Executor框架
Executor框架的主要成员:ThreadPoolExecutor、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor、Future接口、runnable接口、Callable接口和Executors。
通常使用工厂类executors来创建。executors可创建3种类型的ThreadPoolExecutor :SingleThreadExecutor、FixedThreadPool和CachedThreadPool。
1) FixedThreadPool
FixedThreadPool 被称为可重用固定线程数的线程池。
/** * Creates a thread pool that reuses a fixed number of threads * operating off a shared unbounded queue. At any point, at most * {@code nThreads} threads will be active processing tasks. * If additional tasks are submitted when all threads are active, * they will wait in the queue until a thread is available. * If any thread terminates due to a failure during execution * prior to shutdown, a new one will take its place if needed to * execute subsequent tasks. The threads in the pool will exist * until it is explicitly {@link ExecutorService#shutdown shutdown}. * * @param nThreads the number of threads in the pool * @return the newly created thread pool * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code nThreads <= 0} */ public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }
FixedThreadPool 的corePoolSize和maximumPoolSize都被设置为创建FixedThreadPool时指定的参数nThreads。
当线程池中的线程数大于corePoolSize时,这里把KeepAliveTime设置为0L意味着多余的空闲线程会被立即终止。
FixedThreadpool使用无界队列 Linked Blockingqueue作为线程池的工作队列(队列的容量为 Integer. MAX VALUE)。使用无界队列作为王作队列会对线程池带来如下影响。
1)当线程池中的线程数达到 corepoolsize后,新任务将在无界队列中等待,因此线程池中的线程数不会超过 corepoolsize。
2)由于1,使用无界队列时 maximumPoolSize将是一个无效参数。
3)由于1和2,使用无界队列时 keepaliveTime将是一个无效参数。
4)由于使用无界队列,运行中的 FixedThreadpool(未执行方法 shutdown()或 shutdownnow())不会拒绝任务(不会调用 Rejectedexecutionhandler. rejectedexecution方法)。
以下是这三种线程池的应用场景说明:
FixedThreadPool适用于为了满足资源管理的需求,而需要限制当前线程数量的应用场景,它适用于负载比较重的服务器。
SingleThreadExecutor适用于需要保证顺序地执行各个任务;并且在任意时间点,不会有多个线程是活动的应用场景。
CachedThreadPool是大小无界的线程池,适用于执行很多的短期异步任务的小程序,或者是负载较轻的服务器
待续。。。
ThreadPoolExecutor类中execute()和submit()
向线程池提交任务 ThreadPoolExecutor类中execute()和submit()区别 execute()方法实际上是Executor中声明的方法,在ThreadPoolExecutor进行了具体的实现,这个方法是ThreadPoolExecutor的核心方法,通过这个方法可以向线程池提交一个任务,交由线程池去执行。

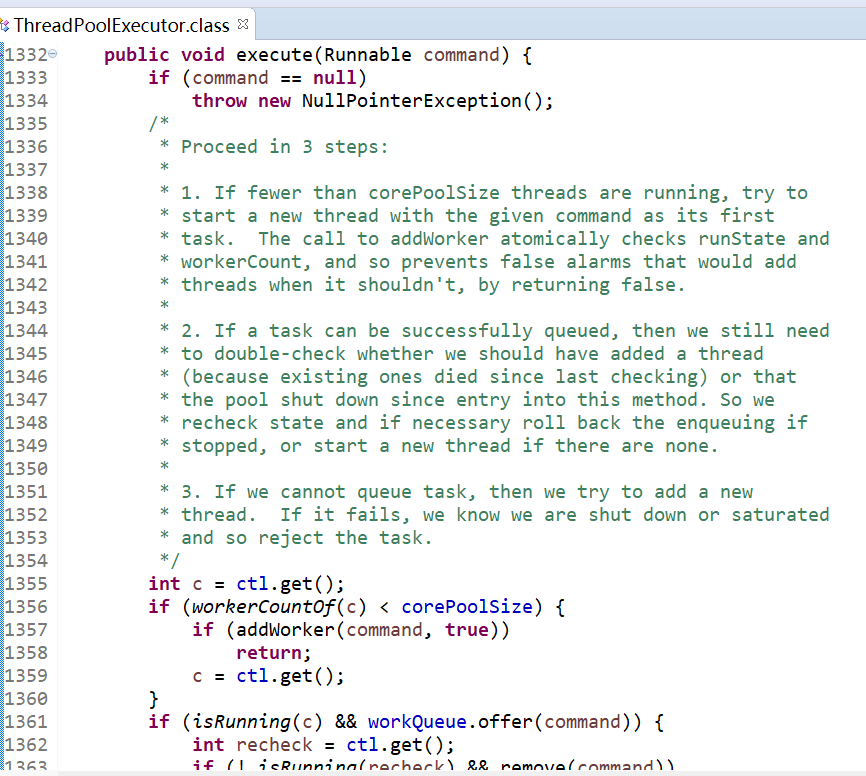
submit()方法是在ExecutorService中声明的方法,在AbstractExecutorService就已经有了具体的实现,在ThreadPoolExecutor中并没有对其进行重写,这个方法也是用来向线程池提交任务的,但是它和execute()方法不同,它能够返回任务执行的结果,通过源码查看submit()方法的实现,会发现它实际上还是调用的execute()方法,只不过它利用了Future来获取任务执行结果。
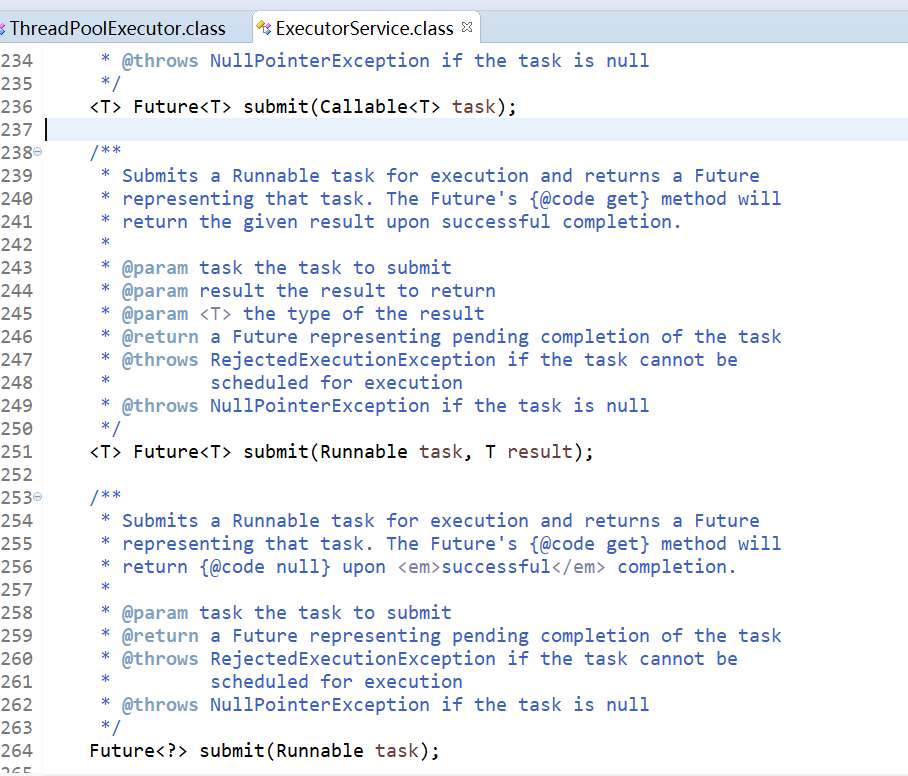
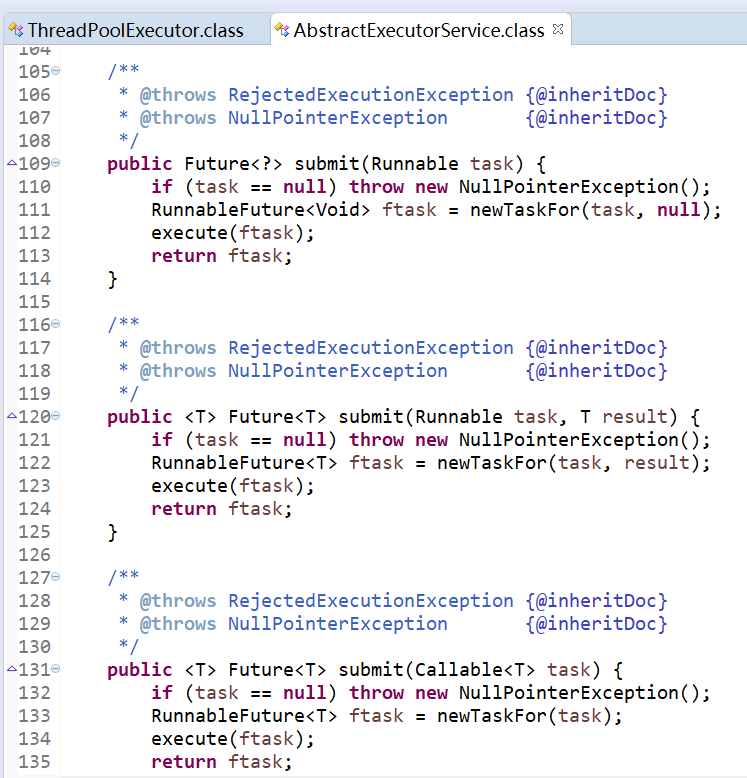
参考:https://www.jb51.net/article/134862.htm
内容来自《java并发编程的艺术》






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)