使用规则执行器代替 if else 判断
业务场景
近日有个需求,需要对之前已有的用户申请规则进行拓展。场景大概如下所示:
if (是否海外用户) {
return false;
}
if (刷单用户) {
return false;
}
if (未付费用户 && 不再服务时段) {
return false
}
if (转介绍用户 || 付费用户 || 内推用户) {
return true;
}
按照上述的条件我们可以得出的结论是:
- 流程主要是基于 and 或者 or 的关系。
- 如果有一个不匹配的话,后续的流程是不用执行的,就是需要具备一个短路的功能。
- 对于目前的现状来说,如果在原有的基础上来改,只要稍微注意一下解决需求不是很大的问题,但是说后面可维护性非常差。
后面进过权衡过后,还是决定将这个部分进行重构一下。
规则执行器
规则执行器设计
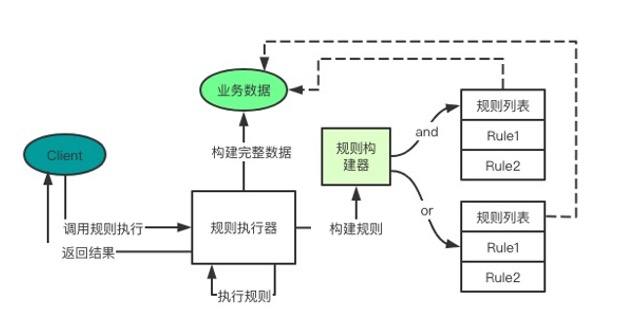
规则的抽象和实现
/**
* 基础规则业务数据
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:24 上午
*/
@Data
public class RuleDTO {
private String address;
private int age;
}
/**
* 具体业务数据
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:47 上午
*/
@Data
public class NationalityRuleDTO extends RuleDTO{
private String nationality;
}
/**
* 规则接口
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:33 上午
*/
public interface Rule {
boolean execute(RuleDTO dto);
}
/**
* 基础规则
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:35 上午
*/
public abstract class BaseRule implements Rule{
public static final String MATCH_ADDRESS_START= "北京";
public static final String MATCH_NATIONALITY_START= "中国";
protected <T> T convert(RuleDTO dto) {
return (T) dto;
}
@Override
public boolean execute(RuleDTO dto) {
return executeRule(convert(dto));
}
protected <T> boolean executeRule(T t) {
return true;
}
}
/**
* 地址规则
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:38 上午
*/
public class AddressRule extends BaseRule{
@Override
public boolean execute(RuleDTO dto) {
System.out.println("AddressRule invoke!");
return dto.getAddress().startsWith(MATCH_ADDRESS_START);
}
}
/**
* 国家规则
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:39 上午
*/
public class NationalityRule extends BaseRule{
@Override
protected <T> T convert(RuleDTO dto) {
NationalityRuleDTO nationalityRuleDto = new NationalityRuleDTO();
if (dto.getAddress().startsWith(MATCH_ADDRESS_START)) {
nationalityRuleDto.setNationality(MATCH_NATIONALITY_START);
}
return (T) nationalityRuleDto;
}
@Override
protected <T> boolean executeRule(T t) {
System.out.println("NationalityRule invoke!");
NationalityRuleDTO nationalityRuleDto = (NationalityRuleDTO) t;
return nationalityRuleDto.getNationality().startsWith(MATCH_NATIONALITY_START);
}
}
执行器
/**
* 规则执行
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:41 上午
*/
public class RuleManage {
private Map<Integer, List<Rule>> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
private static final int AND = 1;
private static final int OR = 0;
public static RuleManage create() {
return new RuleManage();
}
public RuleManage and(List<Rule> ruleList) {
hashMap.put(AND, ruleList);
return this;
}
public RuleManage or(List<Rule> ruleList) {
hashMap.put(OR, ruleList);
return this;
}
public boolean execute(RuleDTO dto) {
for (Map.Entry<Integer, List<Rule>> item : hashMap.entrySet()) {
List<Rule> ruleList = item.getValue();
switch (item.getKey()) {
case AND:
// 如果是 and 关系,同步执行
System.out.println("execute key = " + 1);
if (!and(dto, ruleList)) {
return false;
}
break;
case OR:
// 如果是 or 关系,并行执行
System.out.println("execute key = " + 0);
if (!or(dto, ruleList)) {
return false;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean and(RuleDTO dto, List<Rule> ruleList) {
for (Rule rule : ruleList) {
boolean execute = rule.execute(dto);
if (!execute) {
// and 关系匹配失败一次,返回 false
return false;
}
}
// and 关系全部匹配成功,返回 true
return true;
}
private boolean or(RuleDTO dto, List<Rule> ruleList) {
for (Rule rule : ruleList) {
boolean execute = rule.execute(dto);
if (execute) {
// or 关系匹配到一个就返回 true
return true;
}
}
// or 关系一个都匹配不到就返回 false
return false;
}
}
测试
/**
* @author LiuHuan
* @date 2021/4/23 10:49 上午
*/
public class RuleManageTest {
@Test
public void execute() {
//规则执行器
//优点:比较简单,每个规则可以独立,将规则,数据,执行器拆分出来,调用方比较规整
//缺点:数据依赖公共传输对象 dto
//1. 定义规则 init rule
NationalityRule nationalityRule = new NationalityRule();
AddressRule addressRule = new AddressRule();
//2. 构造需要的数据 create dto
RuleDTO dto = new RuleDTO();
dto.setAge(5);
dto.setAddress("北京");
//3. 通过以链式调用构建和执行 rule execute
boolean ruleResult = RuleManage
.create()
.and(Arrays.asList(nationalityRule, addressRule))
//.or(Arrays.asList(addressRule, nationalityRule))
.execute(dto);
System.out.println("this student rule execute result :" + ruleResult);
}
}
总结
优点
- 比较简单,每个规则可以独立,将规则,数据,执行器拆分出来,调用方比较规整
- Rule 模板类中定义 convert 方法做参数的转换这样可以能够,为特定 rule 需要的场景数据提供拓展
缺点
- 上下 rule 有数据依赖性,如果直接修改公共传输对象 dto 这样设计不是很合理,建议提前构建数据

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号