPE="ext4" /dev/vdb1: UUID="21e91bbc-7bca-4c08-****-88d5b3a2303d" TYPE="ext4" PARTLABEL="mnt" PARTUUID="576235e0-5e04-4b76-****-741cbc7e98cb" /dev/vdb2: UUID="a7dcde59-8f0f-4193-****-362a27192fb1" TYPE="xfs" PARTLABEL="test" PARTUUID="464a9fa9-3933-4365-****-c42de62d2864" - 挂载新分区。
[root@ecshost ~]# mount /dev/vdb2 /mnt
选项五:扩容裸设备文件系统
当数据盘没有创建分区,并且在裸设备上创建了文件系统时,您可以参见以下步骤直接扩容文件系统。
- 查看数据盘的挂载路径,根据返回的文件路径卸载。
[root@ecshost ~]# mount | grep "/dev/vdb" /dev/vdb on /mnt type ext4 (rw,relatime,data=ordered) [root@ecshost ~]# umount /dev/vdb [root@ecshost ~]# mount | grep "/dev/vdb" - 根据文件系统的类型,执行不同的扩容命令。
- ext*:使用root权限执行resize2fs命令扩容文件系统,例如:
resize2fs /dev/vdb - xfs:使用root权限执行xfs_growfs命令扩容文件系统。
说明 新版xfs_growfs根据挂载点识别待扩容设备,例如
xfs_growfs /mnt。您可以运行xfs_growfs --help查看不同版本xfs_growfs的使用方法。- 新版xfs_growfs
xfs_growfs /mnt - 未更新版xfs_growfs
xfs_growfs /dev/vdb
- 新版xfs_growfs
- ext*:使用root权限执行resize2fs命令扩容文件系统,例如:
- 将云盘挂载至挂载点。
mount /dev/vdb /mnt - 运行
df -h查看数据盘扩容结果。显示容量完成扩充,表示扩容成功。[root@ecshost ~]# df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on /dev/vda1 40G 1.6G 36G 5% / devtmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /dev/shm tmpfs 3.9G 460K 3.9G 1% /run tmpfs 3.9G 0 3.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/vdb 98G 37G 61G 37% /mnt tmpfs 783M 0 783M 0% /run/user/0




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律