字符串类——字符串类的创建(下)
1,上篇博文中的 String 创建功能很弱,不能满足开发的需要,本文为这个字符串类开发一系列函数(函数代码已经集成到“字符串类——字符串类的创建(上)”一文中,本节讲述实现原理),使其能够胜任一系列工程开发的需要;
2,字符串类中的常用成员函数:

3,重载数组访问操作符 []:
1,char& operator [] (int i);
1,字符串对象应该能够像字符数组一样,通过每一个下标来访问每一个字符;
2,引用意味着可以被赋值,可以出现在赋值符号左边(此时是对象),给没有被 const 修饰的版本用;
2,char operator [] (int i) const;
1,不能作为左值,所以不能返回引用对象;给 const 修饰的常对象版本使用;
3,注意事项:
1,当 i 取值不合法时,抛出异常:
1,合法范围:(0 <= i) && (i < m_length);
4,重载操作符的声明:
char& operator [] (int i);
char operator [] (int i) const;
5,重载操作符的实现:
1 char& String::operator [] (int i) 2 { 3 if( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) ) 4 { 5 return m_str[i]; // 封装; 6 } 7 else 8 { 9 THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ..."); 10 } 11 } 12 13 char String::operator [] (int i) const 14 { 15 return (const_cast<String&>(*this))[i]; // 在当前版本当中对非 const 代码复用 16 }
4,判断是否已指定字符串开始或结束:
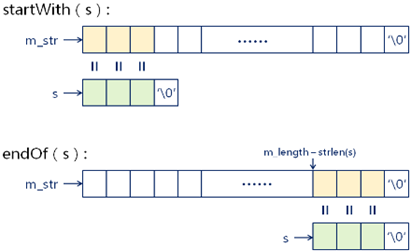
1,bool startWith(const char* s) const;
2,bool startWith(const String& s) const;
3,bool endOf(const char* s) const;
4,bool endOf(const String& s) const;
5,开始或结束成员函数的声明:
1 /* 判断当前的字符对象是否以 s 开头,判断当前的字符对象是否以 s 结束 */ 2 bool startWith(const char* s) const; 3 bool startWith(const String& s) const; 4 bool endOf(const char* s) const; 5 bool endOf(const String& s) const;
6,开始或结束成员函数的定义:
1 /* 比对函数,为 startWith() 和 endOf() 函数服务,前两个参数为字符数组的首地址,第三个参数是字符数组长度;长度范围内字符数组对应元素都相等,返回真; */ 2 bool String::equal(const char* l, const char* r, int len) const 3 { 4 bool ret = true; 5 6 for(int i=0; i<len && ret; i++) // 这里的 ret 看似没用,实则只要有元素不相等就停止循环、非常重要; 7 { 8 ret = ret && (l[i] == r[i]); // 如果有一个位置的字符不相等,则结束比较,返回 false; 9 } 10 11 return ret; 12 } 13 14 /* 判断当前的字符对象是否以 s 开头 */ 15 bool String::startWith(const char* s) const 16 { 17 bool ret = (s != NULL); 18 19 if( ret ) 20 { 21 int len = strlen(s); 22 23 ret = (len < m_length) && equal(m_str, s, len); // 如果参数字符串 s 长度比当前字符串长度更长,直接返回 false; 24 } 25 26 return ret; 27 } 28 29 bool String::startWith(const String& s) const 30 { 31 return startWith(s.m_str); // 代码复用了上面的 32 } 33 34 bool String::endOf(const char* s) const // s 这个字符串是否是以字符开始 35 { 36 bool ret = (s != NULL); 37 38 if( ret ) 39 { 40 int len = strlen(s); 41 char* str = m_str + (m_length - len); // 计算最后 n 个字符表示的字符串; 42 43 ret = (len < m_length) && equal(str, s, len); // 如果参数字符串 s 长度比当前字符串长度更长,直接返回 false; 44 } 45 46 return ret; 47 } 48 49 bool String::endOf(const String& s) const 50 { 51 return endOf(s.m_str); // 代码复用了上面的 52 }
5,在指定位置插入字符串:
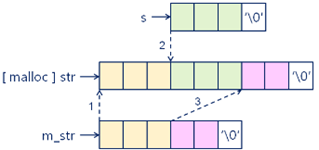
1,String& insert(int i, const char* s);
2,String& insert(int i, const String& s);
3,插入字符串成员函数的声明:
String& insert(int i, const char* s);
String& insert(int i, const String& s);
4,插入字符串成员函数的定义:
1 /* 第 i 个位置插入字符串 s,返回字符串对象是为了实现链式操作 */ 2 String& String::insert(int i, const char* s) 3 { 4 if( (0 <= i) && (i <= m_length) ) 5 { 6 if( (s != NULL) && (s[0] != '\0') ) // 不为空和空字符串; 7 { 8 int len = strlen(s); 9 char* str = reinterpret_cast<char*>(malloc(m_length + len + 1)); 10 11 if( str != NULL ) 12 { 13 strncpy(str, m_str, i); //当前字符串的前 i 个字符拷贝出来到 str 14 strncpy(str + i, s, len); //将参数字符串s全部拷贝到 str+i 上去 15 strncpy(str + i + len, m_str + i, m_length - i); // 将最后字符串拷贝出来 16 str[m_length + len] = '\0'; // 最后添加结束符 17 free(m_str); // 释放当前字符串的堆空间 18 m_str = str; // 使用申请出来的堆空间中的字符串; 19 m_length = m_length + len; 20 } 21 else 22 { 23 THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert String value ..."); 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 else 28 { 29 THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Parameter i is invalid ..."); 30 } 31 32 return *this; 33 } 34 35 String& String::insert(int i, const String& s) 36 { 37 return insert(i, s.m_str); 38 }
6,去掉字符串两端的空白:
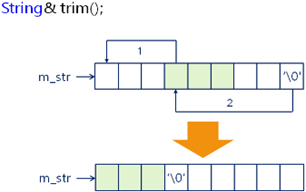
1,String& trim();
2,去掉字符串两端空白成员函数的声明:
String& trim();
3,去掉字符串两端空白成员函数的定义:
1 String& String::trim() 2 { 3 int b = 0; 4 int e = m_length - 1; 5 6 while( m_str[b] == ' ' ) b++; // 确定中间字符串开始位置; 7 while( m_str[e] == ' ' ) e--; // 确定中间字符窜结束位置; 8 9 if( b == 0 ) 10 { 11 m_str[e + 1] = '\0'; // 最开始没有空格的时候; 12 m_length = e + 1; 13 } 14 else 15 { 16 for(int i=0, j=b; j<=e; i++, j++) 17 { 18 m_str[i] = m_str[j]; // 将当前的含有的非空字符挪到前面去; 19 } 20 21 m_str[e - b + 1] = '\0'; // 添加结束符 22 m_length = e - b + 1; // 合法的字符个数; 23 } 24 25 return *this; // 实现链式调用 26 }
7,本节课测试代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include "DTString.h" 3 4 using namespace std; 5 using namespace DTLib; 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 String s = "D.T.Software"; 10 11 cout << s.startWith("D.T.") << endl; 12 cout << s.endOf("Software") << endl; 13 cout << s.startWith("abc") << endl; 14 cout << s.endOf("111") << endl; 15 16 for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++) 17 { 18 cout << s[i] << endl; 19 } 20 21 String s1 = ""; 22 s1.insert(0, "D.T."); 23 s1.insert(4, "Sofgware"); 24 25 for(int i=0; i<s.length(); i++) 26 { 27 cout << s[i] << endl; 28 } 29 30 cout << s1.str() << endl; 31 String s2 = " abc "; 32 33 cout << s2.trim().str() << endl; // 第二个点用了链式操作; 34 35 if( s2.trim().insert(0, "D.T.").endOf("abc") && s2.startWith("D.T.")) // 链式结构 36 { 37 cout << s2.str() << endl; 38 } 39 40 return 0; 41 }
8,在 const 函数中调用非 const 函数:
1,要去掉 const 函数的 const 属性;
2,给非 const 函数加上 const属性;
3,给非 const 函数加上 mutable 属性;



