MySQL事务以及存储引擎
MySQL事务以及存储引擎
一、事务
1. 事务的概念
● 事务是一种机制、一个操作序列,包含了一组数据库操作命令,并且把所有的命令作为一个整体一起向系统提交或撤销操作请求,即这一组数据库命令要么都执行,要么都不执行。
● 事务是一个不可分割的工作逻辑单元,在数据库系统上执行并发操作时,事务是最小的控制单元。
● 事务适用于多用户同时操作的数据库系统的场景,如银行、保险公司及证券交易系统等等。
● 事务通过事务的整体性以保证数据的一致性。
● 事务能够提高在向表中更新和插入信息期间的可靠性。
总结来说,事务是一个操作序列,这些操作要么都执行,要么都不执行,它是一个不可分割的工作单位。
2. 事务的ACID特点
ACID是指在可靠数据库管理系统(DBMS)中,事务(transaction)应该具有的四个特性:原子性(Atomicity)、一致性(Consistency)、隔离性(Isolation)、持久性(Durability),这是可靠数据库所应具备的几个特性。
在事务管理中,原子性是基础,隔离性是手段,一致性是目的,持久性是结果、
(1)原子性
原子性:指事务是一个不可再分割的工作单位,事务中的操作要么都发生,要么都不发生。
事务是一个完整的操作,事务的各元素是不可分的。
事务中的所有元素必须作为一个整体提交或回滚。
如果事务中的任何元素失败,则整个事务将失败。
案例:
A给B转账100元钱的时候,只执行了扣款语句,就提交了,此时如果突然断电,A账号已经发生了扣款,B账号却没收到加款,在生活中就会引起纠纷。这种情况就需要事务的原子性来保证事务要么都执行,要么就都不执行。
(2)一致性
一致性:指在事务开始之前和事务结束以后,数据库的完整性约束没有被破坏。
当事务完成时,数据必须处于一致状态。
当事务开始前,数据库中存储的数据处于一致状态。
当正在进行的事务中,数据可能处于不一致的状态。
当事务成功完成时,数据必须再次回到已知的一致状态。
案例:
对银行转账事务,不管事务成功还是失败,应该保证事务结束后表中A和B的存款总额跟事务执行前一致。
(3)隔离性
隔离性:指在并发环境中,当不同的事务同时操纵相同的数据时,每个事务都有各自的完整数据空间。
对数据进行修改的所有并发事务是彼此隔离的,表明事务必须是独立的,它不应以任何方式依赖于或影响其他事务。
修改数据的事务可在另一个使用相同数据的事务开始之前访问这些数据,或者在另一个使用相同数据的事务结束之后访问这些数据。
①事务之间的相互影响
事务之间的相互影响分为以下几种
- 脏读:一个事务读取了另一个事务未提交的数据,而这个数据是有可能回滚的。
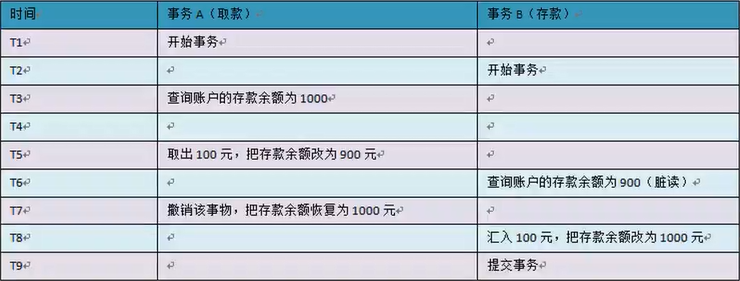
- 不可重复读:一个事务内两个相同的查询却返回了不同数据,这是由于查询时系统中其他事务修改的提交而引起的。
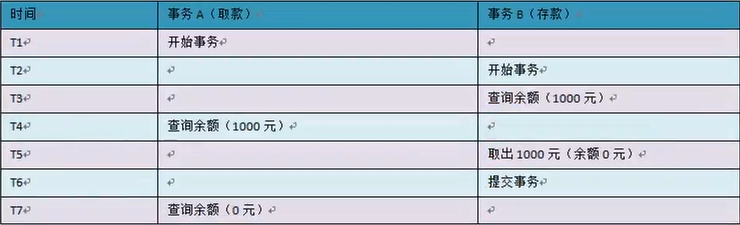
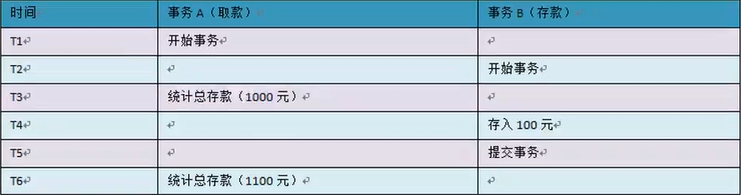
- 幻读:一个事务对一个表中的数据进行了修改,这种修改涉及到表中的全部数据行。同时,另一个事务也修改这个表中的数据,这种修改是向表中插入一行新数据。那么,操作前一个事务的用户会发现表中还有没有修改的数据行,就好像发生了幻觉一样。
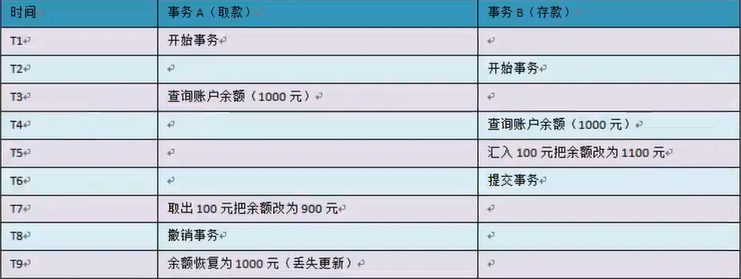
- 丢失更新:两个事务同时读取同一条记录,A先修改记录,B也修改记录(B不知道A修改过),B提交数据后B的修改结果覆盖了A的修改结果。
②MySQL事务支持的四种隔离

- 未提交读(Read Uncommitted)
允许脏读,其他事务只要修改了数据,即使未提交,本事务也能看到修改后的数据值。也就是可能读取到其他会话中未提交事务修改的数据。 - 提交读(Read Committed)
只能读取到已经提交的数据。Oracle等多数数据库默认都是该级别(不重复读)。 - 可重复读(Repeated Read)
可重复度。无论其他事务是否修改并提交了数据,在这个事务中看到的数据值始终不受其他事务影响。MySQL默认使用该隔离级别。 - 串行读(Serializable)
完全串行化的读,每次读都需要获得表级共享锁,读写相互都会堵塞,相当于锁表。
③主流数据库的默认隔离级别
| 主流数据库 | 默认隔离级别 |
|---|---|
| MySQL | repeatable read可重复读 |
| Oracle | read committed提交读 |
| SQL Server | read committed提交读 |
④查询全局事务隔离级别
show global variables like '%isolation%';
select @@global.tx_isolaion;
⑤查询会话事务隔离级别
show session variables like '%isolation%';
select @@session,tx_isolation;
select @@tx_isolation;
⑥设置全局事务隔离级别
set global transaction isolation level read committed;
⑦设置会话事务隔离级别
set session transaction isolation level read committed;
(4)持久性
持久性:在事务完成以后,该事务对数据库所做的更改便持久的保存在数据库之中,并不会被回滚。
不管系统是否发生故障,事务处理的结果都是永久的。
一旦事务被提交,事务的效果会被永久的保留在数据库中。
3. 事务控制语句
begin 或 start transaction:显式的开启一个事务
commit 或 commit work:提交事务,并使已对数据库进行的所有修改变为永久性。
rollback 或 rollback work:回滚会结束用户的事务,并撤销正在进行的所有未提交的数据。
savepoint S1:使用savepoint允许在事务中创建一个回滚点,一个事务中可以有多个savepoint,"S1"代表回滚点名称。savepoint的作用类似于游戏中的存档。
rollback to [savepoint] S1:把事务回滚到标记点。类似于游戏中的读取存档。
(1)案例
mysql> create table account (
-> id int(10) primary key not null,
-> name varchar(40),
-> money double
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc account;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(10) | NO | PRI | NULL | |
| name | varchar(40) | YES | | NULL | |
| money | double | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into account values(1,'A',1000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into account values(2,'B',1000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(2)测试提交事务
①不提交测试
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> update account set money=money-100 where name='A';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit
Bye
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 7
Server version: 5.7.20 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> select * from account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
②提交测试
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> update account set money=money-100 where name='A';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> commit;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 8
Server version: 5.7.20 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(3)测试回滚事务
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> update test.account set money=money+100 where name='A';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> rollback;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(4)测试多点回滚
mysql> begin;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update test.account set money=money+100 where name='A';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> savepoint s1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> update test.account set money=money+100 where name='B';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> savepoint s2;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1100 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into test.account values(3,'C',1000);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1100 |
| 3 | C | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> rollback to s1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 1000 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 10
Server version: 5.7.20 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
4. 使用set设置控制事务
set autocommit=0; #禁止自动提交
set autocommit=1; #开启自动提交,MySQL默认为1
show variables like 'autocommit'; #查看MySQL中的autocommit值
如果没有开启自动提交,当前会话连接的MySQL的所有操作都会当成一个事务直到你输入rollback或commit,当前事务才算结束。当前书屋结束前新的MySQL连接时,无法读取到任何当前会话的操作结果。
如果开启了自动提交,MySQL会把每个sql语句当成一个事务,然后自动的commit。
当然,无论开启与否,begin;commit|rollback;都是独立的事务。
(1)autocommit=0
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> set autocommit=0;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> update test.account set money=money+100 where name='B';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1100 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 11
Server version: 5.7.20 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(2)autocommit=1
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1000 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> set autocommit=1;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> update test.account set money=money+100 where name='B';
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1100 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> quit;
Bye
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 12
Server version: 5.7.20 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> select * from test.account;
+----+------+-------+
| id | name | money |
+----+------+-------+
| 1 | A | 900 |
| 2 | B | 1100 |
+----+------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(3)查看autocommit
mysql> show variables like 'autocommit';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| autocommit | ON |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql> set autocommit=0;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show variables like 'autocommit';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| autocommit | OFF |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
二、MySQL存储引擎
1. 存储引擎的概率
● MySQL中的数据用各种不同的技术存储在文件中,每一种技术都是用不同的存储机制、索引技巧、锁定水平并最终提供不同的功能和能力,这些不同的技术以及配套的功能在MySQL中称为存储引擎。
● 存储引擎是MySQL将数据存储在文件系统中的存储方式或者存储格式。
● MySQL常用的存储引擎为:MyISAM/InnoDB。
● MySQL数据库中的组件,负责执行实际的数据I/O操作。
● MySQL系统中,存储引擎处于文件系统之上,在数据保存到数据文件之前会传输到存储引擎,之后按照各个存储引擎的存储格式进行存储。
2. MyISAM
(1)MyISAM的特点
● MyISAM不支持事务,也不支持外键约束,只支持全文索引,数据文件和索引文件是分开保存的。
● 访问速度快,对事务完整性没有要求
● MyISAM适合查询、插入为主的应用
● MyISAM在磁盘上存储成三个文件,文件名和表名都相同,但是扩展名分别为:
.frm文件存储表结构定义
.MYD(MYData)为数据文件的扩展名
.MYI(MYIndex)为索引文件的扩展名
● 表级锁定形式,数据在更新时锁定整个表
● 数据库在读写过程中相互阻塞
会在数据写入的过程中阻塞用户数据的读取
也会在数据读取的过程中阻塞用户的数据写入
● 数据单独写入或读取,速度过程较快且占用资源相对少
● MyISAM支持的存储格式
静态表
动态表
压缩表
(2)MyISAM支持的存储格式
①静态(固定长度)表
静态表是默认的存储格式。静态表中的字段都是非可变字段,这样每个记录都是固定长度,这种存储方式的优点是存储非常迅速,容易缓存,出现故障容易恢复;缺点是占用的空间通常比动态表多。
②动态表
动态表包含可变字段,记录不是固定长度的,这样存储的优点是占用空间较少,但是频繁的更新、删除记录会产生碎片,需要定期执行optimize table语句或myisamchk -r命令来改善性能,并且出现故障的时候恢复相对比较困难。
③压缩表
压缩表由myisamchk工具创建,占据非常小的空间,因为每条记录都是被单独压缩的,所以只有非常小的访问开支。
(3)MyISAM适用的生产场景分析
● 公司业务不需要事务的支持
● 单方面读取或写入数据比较多的业务
● MyISAM存储引擎数据读写都比较频繁的场景不适合
● 适用读写并发访问相对较低的业务
● 数据修改相对较少的业务
● 对数据业务一致性要求不是非常高的业务
● 服务器硬件资源相对比较差
3. InnoDB
(1)InnoDB特点介绍
● 支持事务,支持4个事务隔离级别
● MySQL从5.5.5版本开始,默认的存储引擎为InnoDB
● 读写阻塞与事务隔离级别相关
● 能非常高效的缓存索引和数据
● 表与主键以簇的方式存储
● 支持分区、表空间,类似于Oracle数据库
● 支持外键约束,5.5前不支持全文索引,5.5后支持全文索引
● 对硬件资源要求还是比较高的场合
● 行级锁定,但是全表扫描仍然会是表级锁定,如update table set a=1 where user like '%zhang%';
● InnoDB中不保存表额行数,如select count(*) from table;时,InnoDB需要扫描一遍整个表来计算有多少行,但是MyISAM只要简单的读出保存好的行数即可。需要注意的是,当count(*)语句包含where条件时MyISAM也需要扫描整个表
● 对于自增长的字段,InnoDB中必须包含只有该字段的索引,但是在MyISAM表中可以和其他字段一起建立组合索引
● 清空整个表时,InnoDB是一行一行的删除,效率非常慢。MyISAM则会重建表。
(2)InnoDB适用生产场景分析
● 业务需要食物的支持
● 行级锁定对高并发有很好的适应能力,但需确保查询是通过索引来完成
● 业务数据更新较为频繁的场景,如论坛、微博等
● 业务数据一致性要求较高,如银行业务
● 硬件设备内存较大,利用InnoDB较好的缓存能力来提高内存利用率,减少磁盘IO的压力
4. MyISAM与InnoDB的区别
| 对比项 | MyISAM | InnoDB |
|---|---|---|
| 事务和外键的支持 | 不支持事务和外键 | 支持事务和外键 |
| 锁表状态 | 表级锁定 | 行级锁定(用like模糊匹配全表扫描时是表级锁定) |
| 并发读写能力 | 不支持MVCC(多版本并发控制,实现了读-写、写-读的并发执行) | 支持MVCC |
| 全文索引的支持 | 支持全文索引 | 5.5版本之前不支持全文索引,5.5之后支持 |
| 硬件要求 | 对硬件要求相对较低,资源消耗较低 | 对硬件要求较高,特别是内存,能提高缓存能力 |
| 存储格式 | 1. 表名.frm(文件存储表结构) 2. 表名.MYD(MYData数据文件) 3. 表名.MYI(MYIndex索引文件) |
1. db.opt(表属性文件) 2. 表名.frm(表结构文件) 3. 表名.ibd(表数据元数据) |
| 适用场景 | MyISAM适用于如资料档案室、商品仓库等数据修改较少,以读为主,单独读取和插入并且不支持事务的场景 | InnoDB适用于如微博、论坛等读写较多,一致性要求高并且支持事务的场景 |
| 读写侧重 | MyISAM更注重于读 | InnoDB更注重于写 |
| 搜查响应速度 | MyISAM搜索、访问速度快 | InnoDB稍慢 |
| 数据完整性 | MyISAM对完整性无要求(不支持事务,ACID特点) | InnoDB具有很好的完整性(支持事务,ACID特点) |
5. 企业选择存储引擎的依据
需要考虑每个存储引擎提供了哪些不同的核心功能及应用场景
● 支持的字段和数据类型
所有引擎都支持通用的数据类型
但不是所有的引擎都支持其他的字段类型,如二进制对象
● 锁定类型:不同存储引擎支持不同级别的锁定
表锁定:MyISAM支持
行锁定:InnoDB支持
● 索引的支持
建立索引在搜索和恢复数据库中的数据时能显著提高性能
不同的存储引擎提供不同的制作索引的技术
有些存储引擎根本不支持索引
● 事务处理的支持
提高在向表中更新和插入信息期间的可靠性
可根据企业业务是否要支持事务选择存储引擎
6. 对于引擎的操作
(1)查看系统支持的存储引擎
show engines;
mysql> show engines;
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
+--------------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)
(2)查看表使用的存储引擎
方法一:
show table status from 库名 where name='表名'\G
mysql> show table status from test where name='account'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Name: account
Engine: InnoDB
Version: 10
Row_format: Dynamic
Rows: 3
Avg_row_length: 5461
Data_length: 16384
Max_data_length: 0
Index_length: 0
Data_free: 0
Auto_increment: NULL
Create_time: 2021-08-30 12:20:16
Update_time: 2021-08-30 12:55:30
Check_time: NULL
Collation: utf8_general_ci
Checksum: NULL
Create_options:
Comment:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
方法二:
use 库名;
show create table 表名;
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> show create table account;
+---------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+---------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| account | CREATE TABLE "account" (
"id" int(10) NOT NULL,
"name" varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
"money" double DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ("id")
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
+---------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
(3)修改存储引擎
①通过alter table修改
use 库名;
alter table 表名 engine=指定引擎;
mysql> use test;
Database changed
mysql> alter table account engine=MyISAM;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> show table status from test where name='account'\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Name: account
Engine: MyISAM
Version: 10
Row_format: Dynamic
Rows: 2
Avg_row_length: 20
Data_length: 40
Max_data_length: 281474976710655
Index_length: 2048
Data_free: 0
Auto_increment: NULL
Create_time: 2021-08-30 13:46:48
Update_time: 2021-08-30 13:46:48
Check_time: NULL
Collation: utf8_general_ci
Checksum: NULL
Create_options:
Comment:
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
②通过修改/etc/my.cnf配置文件,指定默认存储引擎并重启服务
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf
......
[mysqld]
......
default-storage-engine=INNODB
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart mysqld.service
[root@localhost ~]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.20 Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> use test;
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
Database changed
mysql> create table engine_test(id int,engine_name varchar(30));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show create table engine_test;
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| engine_test | CREATE TABLE "engine_test" (
"id" int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
"engine_name" varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
注:此方法只对修改了配置文件并重启mysql服务后新创建的表有效,已经存在的表不会有变更。
③通过create table创建表时指定存储引擎
use 库名;
create table 表名(字段1 数据类型[,...]) engine=MyISAM;
mysql> create table engine_test(id int,engine_name varchar(30)) engine=MyISAM;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> show create table engine_test;
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| engine_test | CREATE TABLE "engine_test" (
"id" int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
"engine_name" varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 |
+-------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)


