图的割点与割边
话说割点概念,应该很好理解:
一个图,如果一个点消失,这个点就不连通,那么这个点就是这个图的割点(无向图)
举个例子: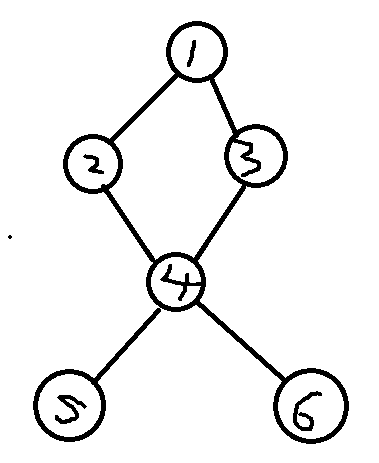
很明显,4就是这个图的割点。
所以怎么求割点呢??
来来来,先上数据:
6 6 1 2 1 3 3 4 2 4 4 5 4 6
嗯,注意这是无向图!!!
做法是这样的
首先,记录每一个点的时间截,也就是dfs第几次搜索到这个点,时间截图如下:

之后,记录每个节点在不经过自己的节点范围内,最小的时间截。
例如从3号点搜索到的4,那么4号点的最小时间截为1号点的1
再例如从4到达的5,那么5的最小时间截是4号点的3(注意可以到达4号点,只是不能经过)
最后,如果一个点的时间截>=它的下一个点的最小时间截,那么这个点就是割点。
举个例子:4号点的下一个点有5和6和2,以5举例,5的最小时间截是3,4的时间截是3,>=5号点最小时间及偶尔,所以4号点是割点。
代码实现我们用到的是dfs,开始每个点的最小时间截,就是自己本身的时间截,然后在通过一条一条边,不断变少。
先呈上代码,然后我们来模拟一下dfs过程:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int n,m; int root; int total=0; int index=0; int head[100010]; int book[100010]; int num[100010],low[100010]; struct edge { int from; int to; int next; }input[100010]; void add_edge(int a,int b) { total++; input[total].from=a; input[total].to=b; input[total].next=head[a]; head[a]=total; } void dfs(int now,int father) { index++; int child=0; num[now]=index; low[now]=index; for(int e=head[now];e!=0;e=input[e].next) { if(num[input[e].to]==0) { child++; dfs(input[e].to,now); low[now]=min(low[now],low[input[e].to]); if(now!=root && low[input[e].to]>=num[now]) book[now]=true; if(now==root && child==2) book[now]=true; } else if(input[e].to!=father) low[now]=min(low[now],num[input[e].to]); } } int main() { cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { int a,b; cin>>a>>b; add_edge(a,b); add_edge(b,a); } root=1; dfs(1,root); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(book[i]) cout<<i<<" "; }
开始还是一直递归,1——3——4——6
然后发现6无法递归,于是返回
到4,发现自己的最小时间截(以下简称low)比6的4要小,所以不改变。
然后到5,发现low还是比5的5要小,所以不改变。
接着到2,发现2的时间截还是更大,所以不改变。返回。
此时,2、5、6的low都比4的时间截大,所以4为截点
之后,发现从一号点每一个连着的点都被走过,所以循环终止
4为截点。
割点完毕。
然后割边
一句话,割边就删一个等于号就好啦。
至于为什么很好想吧?
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> using namespace std; int n,m; int total=0; int index=0; int head[100010]; int num[100010],low[100010]; struct edge { int from; int to; int next; }input[100010]; void add_edge(int a,int b) { total++; input[total].from=a; input[total].to=b; input[total].next=head[a]; head[a]=total; } void dfs(int now,int father) { index++; num[now]=index; low[now]=index; for(int e=head[now];e!=0;e=input[e].next) { if(num[input[e].to]==0) { dfs(input[e].to,now); low[now]=min(low[now],low[input[e].to]); if(low[input[e].to]>num[now]) cout<<now<<"->"<<input[e].to<<endl; } else if(input[e].to!=father) low[now]=min(low[now],num[input[e].to]); } } int main() { cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) { int a,b; cin>>a>>b; add_edge(a,b); add_edge(b,a); } dfs(1,1); }
嗯,就关注



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号