C# Socket编程 同步以及异步通信
套接字简介:套接字最早是Unix的,window是借鉴过来的。TCP/IP协议族提供三种套接字:流式、数据报式、原始套接字。其中原始套接字允许对底层协议直接访问,一般用于检验新协议或者新设备问题,很少使用。
套接字编程原理:延续文件作用思想,打开-读写-关闭的模式。
C/S编程模式如下:
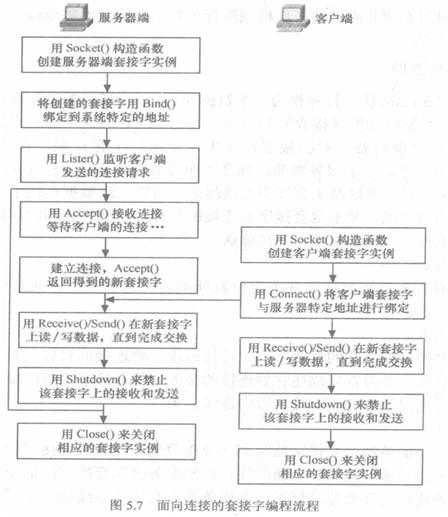
Ø 服务器端:
打开通信通道,告诉本地机器,愿意在该通道上接受客户请求——监听,等待客户请求——接受请求,创建专用链接进行读写——处理完毕,关闭专用链接——关闭通信通道(当然其中监听到关闭专用链接可以重复循环)
Ø 客户端:打开通信通道,连接服务器——数据交互——关闭信道。
Socket通信方式:
Ø 同步:客户端在发送请求之后必须等到服务器回应之后才可以发送下一条请求。串行运行
Ø 异步:客户端请求之后,不必等到服务器回应之后就可以发送下一条请求。并行运行
套接字模式:
Ø 阻塞:执行此套接字调用时,所有调用函数只有在得到返回结果之后才会返回。在调用结果返回之前,当前进程会被挂起。即此套接字一直被阻塞在网络调用上。
Ø 非阻塞:执行此套接字调用时,调用函数即使得不到得到返回结果也会返回。
套接字工作步骤:
Ø 服务器监听:监听时服务器端套接字并不定位具体客户端套接字,而是处于等待链接的状态,实时监控网络状态
Ø 客户端链接:客户端发出链接请求,要连接的目标是服务器端的套接字。为此客户端套接字必须描述服务器端套接字的服务器地址与端口号。
Ø 链接确认:是指服务器端套接字监听到客户端套接字的链接请求时,它响应客户端链接请求,建立一个新的线程,把服务器端套接字的描述发送给客户端,一旦客户端确认此描述,则链接建立好。而服务器端的套接字继续处于监听状态,继续接受其他客户端套接字请求。
在TCP/IP网络中,IP网络交互分类两大类:面向连接的交互与面向无连接的交互。

Socket构造函数:public socket(AddressFamily 寻址类型, SocketType 套接字类型, ProtocolType 协议类型)。但需要注意的是套接字类型与协议类型并不是可以随便组合。
|
SocketType |
ProtocolType |
描述 |
||||||
|
Stream |
Tcp |
面向连接 |
||||||
|
Dgram |
Udp |
面向无连接 |
||||||
|
Raw |
Icmp |
网际消息控制 |
||||||
|
Raw |
Raw |
基础传输协议 |
||||||
|
Socket类的公共属性: |
||||||||
|
属性名 |
描述 |
|||||||
|
AddressFamily |
获取Socket的地址族 |
|||||||
|
Available |
获取已经从网络接收且可供读取的数据量 |
|||||||
|
Blocking |
获取或设置一个值,只是socket是否处于阻塞模式 |
|||||||
|
Connected |
获取一个值,指示当前连接状态 |
|||||||
|
Handle |
获取socket的操作系统句柄 |
|||||||
|
LocalEndPoint |
获取本地终端EndPoint |
|||||||
|
RemoteEndPoint |
获取远程终端EndPoint |
|||||||
|
ProtocolType |
获取协议类型 |
|||||||
|
SocketType |
获取SocketType类型 |
|||||||
|
Socket常用方法: |
||||||||
|
Bind(EndPoint) |
服务器端套接字需要绑定到特定的终端,客户端也可以先绑定再请求连接 |
|||||||
|
Listen(int) |
监听端口,其中parameters表示最大监听数 |
|||||||
|
Accept() |
接受客户端链接,并返回一个新的链接,用于处理同客户端的通信问题 |
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
Send() |
发送数据 |
|||||||
|
Send(byte[]) |
简单发送数据 |
|||||||
|
Send(byte[],SocketFlag) |
使用指定的SocketFlag发送数据 |
|||||||
|
Send(byte[], int, SocketFlag) |
使用指定的SocketFlag发送指定长度数据 |
|||||||
|
Send(byte[], int, int, SocketFlag) |
使用指定的SocketFlag,将指定字节数的数据发送到已连接的socket(从指定偏移量开始) |
|||||||
|
Receive() |
接受数据 |
|||||||
|
Receive(byte[]) |
简单接受数据 |
|||||||
|
Receive (byte[],SocketFlag) |
使用指定的SocketFlag接受数据 |
|||||||
|
Receive (byte[], int, SocketFlag) |
使用指定的SocketFlag接受指定长度数据 |
|||||||
|
Receive (byte[], int, int, SocketFlag) |
使用指定的SocketFlag,从绑定的套接字接收指定字节数的数据,并存到指定偏移量位置的缓冲区 |
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
Connect(EndPoint) |
连接远程服务器 |
|||||||
|
ShutDown(SocketShutDown) |
禁用套接字,其中SocketShutDown为枚举,Send禁止发送,Receive为禁止接受,Both为两者都禁止 |
|||||||
|
Close() |
关闭套接字,释放资源 |
|||||||
|
异步通信方法: |
||||||||
|
BeginAccept(AsynscCallBack,object) |
开始一个一步操作接受一个连接尝试。参数:一个委托。一个对象。对象包含此请求的状态信息。其中回调方法中必须使用EndAccept方法。应用程序调用BegineAccept方法后,系统会使用单独的线程执行指定的回调方法并在EndAccept上一直处于阻塞状态,直至监测到挂起的链接。EndAccept会返回新的socket对象。供你来同远程主机数据交互。不能使用返回的这个socket接受队列中的任何附加连接。调用BeginAccept当希望原始线程阻塞的时候,请调用WaitHandle.WaitOne方法。当需要原始线程继续执行时请在回调方法中使用ManualResetEvent的set方法 |
|||||||
|
BeginConnect(EndPoint, AsyncCallBack, Object) |
回调方法中必须使用EndConnect()方法。Object中存储了连接的详细信息。 |
|||||||
|
BeginSend(byte[], SocketFlag, AsyncCallBack, Object) |
|
|||||||
|
BegineReceive(byte[], SocketFlag, AsyncCallBack, Object) |
|
|||||||
|
BegineDisconnect(bool, AsyncCallBack, Object) |
|
|||||||
给出同步通信与异步通信的示例:
|
同步通信: |
|
预定义结构体,同步通信没有多线程异步委托回调,所以无需预定义结构体 |
|
客户端Client: |
|
class Program { static void Main() { try{ int port = 2000; string host = "127.0.0.1"; IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse(host); IPEndPoint ipe = new IPEndPoint(ip, port);//把ip和端口转化为IPEndPoint实例 Socket c = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream,ProtocolType.Tcp);//创建一个Socket Console.WriteLine("Conneting..."); c.Connect(ipe);//连接到服务器 string sendStr = "hello!This is a socket test"; byte[] bs = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(sendStr); Console.WriteLine("Send Message"); c.Send(bs, bs.Length, 0);//发送测试信息 string recvStr = ""; byte[] recvBytes = new byte[1024]; int bytes; bytes = c.Receive(recvBytes, recvBytes.Length, 0);//从服务器端接受返回信息 recvStr += Encoding.ASCII.GetString(recvBytes, 0, bytes); Console.WriteLine("Client Get Message:{0}", recvStr);//显示服务器返回信息 c.Close(); } catch (ArgumentNullException e){ Console.WriteLine("ArgumentNullException: {0}", e); } catch (SocketException e){ Console.WriteLine("SocketException: {0}", e); } Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to Exit"); Console.ReadLine(); } } |
|
服务器端: |
|
class Program { static void Main() { try{ int port = 2000; string host = "127.0.0.1"; IPAddress ip = IPAddress.Parse(host); IPEndPoint ipe = new IPEndPoint(ip, port); Socket s = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream,ProtocolType.Tcp);//创建一个Socket类 s.Bind(ipe);//绑定2000端口 s.Listen(0);//开始监听 Console.WriteLine("Wait for connect"); Socket temp = s.Accept();//为新建连接创建新的Socket。 Console.WriteLine("Get a connect"); string recvStr = ""; byte[] recvBytes = new byte[1024]; int bytes; bytes = temp.Receive(recvBytes, recvBytes.Length, 0);//从客户端接受信息 recvStr += Encoding.ASCII.GetString(recvBytes, 0, bytes); Console.WriteLine("Server Get Message:{0}", recvStr);//把客户端传来的信息显示出来 string sendStr = "Ok!Client Send Message Sucessful!"; byte[] bs = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(sendStr); temp.Send(bs, bs.Length, 0);//返回客户端成功信息 temp.Close(); s.Close(); } catch (ArgumentNullException e){ Console.WriteLine("ArgumentNullException: {0}", e);} catch (SocketException e){ Console.WriteLine("SocketException: {0}", e);} Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to Exit"); Console.ReadLine(); } } |
|
|
|
异步通信: |
|
客户端Client: |
|
预定义结构体,用于异步委托之间的传递。用户根据自己需要定制即可 |
|
public class StateObject { // Client socket. public Socket workSocket = null; // Size of receive buffer. public const int BufferSize = 256; // Receive buffer. public byte[] buffer = new byte[BufferSize]; // Received data string. public StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); } |
|
正文: |
|
public class AsynchronousClient { // The port number for the remote device. private const int port = 11000; // ManualResetEvent instances signal completion. private static ManualResetEvent connectDone = new ManualResetEvent(false); private static ManualResetEvent sendDone = new ManualResetEvent(false); private static ManualResetEvent receiveDone = new ManualResetEvent(false); // The response from the remote device. private static String response = String.Empty;
private static void StartClient(){ // Connect to a remote device. try{ // Establish the remote endpoint for the socket. // The name of the remote device is "host.contoso.com". IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.Resolve("host.contoso.com"); IPAddress ipAddress = ipHostInfo.AddressList[0]; IPEndPoint remoteEP = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, port);
// Create a TCP/IP socket. Socket client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
// Connect to the remote endpoint. client.BeginConnect(remoteEP, new AsyncCallback(ConnectCallback), client); connectDone.WaitOne();
// Send test data to the remote device. Send(client, "This is a test<EOF>"); sendDone.WaitOne();
// Receive the response from the remote device. Receive(client); receiveDone.WaitOne();
// Write the response to the console. Console.WriteLine("Response received : {0}", response);
// Release the socket. client.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); client.Close(); } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());} }
private static void ConnectCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { try{ // Retrieve the socket from the state object. Socket client = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
// Complete the connection. client.EndConnect(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Socket connected to {0}", client.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
// Signal that the connection has been made. connectDone.Set(); } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());} }
private static void Receive(Socket client) { try{ // Create the state object. StateObject state = new StateObject(); state.workSocket = client;
// Begin receiving the data from the remote device. client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());} }
private static void ReceiveCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { try{ // Retrieve the state object and the client socket // from the asynchronous state object. StateObject state = (StateObject)ar.AsyncState; Socket client = state.workSocket;
// Read data from the remote device. int bytesRead = client.EndReceive(ar);
if (bytesRead > 0){ // There might be more data, so store the data received so far. state.sb.Append(Encoding.ASCII.GetString(state.buffer, 0, bytesRead));
// Get the rest of the data. client.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReceiveCallback), state); } else{ // All the data has arrived; put it in response. if (state.sb.Length > 1) { response = state.sb.ToString(); } // Signal that all bytes have been received. receiveDone.Set(); } } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());} }
private static void Send(Socket client, String data) { // Convert the string data to byte data using ASCII encoding. byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(data);
// Begin sending the data to the remote device. client.BeginSend(byteData, 0, byteData.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(SendCallback), client); }
private static void SendCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { try{ // Retrieve the socket from the state object. Socket client = (Socket)ar.AsyncState;
// Complete sending the data to the remote device. int bytesSent = client.EndSend(ar); Console.WriteLine("Sent {0} bytes to server.", bytesSent);
// Signal that all bytes have been sent. sendDone.Set(); } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());} }
public static int Main(String[] args) { StartClient(); return 0; } } |
|
服务器端Server: |
|
预定义结构体,用于异步委托之间的传递。同客户端的一致。不再赘述 |
|
正文: |
|
// State object for reading client data asynchronously public class AsynchronousSocketListener { // Thread signal. public static ManualResetEvent allDone = new ManualResetEvent(false); public AsynchronousSocketListener(){} public static void StartListening() { // Data buffer for incoming data. byte[] bytes = new Byte[1024]; // Establish the local endpoint for the socket. // The DNS name of the computer // running the listener is "host.contoso.com".
//IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.Resolve(Dns.GetHostName()); IPHostEntry ipHostInfo = Dns.Resolve("127.0.0.1"); IPAddress ipAddress = ipHostInfo.AddressList[0]; IPEndPoint localEndPoint = new IPEndPoint(ipAddress, 11000); // Create a TCP/IP socket. Socket listener = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork,SocketType.Stream,ProtocolType.Tcp); // Bind the socket to the local endpoint and listen for incoming connections. try{ listener.Bind(localEndPoint); listener.Listen(100); while (true){ // Set the event to nonsignaled state. allDone.Reset(); // Start an asynchronous socket to listen for connections. Console.WriteLine("Waiting for a connection..."); listener.BeginAccept(new AsyncCallback(AcceptCallback),listener); // Wait until a connection is made before continuing. allDone.WaitOne(); } } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString());} Console.WriteLine("\nPress ENTER to continue..."); Console.Read(); } public static void AcceptCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { // Signal the main thread to continue. allDone.Set(); // Get the socket that handles the client request. Socket listener = (Socket)ar.AsyncState; Socket handler = listener.EndAccept(ar); // Create the state object. StateObject state = new StateObject(); state.workSocket = handler; handler.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0,newAsyncCallback(ReadCallback), state); } public static void ReadCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { String content = String.Empty; // Retrieve the state object and the handler socket // from the asynchronous state object. StateObject state = (StateObject)ar.AsyncState; Socket handler = state.workSocket; // Read data from the client socket. int bytesRead = handler.EndReceive(ar); if (bytesRead > 0) { // There might be more data, so store the data received so far. state.sb.Append(Encoding.ASCII.GetString(state.buffer, 0, bytesRead)); // Check for end-of-file tag. If it is not there, read // more data. content = state.sb.ToString(); if (content.IndexOf("<EOF>") > -1){ // All the data has been read from the // client. Display it on the console. Console.WriteLine("Read {0} bytes from socket. \n Data : {1}", content.Length, content); // Echo the data back to the client. Send(handler, "Server return :" + content); } else{ // Not all data received. Get more. handler.BeginReceive(state.buffer, 0, StateObject.BufferSize, 0, new AsyncCallback(ReadCallback), state); } } } private static void Send(Socket handler, String data){ // Convert the string data to byte data using ASCII encoding. byte[] byteData = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(data); // Begin sending the data to the remote device. handler.BeginSend(byteData, 0, byteData.Length, 0, new AsyncCallback(SendCallback), handler); } private static void SendCallback(IAsyncResult ar) { try{ // Retrieve the socket from the state object. Socket handler = (Socket)ar.AsyncState; // Complete sending the data to the remote device. int bytesSent = handler.EndSend(ar); Console.WriteLine("Sent {0} bytes to client.", bytesSent); handler.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both); handler.Close(); } catch (Exception e){ Console.WriteLine(e.ToString()); } } public static int Main(String[] args) { StartListening(); return 0; } } |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号