线性表的链式存储——单链表的实现
1,本文目标:

1,完成链式存储结构线性表的实现;
2,LinkList 设计要点:
1,类模板,通过头结点访问后继结点;
2,定义内部结点类型 Node,用于描述数据域和指针域;
3,实现线性表的关键操作(增删查等);
3,链表的定义:
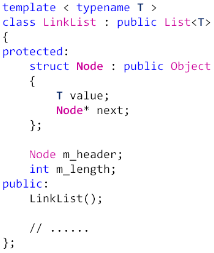
4,LinkList 链表的实现:
1 #ifndef LINKLIST_H 2 #define LINKLIST_H 3 4 #include "List.h" 5 #include "Exception.h" 6 7 /* 链表三要素:长度、头结点、指针域。 */ 8 namespace DTLib 9 { 10 11 template <typename T> 12 class LinkList : public List<T> 13 { 14 protected: 15 struct Node : public Object // 所有的类都继承自 Object,使类在有统一的“堆空间特性”; 16 { 17 T value; 18 Node* next; 19 }; 20 /*设法在构造头结点的时候,不去构造泛指类型的构造函数;以免泛指类型有异常产生,而此刻如果只是定义链表对象没有插入数据的话,就会构造链表对象的成员变量头结点、此时头结点就会调用普通结点中构造泛指类型的构造函数来构造头结点对象,从而产生异常;舍弃了 Node* m_header 的构造方式*/ 21 22 mutable struct : public Object // 构造头结点的时候,设法不去调用泛指类型的函数;构造匿名类型的结构,为了保证结构相同,这里也继承了Object,因为 Object 中有虚函数,这样也会改变子类的结构的,此时不继承的话 reinterpret_cast解释 m_header 和 Node 的不同呢,就会有异常产生; 23 { 24 char reserved[sizeof(T)]; // 定义数组,没有实际作用,仅仅用于占空间 25 Node* next; 26 }m_header; // 头结点对象在内存布局上面和上面结构Node结构体没有任何差异,有差异仅在于不管T为何对象,都不会调用T的构造函数(如果有); 27 28 int m_length; // 定义链表的长度 29 Node* m_current; // 定义遍历函数当前游标的位置 30 int m_step; // 定义遍历函数遍历的步幅,这里实//质是通过成员变量 m_step 将 move() 中的参数 setp 传递到 next()中来控制移动的步幅; 31 32 Node* position(int i) const // O(n) 第 i 个节点,但是下标为 i - 1 33 { 34 Node* ret = reinterpret_cast<Node*>(&m_header); // 这里虽然 m_header 内存布局和 Node 相同,但是类型不同不能直接初始化; reinterpret_cast 在底层重新解释,所以对象内部布局一定要相同,一般只能用于指针类型及整数和指针类型的强制类型转换; 35 36 for(int p=0; p<i; p++) // 移动的个数和位置是一样的 37 { 38 ret = ret->next; 39 } 40 41 return ret; 42 } 43 44 virtual Node* creat() // 这样的封装是因为面向对象里面的主导思想有封装,所以采纳这样的封装;在 LinkList 中没有多大意义,但对于后续学习有很大的意义,更有利于增强扩展性 45 { 46 return new Node(); // 链表是建立在堆空间上的 47 } 48 49 virtual void destroy(Node* pn) // 这样的封装是因为面向对象里面的主导思想有封装,所以采纳这样的封装;在 LinkList 中没有多大意义,但对于后续学习有很大的意义,更有利于增强扩展性 50 { 51 delete pn; //只能对堆空间来释放空间,如果不是堆空间,则程序会不稳定; 52 } 53 54 public: 55 LinkList() 56 { 57 m_header.next = NULL; 58 m_length = 0; 59 m_current = NULL; 60 m_step = 1; // 默认的每次移动一个步幅; 61 } 62 63 bool insert(const T& e) // 在线性表的尾部默认的插入一个元素,所以 i 省略了; 64 { 65 return insert(m_length, e); 66 } 67 68 bool insert(int i, const T& e) //(n) 实现步骤和线性表大同小异 69 { 70 bool ret = ((0 <= i) && (i <= m_length)); 71 72 if( ret ) 73 { 74 Node* node = creat(); // 从堆空间申请一个对象出来;取决于调用的是哪个具体的对象,因为位虚函数; 75 76 if( node != NULL ) 77 { 78 Node* current = position(i); // O(n),不能随机访问数据元素,这是链表的缺点; 79 80 node->value = e; 81 node->next = current->next; 82 current->next = node; 83 m_length++; 84 } 85 else 86 { 87 THROW_EXCEPTION(NoEnoughMemoryException, "No memory to insert new element ..."); 88 } 89 } 90 91 return ret; 92 } 93 94 bool remove(int i) // O(n) 95 { 96 bool ret = ( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) ); 97 98 if( ret ) 99 { 100 Node* current = position(i); // O(n) 101 Node* toDel = current->next; // 这里不用判断是否为空,一定不为空; 102 103 if( m_current == toDel) // 这个步骤是为了放置 m_current 仍旧指向被删除的元素; 104 { 105 m_current = toDel->next; 106 } 107 108 current->next = toDel->next; 109 m_length--; 110 destroy(toDel); 111 } 112 113 return ret; 114 } 115 116 bool set(int i, const T& e) 117 { 118 bool ret = ( (0 <= i) && (i < m_length) ); 119 120 if( ret ) 121 { 122 position(i)->next->value = e; // O(n) 123 } 124 125 return ret; 126 } 127 128 virtual T get(int i) const 129 { 130 T ret; 131 132 if( get(i, ret) ) 133 { 134 return ret; 135 } 136 else 137 { 138 THROW_EXCEPTION(IndexOutOfBoundsException, "Invalid parameter i to get element ..."); 139 } 140 141 return ret; 142 } 143 144 bool get(int i, T& e) const // const 表明不能够修改任何成员变量的值; 145 { 146 bool ret = ( (0 <= i) && (i <= m_length) ); 147 148 if( ret ) 149 { 150 e = position(i)->next->value; // O(n) 151 } 152 153 return ret; 154 } 155 156 int find(const T& e) const // 发现当前值为 e 的节点所处的链表 位置 i ; 157 { 158 int ret = -1; 159 int i = 0; 160 Node* node = m_header.next; 161 162 while( node ) // O(n) 163 { 164 if(node->value == e) 165 { 166 ret = i; 167 break; 168 } 169 else 170 { 171 node = node->next; 172 i++; 173 } 174 } 175 176 return ret; 177 } 178 179 int length() const // O(1) 180 { 181 return m_length; 182 } 183 184 void clear() // O(n) 185 { 186 while( m_header.next ) 187 { 188 Node* toDel = m_header.next; 189 m_header.next = toDel->next; // 做完这里的指针操作证明对应的结点已经从链表中剥离出来了,所以先减长度; 190 m_length--; 191 destroy(toDel); // 做完其他操作在销毁,保证异常安全; 192 } 193 } 194 195 /* 以下四个函数move(),end(),next(),current()是为了将遍历输出函数时间复杂度由O(n*n)降为O(n);其中 move() 函数时间复杂度为 i,其后三个函数在 for() 循环中加起来的时间复杂度为才为 O(n),很经典 */ 196 197 virtual bool move(int i, int step = 1) // 从第 i 个位置移动,每次移动 1 个位置; O(n) 198 { 199 bool ret = ( (0<= i) && (i<m_length) && (0<step)); 200 201 if( ret ) 202 { 203 m_current = position(i)->next; // 定位到节点i,不是第 i 个节点,所以要加上next,这里时间复杂度严格来说是 i,配合着后面的 next() 函数的移动,则最终的时间复杂度才是 n; 204 m_step = step; // 将每次要移动的值传进来 205 } 206 return ret; 207 } 208 209 virtual bool end() // 判断当前的游标是否结束 210 { 211 return (m_current == NULL); // 这里不可写成赋值了 212 } 213 214 virtual T current() // 获取游标当前位置的值 215 { 216 if( !end() ) // m_current != NULL ==> !end(),这里是判断当前指针的有效性; 217 { 218 return m_current->value; 219 } 220 else 221 { 222 THROW_EXCEPTION(InvalidOperationException, "No value at current position ..."); 223 } 224 } 225 226 virtual bool next() // 移动游标 227 { 228 int i = 0; 229 230 while( (i<m_step) && (!end()) ) // 这里的 !end() 是为了判m_step 步幅是否会将指针指向空,所以在 move() 不用判断 step 的小于范围; 231 { 232 m_current = m_current->next; 233 i++; 234 } 235 236 return (i == m_step); 237 } 238 239 ~LinkList() // O(n) 240 { 241 clear(); // 构造函数和析构函数中不会发生多态;不管是直接调用的虚函数,还是间接调用的虚函数,都是直接调用的当前类中的实现版本;如果当前的单链表需要销毁,销毁前先将单链表里面每一个对象删除了,最后摧毁当前的单链表对象; 242 } 243 }; 244 } 245 #endif // LINKLIST_H
5,问题:
1,头结点是否存在隐患?
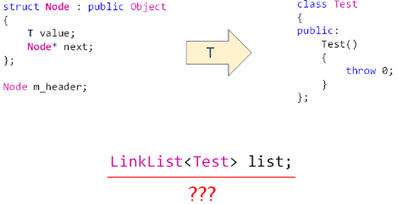
1,设法在构造头结点的时候,不去构造泛指类型的构造函数;以免泛指类型有异常产生,而此刻如果只是定义链表对象没有插入数据的话,就会构造链表对象的成员变量头结点、此时头结点就会调用普通结点中构造泛指类型的构造函数来构造头结点对象,从而产生异常;
2,用匿名结构体加上占位空间来解决问题,见 5 中代码实现;
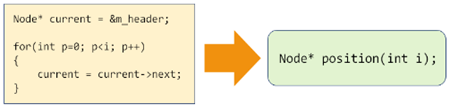
2,实现代码是否需要优化?
1,insert、remove、get、set 等操作都涉及元素定位;
6,小结:
1,通过类模板实现链表,包含头结点成员和长度成员;
2,定义节点类型,并通过堆中的结点队形构成链式存储;
3,为了避免构造错误的隐患,头结点类型需要重定义;
4,代码优化是编码完成后必不可少的环节;
此文为作者学习唐佐林老师的学习笔记,仅为交流共享之用,由此带来的后果,与作者无关;转载请注明转载出处;难免有错,欢迎指正,联系方式qunchao24@sina.com。





