算法图解(二)
一、分而治之(divide and conquer,D&C)
d&c解决问题的两个步骤:
1.找基线条件(最小单位)or(只剩一个或为空);
2.将问题的规模缩小,不断递归直到基线条件;
利用循环求和:
1 def sum(arr): 2 total = 0 3 for i in arr: 4 total += i 5 return total 6 7 print(sum([1,2,3,4]))
利用D&C求和:

1 def sum(arr): 2 if arr == []: 3 return 0 4 elif len(arr) == 1: 5 return arr[0] 6 else: 7 first = arr[0] 8 arr = arr[1:] 9 return first + sum(arr) 10 11 print(sum([12,13,14,15]))
答案:
1 def diy_sum(arr): 2 if not arr: 3 return 0 4 elif len(arr) == 1: 5 return arr[0] 6 else: 7 return arr.pop(0)+ sum(arr) 8 9 print(diy_sum([12,13,14,15]))
编写一个递归函数来计算列表包含的元素数:
1 def count_elements(arr): 2 if not arr: 3 return 0 4 elif len(arr) == 1: 5 return 1 6 else: 7 return 1 + count_elements(arr[1:]) 8 9 print(ele_num([12,'dc',22,'c']))
找出列表中最大的数字:
循环:
1 def find_max(arr): 2 if not arr: 3 return None 4 elif len(arr) == 1: 5 return arr[0] 6 else: 7 max = arr[0] 8 for i in range(len(arr)-1): 9 for j in arr[1:]: 10 if max < j: 11 max = j 12 return max 13 14 print(find_max([2,21,3,56,7,8,22]))
D&C:
1 def bigger(int1,int2): 2 if int1 <= int2: 3 return int2 4 else: 5 return int1 6 7 def find_biggest(arr): 8 if not arr: 9 return None 10 elif len(arr) == 1: 11 return arr[0] 12 elif len(arr) == 2: 13 return bigger(arr[0],arr[1]) 14 else: 15 max= arr[0] 16 return bigger(max,find_biggest(arr[1:])) 17 18 print(find_biggest([2,21,3,56,7,8,22]))
二分查找:
1 def find(arr,item,low,high): 2 if low > high: 3 return None 4 else: 5 mid = int((low+high)/2) 6 guess = arr[mid] 7 8 if guess == item: 9 return mid 10 11 elif guess < item: 12 low = mid + 1 13 return find(arr,item,low,high) 14 15 elif guess > item: 16 high = mid - 1 17 return find(arr,item,low,high) 18 19 def binary_search(list,target): 20 return find(list,target,0,len(list)-1) 21 22 arr = [1,2,5,6,7,8,9,12] 23 target = 7 24 print(binary_search(arr,target))
二、D&C典范:快速排序

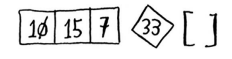
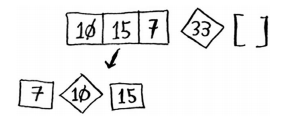
1 def quicksort(arr): 2 if len(arr) < 2: 3 return arr 4 else: 5 pivot = arr[0] 6 less = [i for i in arr[1:] if pivot >= i] #由所有小于基准值的元素组成的子数组 7 greater = [i for i in arr[1:] if pivot < i] #由所有大于基准值的元素组成的子数组 8 return quicksort(less) + [pivot] + quicksort(greater) 9 print(quicksort([10,3,4,6,2,5,11]))
1 a = [4,5] 2 b = [2,1] 3 a + b
[4, 5, 2, 1]
快速排序的速度取决于基准值。
最糟情况:
取第一个元素为基准,且数组是有序的:

调用栈非常长,栈长O(n),调用栈的每层都涉及O(n)个元素,时间复杂度O(n2)。
最佳情况(平均情况:随机选择基准值):
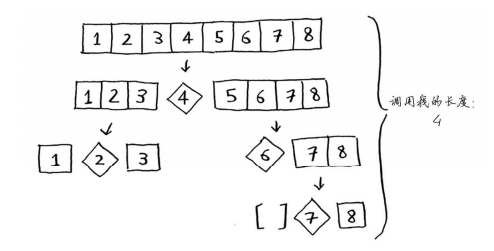
调用栈短的多,栈长O(logn),每层需要的时间为O(n),时间复杂度O(nlogn)。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号