查找两个单词链表共同后缀的起始结点
描述
假定采用带头结点的单链表保存单词,当两个单词有相同的后缀时,则可共享相同的后缀空间。例如,“loading”和“being”的存储映像如下图所示:
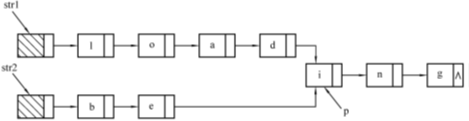
设str1和str2分别指向两个单词所在单链表的头结点,请实现一个时间上尽可能高效的算法,找出由str1和str2所指的两个链表共同后缀的起始位置的结点,输出该结点对应的字符(如图中的字符i)
输入
多组数据,每组数据有三行,第一行为链表str1和str2的长度n和m,第二行为链表str1的n个元素,第三行为链表str2的m个元素(元素之间用空格分隔)。n=0且m=0时输入结束。
输出
对于每组数据输出一行,为共同后缀的起始位置结点对应的字符。
输入样例 1
7 5 l o a d i n g b e i n g 7 9 f l u e n c y f r e q u e n c y 0 0
输出样例 1
i u
注意main函数中用一个getchar()来吸收回车。
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<math.h> #define MAXSIZE 1000 #define OVERFLOW -2 #define ERROR 0 #include<iostream> using namespace std; typedef struct LNode{ char word; struct LNode *next; }LNode,* LinkList; void Inist_List(LinkList& L,int n){ L=new LNode; L->next=NULL; LinkList p; while(n--){ p=new LNode; scanf("%c",&p->word); getchar(); p->next=L->next; L->next=p; } } void Find_word(LinkList L1,LinkList L2){ LinkList p=L1,q=L2; while(p->next&&q->next){ if(p->next->word==q->next->word){ p=p->next; q=q->next; } else { printf("%c\n",p->word); break; } } } int main(){ while(1){ LinkList L1,L2; int m,n; scanf("%d%d",&m,&n); getchar(); if(m==0&&n==0) return 0; Inist_List(L1,m); Inist_List(L2,n); Find_word(L1,L2); } return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号