ggplot2(11) 总结回顾&案例练习
从2020年2月20到2月27日,3月13日到2020年3月16日,学习了ggplot2:数据分析与图形艺术(哈德利·威克姆 著 统计之都 译),历时12天。另外,3月6日到3月9日参加了美赛,也用到了刚学的ggplot2。
- qplot:基本掌握,可以快速绘图,不局限于数据框;
- 语法:有所了解,不大涉及具体应用;
- 图层:了解;
- 工具箱:重点,各种绘图形式;
- 标度,定位:修饰,细化;
- 输出:ggsave;布局:一页多图;
- 数据操作:ddply、transform、colwise、melt。
用平板看的书,在电脑编辑代码和博客。

如果有需要书籍资源的小伙伴可以评论留下邮箱……
其他各章链接:
- ggplot2(1) 简介
- ggplot2(2) 从qplot开始入门
- ggplot2(3) 语法突破
- ggplot2(4) 用图层构建图像
- ggplot2(5) 工具箱
- ggplot2(6) 标度、坐标轴和图例
- ggplot2(7) 定位
- ggplot2(8) 精雕细琢
- ggplot2(9) 数据操作
- ggplot2(10) 减少重复性工作
下面通过几个示例进行练习,同时以便以后套用。
1. 当当网数据
目标网址:http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-recent7-0-0-1-1
共25页,结尾数字从1~25
1.1 爬取数据
所用程序包:
- dplyr:进行管道操作;
- stringr:使用str_c函数对网页地址字符串进行处理,以便同时提取多个网页的信息;
- xml2:使用其中的read_html函数读取网页;
- rvest:使用其中的html_nodes从网页文件中选择节点,html_text获取网页信息。
观察其网页结构,以第一本书为例:
<div class="list_num red">1.</div> <div class="pic"><a href="http://product.dangdang.com/28473192.html" target="_blank"><img src="http://img3m2.ddimg.cn/0/27/28473192-1_l_3.jpg" alt="你当像鸟飞往你的山(比尔·盖茨年度特别推荐,登顶《纽约时报》畅销榜80 周!多一个人读到这个真实故事,就多一个人勇敢做自己!)" title="你当像鸟飞往你的山(比尔·盖茨年度特别推荐,登顶《纽约时报》畅销榜80 周!多一个人读到这个真实故事,就多一个人勇敢做自己!)"/></a></div> <div class="name"><a href="http://product.dangdang.com/28473192.html" target="_blank" title="你当像鸟飞往你的山(比尔·盖茨年度特别推荐,登顶《纽约时报》畅销榜80 周!多一个人读到这个真实故事,就多一个人勇敢做自己!)">你当像鸟飞往你的山(比尔·盖茨年度特别推荐,登顶《纽约时报》<span class='dot'>...</span></a></div> <div class="star"><span class="level"><span style="width: 93.8%;"></span></span><a href="http://product.dangdang.com/28473192.html?point=comment_point" target="_blank">121975条评论</a><span class="tuijian">99.9%推荐</span></div> <div class="publisher_info"><a href="http://search.dangdang.com/?key=塔拉" title="塔拉 · 韦斯特弗 著 , 新经典 出品" target="_blank">塔拉</a> · <a href="http://search.dangdang.com/?key=韦斯特弗" title="塔拉 · 韦斯特弗 著 , 新经典 出品" target="_blank">韦斯特弗</a> 著 , <a href="http://search.dangdang.com/?key=新经典" title="塔拉 · 韦斯特弗 著 , 新经典 出品" target="_blank">新经典</a> 出品</div> <div class="publisher_info"><span>2019-11-01</span> <a href="http://search.dangdang.com/?key=南海出版公司" target="_blank">南海出版公司</a></div> <div class="price"> <p> <span class="price_n">¥59.00</span> <span class="price_r">¥59.00</span> (<span class="price_s">10.0折</span>) </p> <p class="price_e">电子书:<span class="price_n">¥35.40</span></p> <div class="buy_button"> <a ddname="加入购物车" name="" href="javascript:AddToShoppingCart('28473192');" class="listbtn_buy">加入购物车</a> <a name="" href="http://product.dangdang.com/1901169911.html" class="listbtn_buydz" target="_blank">购买电子书</a> <a ddname="加入收藏" id="addto_favorlist_28473192" name="" href="javascript:showMsgBox('addto_favorlist_28473192',encodeURIComponent('28473192&platform=3'), 'http://myhome.dangdang.com/addFavoritepop');" class="listbtn_collect">收藏</a> </div> </div>
因此可设计代码如下:
library(xml2)
library(dplyr)
library(stringr)
library(rvest)
books<-data.frame()
#使用for循环进行批量数据爬取
for(i in 1:25){
web<-read_html(str_c("http://bang.dangdang.com/books/bestsellers/01.00.00.00.00.00-recent7-0-0-1-",i),encoding="gbk")
#排名
rank<-web%>%html_nodes(".list_num")%>%html_text()
#书名
name<-web%>%html_nodes(".name a")%>%html_text()
#作者
author<-web%>%html_nodes(".star+ .publisher_info")%>%html_text()
#价格
price<-web%>%html_nodes("p:nth-child(1) .price_n")%>%html_text()
#原价
original_price<-web%>%html_nodes("p:nth-child(1) .price_r")%>%html_text()
#折扣
discount<-web%>%html_nodes("p:nth-child(1) .price_s")%>%html_text()
#评论数
review<-web%>%html_nodes(".star")%>%html_text()
#创建数据框并存储以上信息
book<-data_frame(rank,name,author,price,original_price,
discount,review)
books<-rbind(books,book)
}
#将数据写入csv文档
#write.csv(books,file="books.csv")
以上代码将数据写入数据框中,如果有必要可以用write.csv函数写出。
1.2 数据清理
#查看数据格式 str(books)
Classes ‘tbl_df’, ‘tbl’ and 'data.frame': 500 obs. of 7 variables:
$ rank : chr "1." "2." "3." "4." ...
$ name : chr "你当像鸟飞往你的山(比尔·盖茨年度特别推荐,登顶《纽约时报》..." "小熊和最好的爸爸(全7册)" "神奇校车·桥梁书版(全20册)" "人间失格(日本小说家太宰治的自传体小说,李现推荐)" ...
$ author : chr "塔拉 · 韦斯特弗 著 , 新经典 出品" "(荷)阿兰德·丹姆 著,(荷)亚历克斯·沃尔夫 绘,漆仰平,爱桐 译" "乔安娜柯尔 著 布鲁斯迪根 图 施芳 译" "(日)太宰治 著,杨伟 译" ...
$ price : chr "¥59.00" "¥34.70" "¥148.50" "¥18.80" ...
$ original: chr "¥59.00" "¥35.00" "¥150.00" "¥25.00" ...
$ discount: chr "10.0折" "9.9折" "9.9折" "7.5折" ...
$ review : chr "121994条评论99.9%推荐" "1035562条评论99.7%推荐" "872932条评论99.9%推荐" "1667777条评论100%推荐" ...
提取有用信息并进行格式转换:
SUB<-function(t,REG)
{
m<-gregexpr(REG, t)
start<-m[[1]]
stop<-start+attr(m[[1]],"match.length")-1
l<-length(start)
r<-rep("1",l)
for(i in 1:l)
{
r[i]<-substr(t,start[i],stop[i])
}
return(r)
}
#修改数据类型
books$rank<-lapply(books$rank,SUB,REG="[0-9]+")%>%as.integer()
books$price<-lapply(books$price,SUB,REG="[0-9.]+$")%>%as.numeric()
books$original<-lapply(books$original,SUB,REG="[0-9.]+$")%>%as.numeric()
books$discount<-lapply(books$discount,SUB,REG="^[0-9.]+")%>%as.numeric()
books$review<-lapply(books$review,SUB,REG="^[0-9]+")%>%as.integer()
books<-books[c(-2,-3)]
books<-books[!apply(is.na(books),1,sum),]
1.3 绘图
cor(books) cor.test(books$review,books$rank)
rank price original discount review
rank 1.00000000 -0.06882118 -0.05829241 -0.05690682 -0.35888334
price -0.06882118 1.00000000 0.98859115 0.16187930 0.05107963
original -0.05829241 0.98859115 1.00000000 0.05381846 0.05132552
discount -0.05690682 0.16187930 0.05381846 1.00000000 -0.07028547
review -0.35888334 0.05107963 0.05132552 -0.07028547 1.00000000
Pearson's product-moment correlation
data: books$review and books$rank
t = -8.5718, df = 497, p-value < 2.2e-16
alternative hypothesis: true correlation is not equal to 0
95 percent confidence interval:
-0.4330207 -0.2799231
sample estimates:
cor
-0.3588833
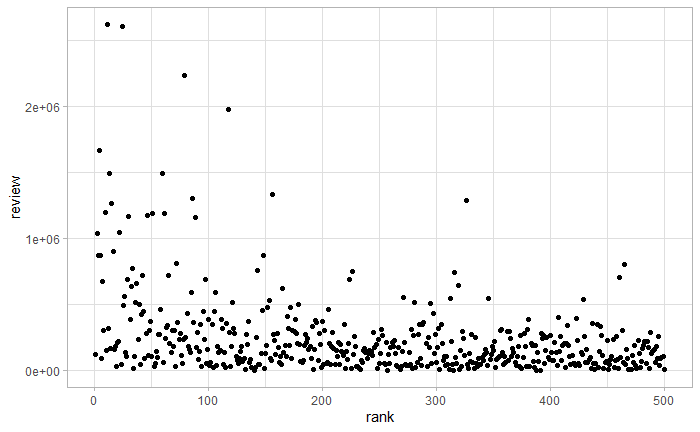
通过相关系数和相关性检验,可以看到书籍排名和评论数目有相关关系,排名越靠前,评论数目越多。画出二者散点图,如下图所示。
qplot(rank,review,data=books)
画出书籍价格分布直方图,如下图所示。
library(ggplot2) theme_set(theme_light()) qplot(price,data=books,geom="histogram",xlim=c(0,200))+labs(title="Histogram of the price distribution of popular books")+theme(plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5))

p1<-ggplot(data=books,
aes(review,price,colour=rank,alpha=I(1/3)))+
guides(colour=FALSE)+
geom_point()+
scale_x_continuous(breaks=c(0,1e6,2e6),labels=expression(0,1%*%10^6,2%*%10^6))+
annotate('segment',x=5e5,xend=1.05e6,y=110,yend=300,colour="red",arrow=arrow())
p2<-p1+aes(size=I(0.5),alpha=I(1))+labs(x=NULL,y=NULL)+
scale_x_continuous(expand=c(0,0),limits=c(0,5e5),
breaks=c(0,2e5,4e5),labels=expression(0,2%*%10^5,4%*%10^5))+
scale_y_continuous(expand=c(0,0),limits=c(0,150))
library(grid)
pdf("test.pdf",width=4,height=3)
p1
print(p2,vp=viewport(x=0.74,y=0.74,width=0.5,height=0.5))
dev.off()
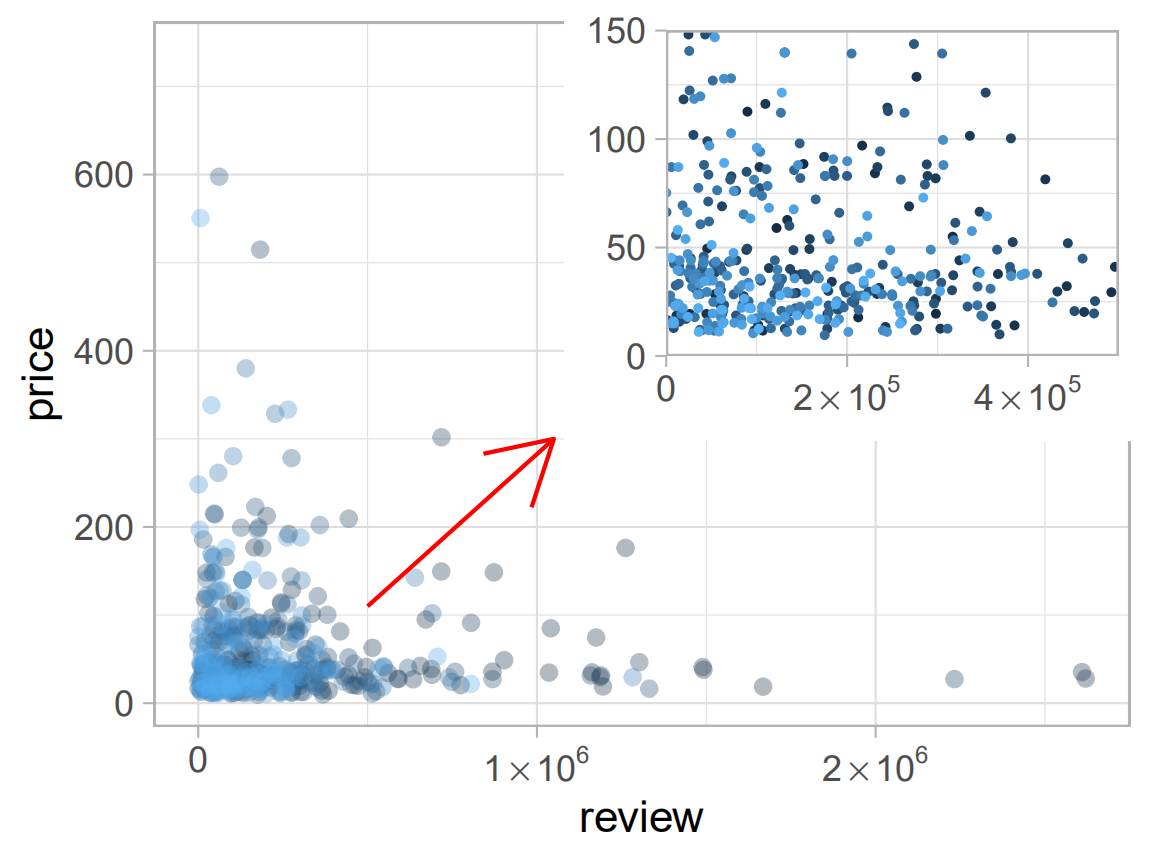
通过上例,练习了散点图绘制,颜色标度及一页多图(子图)操作。
关于R语言爬虫,学习自:
关于箭头绘制,学习自:
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/ask/119325/answer/214891
https://www.cnblogs.com/xihehe/p/8309480.html
2. 电力数据
国家统计局→统计数据→年度数据→能源→电力平衡表→时间:2000-2017
http://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01
2.1 清理数据
从国家统计局下载csv格式的文件,读入并选取电力生产量相关数据。
library(dplyr)
library(reshape2)
electricity<-read.csv("电力平衡表.csv",header=FALSE)
production<-electricity[5,-1]%>%t()%>%as.numeric()
hydraulic<-electricity[6,-1]%>%t()%>%as.numeric()
thermal<-electricity[7,-1]%>%t()%>%as.numeric()
nuclear<-electricity[8,-1]%>%t()%>%as.numeric()
wind<-electricity[9,-1]%>%t()%>%as.numeric()
st<-as.Date("2000","%Y")
en<-as.Date("2017","%Y")
time<-seq(en,st,by="-1 year")
ee<-data.frame(time,production,hydraulic,thermal,nuclear,wind)
ee<-melt(ee,id="time")
2.2 绘图
程序包:
- showtext、Cairo:解决汉字的字体问题;
- grid:用于矩形网络输出。
library(showtext)
library(Cairo)
library(ggplot2)
library(grid)
font_add("song","song.ttf")
CairoPDF("ee1.pdf",width=8,height=6)
grid.newpage()
pushViewport(viewport(layout = grid.layout(3, 3)))
vplayout <- function(x, y) viewport(layout.pos.row = x, layout.pos.col = y)
showtext_begin()
theme_set(theme_light())
my_theme<-theme(axis.title.x=element_text(size=10,family="song",hjust=1),
axis.title.y=element_text(size=10,family="song",hjust=1),
axis.text.y=element_text(angle=90),
plot.title=element_text(hjust=0.5,family="song"))
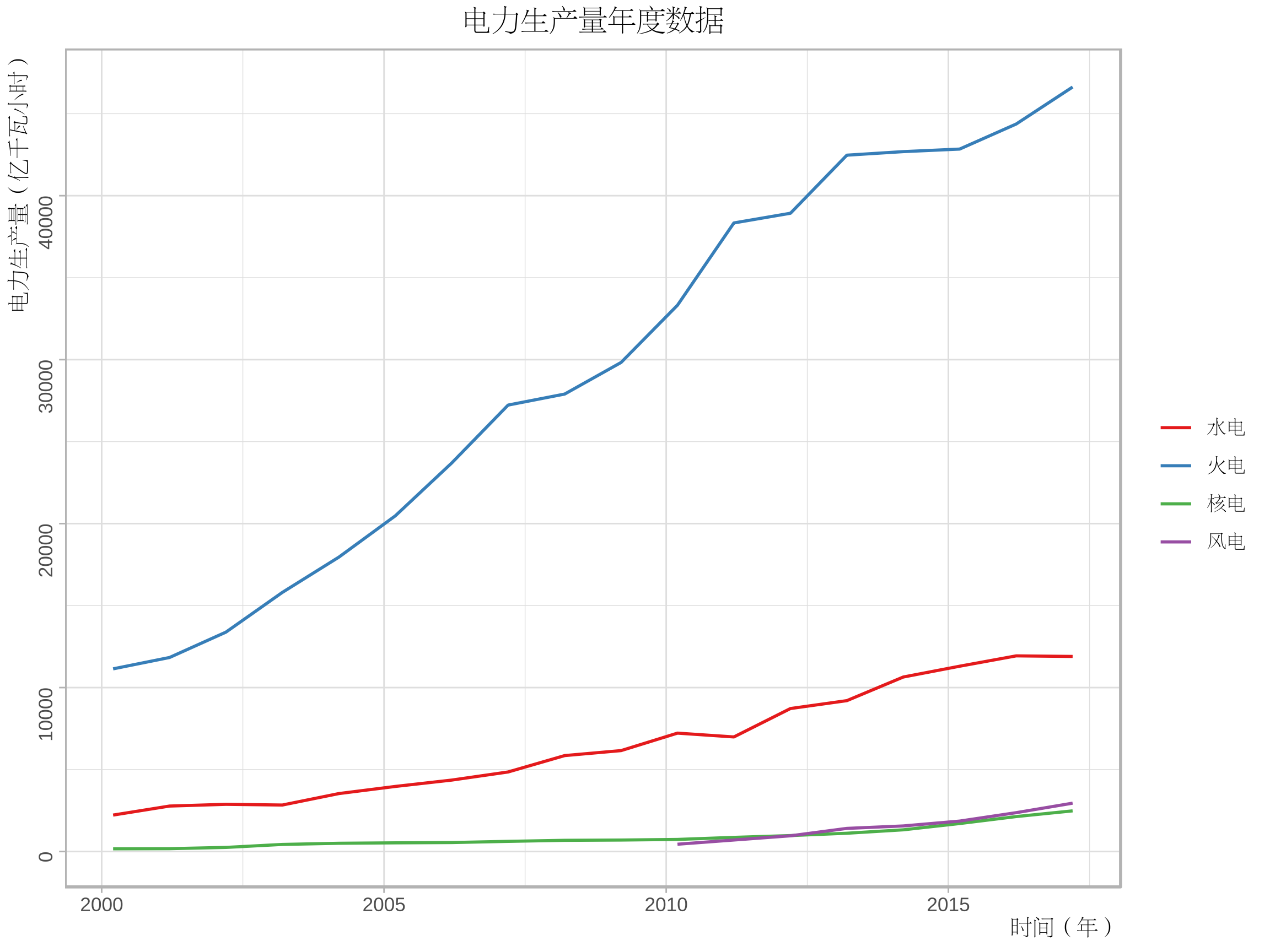
p1<-ggplot(data=ee[ee$variable=="production",],aes(time,value))+geom_line()+
labs(x="时间(年)",y="电力生产总量(亿千瓦小时)")+
ggtitle("")+my_theme
p2<-ggplot(data=ee[ee$variable!="production",],aes(time,value))+geom_line()+
labs(x="时间(年)",y="电力生产量(亿千瓦小时)")+
facet_wrap(~variable,nrow=2,ncol=2,scales="free_y",
labeller=as_labeller(c("hydraulic"="水电","thermal"="火电","nuclear"="核电","wind"="风电")))+
ggtitle("电力生产量年度数据")+my_theme+theme(plot.title=element_text(hjust=0))
print(p1,vp=vplayout(1:3,1))
print(p2,vp=vplayout(1:3,2:3))
showtext_end()
dev.off()
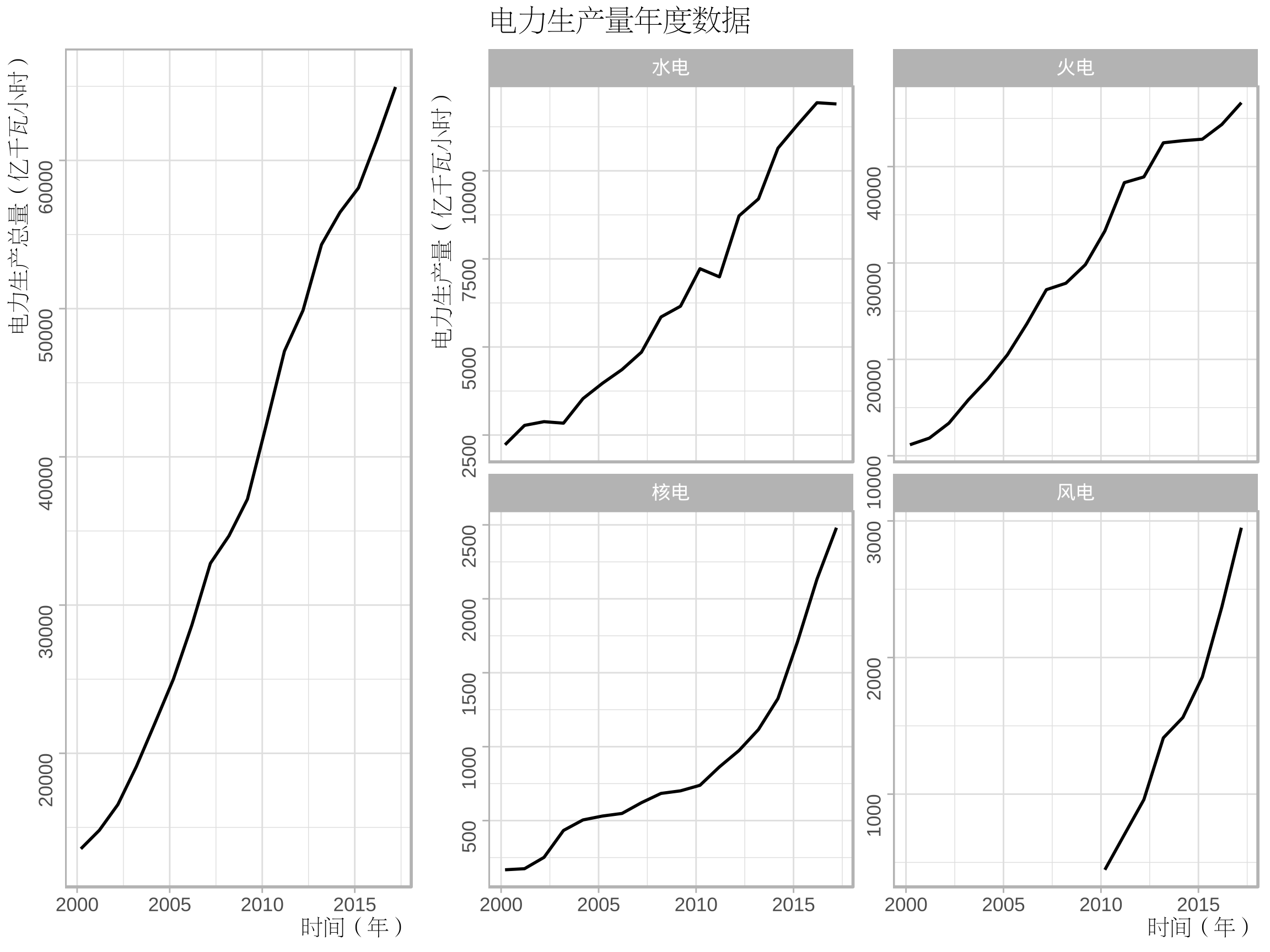
关于ggplot2分面标签的修改,学习自:https://ggplot2.tidyverse.org/reference/as_labeller.html
CairoPDF("ee2.pdf",width=8,height=6)
showtext_begin()
theme_set(theme_light())
p3<-ggplot(data=ee[ee$variable!="production",],aes(time,value,colour=variable))+geom_line()
p3+labs(x="时间(年)",y="电力生产量(亿千瓦小时)")+
scale_colour_brewer(palette = "Set1","",breaks=c("hydraulic","thermal","nuclear","wind"),
labels=c("水电","火电","核电","风电"))+
ggtitle("电力生产量年度数据")+my_theme+theme(legend.text=element_text(family="song"))
showtext_end()
dev.off()
关于中文字体的设置,学习自:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/97c915e66ff4
3. 2019美赛C题数据
3.1 数据清洗
题目背景是美国正在经历关于使用合成和非合成阿片类药物的国家危机,第一份文件(MCM_NFLIS_Data.xlsx)中包含了美国5个州各县2010到2017年麻醉镇痛药(合成阿片类药物)和海洛因的药物案件计数。
下面我们对这个文件中的数据进行可视化探索,绘制出这五个州在8年中海洛因案件计数的变化情况。
首先导入数据并进行数据清洗。
library(xlsx)
library(dplyr)
library(tidyverse)
#读取数据
drug<-read.xlsx("MCM_NFLIS_Data.xlsx","Data")
#筛选数据
drug<-drug[drug$SubstanceName=="Heroin",]
#分类汇总
Heroin<-tapply(drug$DrugReports,paste(drug$YYYY,drug$State),sum)
Heroin<-data.frame(id=names(Heroin),num=Heroin)%>%
separate(col=id,into=c("date","state"),sep=" ")
row.names(Heroin)<-1:dim(Heroin)[1]
这里我们只保留的海洛因的相关数据,并且按照州名和年份进行了分类汇总。
- 由于原文件是xlsx文件,需要使用xlsx包;
- 采用tidyverse包中的separate函数,可以轻松拆分列,类似于excel数据菜单中的分列操作。
3.2 折线图
采用gganimate中的函数绘制动图GIF,代码如下。
library(ggplot2)
library(gganimate)
theme_set(theme_light())
#绘制图像
p1<-ggplot(data=Heroin,aes(as.Date(date,"%Y"),num,colour=state))
p1+geom_point()+geom_line()+labs(x="time(year)",y="Drug Reports Number")+
ggtitle("State total count of Heroin")+
theme(axis.title.x=element_text(hjust=1),
axis.title.y=element_text(hjust=1),
axis.text.y=element_text(angle=90),
plot.title=element_text(hjust=0.5))+
transition_manual(date,cumulative=TRUE)
- 设置主题为light,图形更清晰;
- 采用cumulative = TRUE,累加展示图形。

可以看到总体上OH州情况最为严重,但后两年情况有所缓解,WV州情况相对比较乐观。
3.3 地图
library(maps)
library(plyr)
Heroin<-left_join(Heroin,data.frame(state=state.abb,region=state.name),by="state")
Heroin$region<-tolower(Heroin$region)
states<-map_data("state",unique(Heroin$region))
mapdata<-merge(states,Heroin,by="region")
mid_range<-function(x) mean(range(x,na.rm=TRUE))
centres<-ddply(mapdata,.(state),colwise(mid_range,.(lat,long)))
#对中心位置进行微调
centres[centres$state %in% c("KY","VA"),c("lat")]<-
centres[centres$state %in% c("KY","VA"),c("lat")]-0.5
library(RColorBrewer)
myPalette<-colorRampPalette(brewer.pal(9,"YlOrRd"))
ggplot(data=mapdata,aes(long,lat,group=group,fill=num))+geom_polygon()+
labs(x="longitude",y="latitude",
title="The quantitative distribution of heroin reports by state",
subtitle="Year:{current_frame}")+
scale_fill_gradientn(colours=myPalette(9))+
guides(fill=guide_legend(title=" State total\ncount of Heroin"))+
theme(plot.title=element_text(hjust=0.5),
plot.subtitle=element_text(hjust=0.5))+
geom_text(aes(label=state,group = NULL,fill=NULL), data = centres, size = 8, angle = 45)+
transition_manual(as.integer(date))
- state.abb,state.name用于获取美国州名和简称;
- tolower把字母转换为小写,便于匹配;
- 采用map_data函数获取地图信息;
- 计算所有点的横纵坐标(经纬度)的均值作为州的中心,因为有的州形状比较特殊,可以对中心位置centres进行微调;
- 将RColorBrewer包中的配色应用到连续颜色标度,需要使用colorRampPalette、brewer.pal函数。

从上图中可以看出各州形势变换情况,与折线图反映的信息一致。
关于地图的绘制以及标签的添加,回顾了:https://www.cnblogs.com/dingdangsunny/p/12354072.html#_label6
关于动图的绘制,学习自以下两篇文章:
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42933967/article/details/96200053
https://github.com/thomasp85/gganimate
4. 2020美赛C题数据
在其创建的在线市场中,亚马逊为客户提供了对购买进行评分和评价的机会。个人评级(称为“星级”)使购买者可以使用1(低评级,低满意度)到5(高评级,高满意度)的等级来表示他们对产品的满意度。
文件中给出了3种产品(微波炉,婴儿奶嘴和吹风机)的历史星级评价信息,下面对这些信息进行简单的可视化。
4.1 数据清洗
首先读入数据:
library(readr)#用来读入tsv数据
#读取原始数据
hair_dryer <- read_tsv("hair_dryer.tsv")
hair_dryer <- hair_dryer[dim(hair_dryer)[1]:1,]
microwave <- read_tsv("microwave.tsv")
microwave <- microwave[dim(microwave)[1]:1,]
pacifier <- read_tsv("pacifier.tsv")
pacifier <- pacifier[dim(pacifier)[1]:1,]
由于题目中给的是tsv格式的数据,这里采用readr包读取。
数据预处理:
#数据预处理 hair_dryer$class<-"hair_dryer" microwave$class<-"microwave" pacifier$class<-"pacifier" #合并数据为data,便于整体分析 data<-rbind(hair_dryer,microwave,pacifier) data<-as.data.frame(data) data$class<-as.factor(data$class) #将变量转化为合适的类型 data$review_date <- as.Date(data$review_date, format = "%m/%d/%Y")
4.2 产品评论数目折线图
library(ggplot2)
library(plyr)
#3种不同产品的每年的评论总数变化图
review_count<-ddply(data,.(review_date,class),nrow)
names(review_count)<-c("review_date","class","count")
data<-left_join(data,review_count,by=c("review_date","class"))
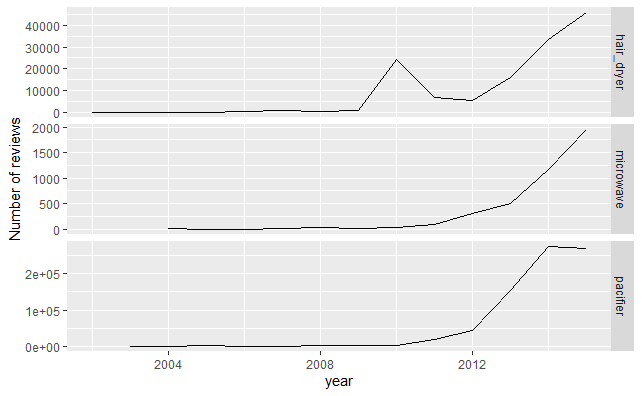
p1<-ggplot(data,aes(as.integer(format.Date(review_date,"%Y")),count))
p1+stat_summary(fun.y="sum",geom="line")+facet_grid(class~.,scales="free_y")+
labs(x="year",y="Number of reviews")
4.3 星级变化图
#3种不同产品2010~2015年每月的平均star_rating变化图
p2<-ggplot(data[data$review_date>as.Date("2010","%Y"),],aes(as.integer(format(review_date,"%m")),star_rating,colour=class))
p2+stat_summary(fun.y="mean",geom="line")+facet_wrap(~as.integer(format.Date(review_date,"%Y")),nrow=2,ncol=3)+
labs(x="month",y="average of star rating")+
ggtitle("Average star rating of each month for 3 kinds of products")
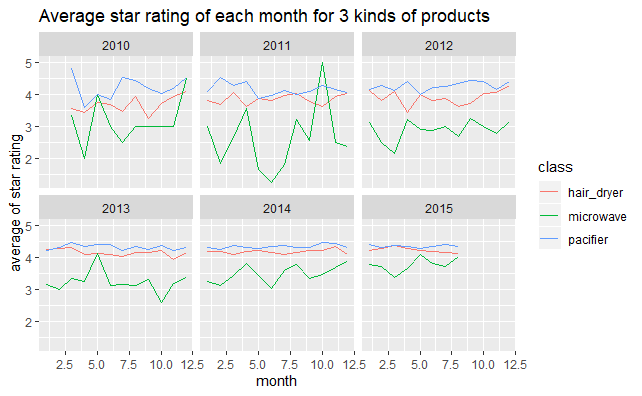
这里复习了ggplot2统计摘要stat_summary的使用方法,可以直接在原始数据基础上得到具有概括性的图形。
5.疫情数据
数据来源于:https://news.qq.com/zt2020/page/feiyan.htm(腾讯新闻网)
数据采集于2020年3月15日。
关于数据采集,参考:https://blog.csdn.net/xufive/article/details/104093197
不得不说R在爬虫方面确实比不上python方便,所以……赶快溜去学python了
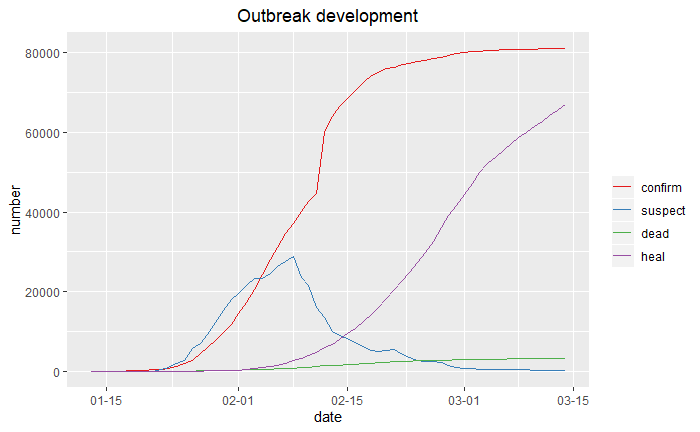
5.1 折线趋势图
首先读入准备的数据。
news<-read.csv("疫情防控.csv",stringsAsFactors=FALSE)
dis<-read.csv("distribution.csv")
ten<-read.csv("tendency.csv")
利用ggplot2绘图:
library(reshape2)
library(ggplot2)
library(scales)
ten<-melt(ten,id="date")
ten$date<-as.Date(ten$date)
p1<-ggplot(data=ten,aes(date,value,colour=variable))+geom_line()
p1+labs(x="date",y="number")+
scale_x_date(labels=date_format("%m-%d"))+
scale_colour_brewer(palette="Set1","")+
ggtitle("Outbreak development")+
theme(plot.title=element_text(hjust=0.5))
5.2 地区分布图(中国地图)
library(maptools)
library(dplyr)
map_data<-readShapePoly('bou2_4p.shp')
x <- map_data@data%>%
data.frame(id=as.character(seq(0:924)-1))
china_map <- fortify(map_data)%>%
left_join(x,by="id")
SUB<-function(t,REG)
{
m<-gregexpr(REG, t)
start<-m[[1]]
stop<-start+attr(m[[1]],"match.length")-1
l<-length(start)
r<-rep("1",l)
for(i in 1:l)
{
r[i]<-substr(t,start[i],stop[i])
}
return(r)
}
china_map$province<-lapply(china_map$NAME,SUB,REG="^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{2}")%>%unlist()
dis$province<-lapply(dis$province,SUB,REG="^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{2}")%>%unlist()
china_map<-left_join(china_map,dis,by="province")
library(RColorBrewer)
myPalette <- colorRampPalette(brewer.pal(9, "YlOrRd"))
p2<-ggplot(china_map,aes(x=long,y=lat,group=group,fill=log(confirm))) +
geom_polygon(colour="grey")
p2+coord_map("polyconic")+
labs(x="longitude",y="latitude",
title="Cumulative number of confirmed cases",
subtitle="(as of 15 March)")+
scale_fill_gradientn(colours = myPalette(9))+
guides(fill=guide_legend(title=" Number of \nconfirmed cases\n (logarithm)"))+
theme(plot.title=element_text(hjust=0.5),
plot.subtitle=element_text(hjust=0.5))
- 这里首先需要用maptools包中的readShapePoly函数读入我们的中国地图数据并进行适当的格式转换。
- 由于两个数据框对于省份一个是简称一个是全称,所以均提取前两个汉字进行匹配。
- 疫情数据中包含澳门,在地图数据中没有包含,因此这里没有画出澳门的数据情况。
- 由于湖北数值很大,所以取了对数;如果先用cut函数对confirm数值进行适当的切分,转换为离散型,效果应该也是不错的。
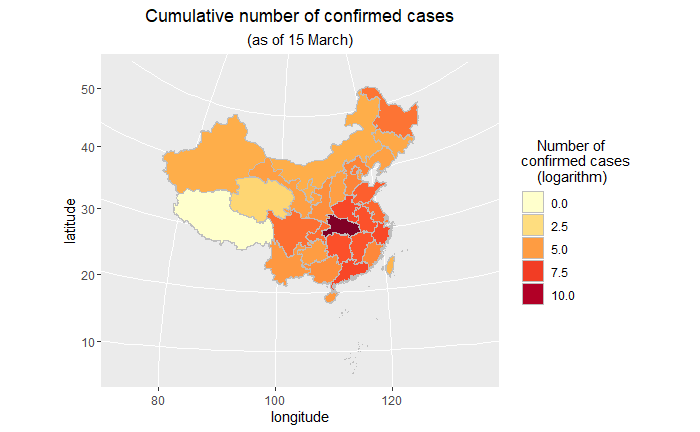
关于用ggplot2画中国地图,学习自:
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6bc5205e0102vma9.html
5.3 词云图
绘制了中国社会组织公共服务平台关于疫情防控的报道的词云图。
http://www.chinanpo.gov.cn/1944/125174/nextindex.html
library(jiebaR)
library(wordcloud2)
library(tidytext)
#读入停用词
stopwords<-readLines("stopwords.txt")
#分离出词汇表:使用jieba对文本进行处理
eng=worker()
word<-segment(news$body,eng)
word<-word[!(word %in% stopwords)]
counts<-table(word)%>%
data.frame()
counts%>%
top_n(200)%>%
wordcloud2(fontFamily="微软雅黑",color="random-dark",
backgroundColor="white")
这里采用jieba分词,并读入了停用词表进行剔除,得到结果如下。

这段时间,新型冠状病毒”疫情,一直牵动着全国人民的心,战胜病毒,人人有责。从3月11到15日,湖北新增病例连续5天个位数;3月15日,湖北全省新增新冠肺炎确诊病例4例,其中武汉市4例,其他16个市州均为0例。不松懈,继续加油!我们坚信,在党中央、国务院的坚强领导下,在全国人民的共同努力下,我们一定会取得疫情防控阻击战的最终胜利!
最后,向钟院士致敬,向一线工作者致敬。感谢他们能够在国难当前坚决做到牢记使命、不图虚名、坚守底线、一心为民。
对上面提到链接的博主表示真诚的感谢,欢迎小伙伴们批评指正!
本文所用的数据、代码(包括地图文件、字体文件、停用词表等)都已打包上传到百度网盘,永久有效:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1RU4fJHW9V5U-zRqqXk9nhA
提取码:asnc
复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦



