偏左红黑树
红黑树是一种性能非常优秀的数据结构,关键在于它能保证最坏的性能也是对数的。红黑树的本质是一棵2-3树。
算法4里对2-3树,偏左红黑树的描述更简单和直观,比算法导论更容易理解。算法导论里实现红黑树插入删除要几百行代码,而LLRB只需要几十行。
红黑树前置准备:
2-3树定义:
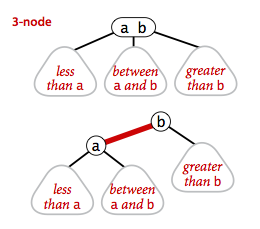
2-3树的主要特点就是树由普通的2节点和一种三节点组成。2节点和二叉查找树中的特性相同。对于3节点,它的键有两个,并且有三个链接,左链接指向的左子树中的所有元素都小于3节点中的两个键,中间链接指向的子树大小在两个键之间,右链接指向的子树中的元素都大于两个键。

查找
对于查找操作和二叉查找树基本相同,递归比较要查找的键和树的根节点,小于就向左继续查找,大于就向右查找,相等就查找命中。不同的就是对于3节点,还要有中间节点的情况,在三节点两个键的大小之间的情况,要向中间子树递归。最后如果查找到叶节点的空连接就直接返回null。
插入
2-3树的插入相对来说是比较复杂的,因为它是保证树本身平衡性的关键。我们分几种情况来论述。
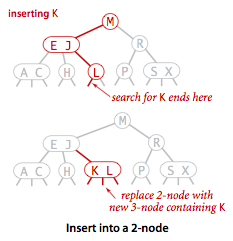
向2节点插入
插入先是要查找,查找到了就直接更新,如果未命中就插入新元素,插入新元素一定是在叶节点的空连接上,如果叶节点是一个2节点,那么就直接插入,让特们合成一个3节点。显然这时树高没有变化。示意图如下
向3节点插入
假如向一个3节点中插入,我们首先可以做的是像2节点一样把他们暂时合在一起形成一个4节点(有三个元素),然后再对这个4节点进行分解,将中间的元素插入他们的父元素剩下两个元素变成两个2节点。注意:只能是中间的元素拿上去,因为这样才能保证树的有序性,即左边和右边的元素相对于根元素的大小关系,然后再考察父节点,如父节点原来是一个2节点,那么此时直接插入将其变成一个3节点,插入操作就完成了。

如果原来父节点就是一个3节点,那么依然可以再重复这个过程,不断将中间元素加入父节点,如果这个过程持续到了根节点,那么我们就分裂形成的一个暂时的4节点的根节点,得到三个2节点,同时整个的树高增加1。
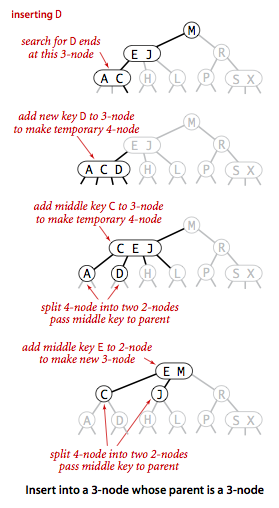
这种插入相当于把元素插入这个会引起树的高度变化的不利因素放在3节点中储存起来,随着3节点的插入将这种不利因素不断传导至根节点,然后通过根节点的分裂将整个的树高加1,可以看出,3节点以及相关的插入方法是保证平衡性的关键,也可以看出2-3树的生长是从下往上通过根节点生长的。2-3树就可以实现在最坏条件下也有对数性能。
下面我们就可以看到一种2-3树的具体实现——红黑二叉查找树,以下简称红黑树。
我们用红链接即一条红色的左链接来表示3节点,而2节点就用普通的黑色连接来表示。
那么一棵红黑树应该是完美黑色平衡的,即从任意空连接出发到根节点所经历的黑连接数目应该是相同的。
再加入一个条件:没有任意一个节点同时和两个红链接相连,那么此时红黑树就可以和2-3树一一对应。
public class RedBlackBST<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> { private static final boolean RED = true; private static final boolean BLACK = false; private Node root; // root of the BST private class Node { private Key key; // key private Value val; // associated data private Node left, right; // links to left and right subtrees private boolean color; // color of parent link private int size; // subtree count public Node(Key key, Value val, boolean color, int size) { this.key = key; this.val = val; this.color = color; this.size = size; } } }
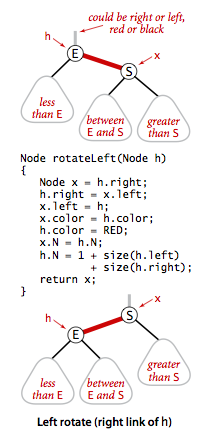
红黑树的插入或删除,可能会改变原来的平衡性,我们只需要左旋,右旋,变色三个操作,即可恢复平衡性
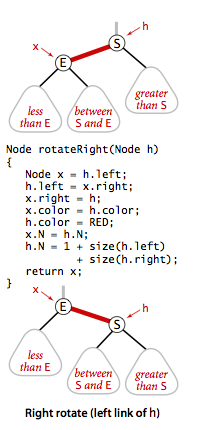
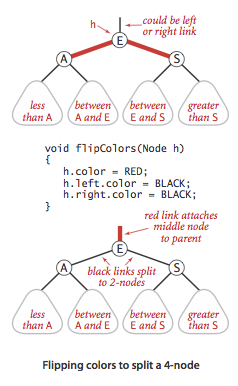
查找
红黑树的查找算法和二叉查找树的查找算法是完全一样的,也就是说,对于查找算法来说,红黑树中节点或者说链接的颜色是没有用到的,但是没有关系,虽然红黑树只是黑链接平衡,但是即使不考虑颜色的查找,整个树也不会出现像二叉树里面那种最极端的情况,所以性能依然是有保障的。
插入
红黑树的插入的算法是比较复杂的,对于2-3树来说相对较简单,但是在具体实现的时候,每个3节点中是有着具体结构的,那么我们在插入后就要调节这些具体的结构,才能实现2-3树中的功能。
向2节点插入
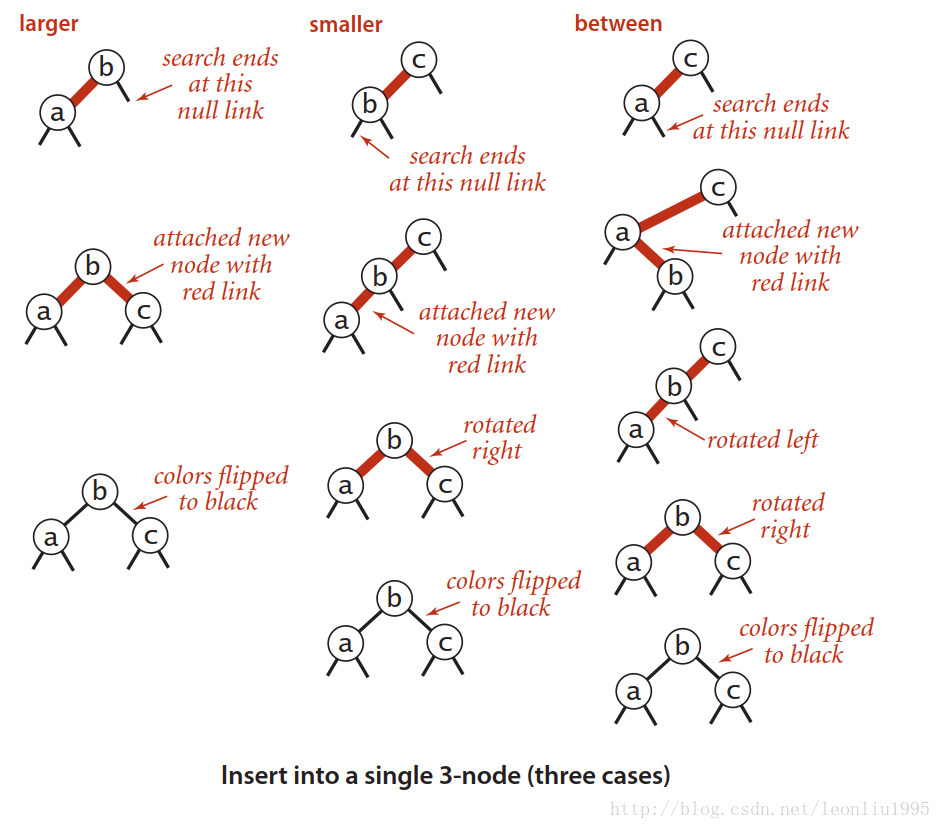
在2-3树中向2节点插入非常简单,直接合并成一个3节点就行。但是具体实现时,因为相对于父节点可能有大有小,那么在插入的时候就可能在父节点的左边或者右边,而红链接只能是左链接,那么当在右边插入的时候,就需要进行旋转操作将右链接变成左链接。
向3节点插入
向3节点插入就更加复杂了,因为此时不仅有插入方向的问题,还有父节点也是红色的问题,我们要调整几个节点的结构,实现2-3树中将中间节点插入到父节点的操作。这里主要分三种情况。
1
如果插入后一个节点的两个子节点都是红色的,那么我们通过flipColors()可以很容易的实现2-3树中将中间节点插入父节点,两边节点独立成两个2节点,同时保持有序性(这里默认中间节点是黑色的,因为默认在插入之前整个树是有序的,这个可以通过正确的插入来保证)。
2
第二种情况下,需要先将第一个红链接进行右旋转,这样就变成了第一种情况,可以按照情况1 处理
3
第三种情况下,需要先将下面的红链接进行左旋转就变成了第二种情况,然后就可以按照第二种情况处理
/*************************************************************************** * Red-black tree insertion. ***************************************************************************/ /** * Inserts the specified key-value pair into the symbol table, overwriting the old * value with the new value if the symbol table already contains the specified key. * Deletes the specified key (and its associated value) from this symbol table * if the specified value is {@code null}. * * @param key the key * @param val the value * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code key} is {@code null} */ public void put(Key key, Value val) { if (key == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("first argument to put() is null"); if (val == null) { delete(key); return; } root = put(root, key, val); root.color = BLACK; // assert check(); } // insert the key-value pair in the subtree rooted at h private Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val) { if (h == null) return new Node(key, val, RED, 1); int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key); if (cmp < 0) h.left = put(h.left, key, val); else if (cmp > 0) h.right = put(h.right, key, val); else h.val = val; // fix-up any right-leaning links if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h); if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h); if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h); h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1; return h; }
可以看出,算法4的插入比算法导论简洁很多
只需要三步调整
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);
删除最小值最大值和删除
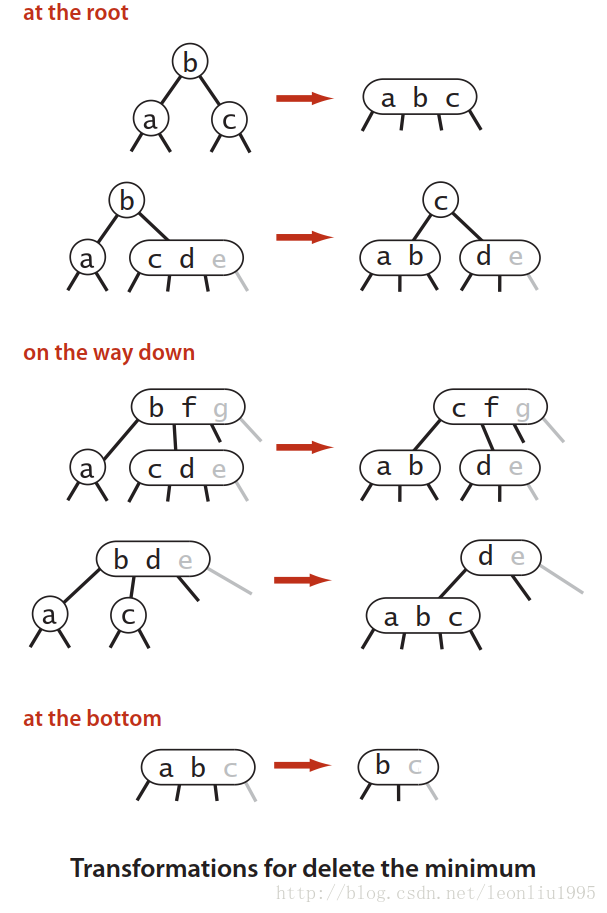
删除比较麻烦,我们先考虑删除最小值,当我们删除一个3节点中的元素的时候倒还好,直接删除之后留下了一个2节点,树的平衡性没有发生变化。但是直接删除2节点会造成树的高度的变化。所以,我们还是要处理一下,从上往下进行变换,最终的目标就是保证在删除的时候当前节点不只是一个2节点。
删除最小值
最小值在最左边,我们沿着左边下去的时候需要合并三个2节点形成一个4节点,或者右边是三节点的话从右边节点“借”一个形成一个3节点或者4节点,这样就能保证当前节点大于2节点
/** * Removes the smallest key and associated value from the symbol table. * @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty */ public void deleteMin() { if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("BST underflow"); // if both children of root are black, set root to red if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right)) root.color = RED; root = deleteMin(root); if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK; // assert check(); } // delete the key-value pair with the minimum key rooted at h private Node deleteMin(Node h) { if (h.left == null) return null; if (!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left)) h = moveRedLeft(h); h.left = deleteMin(h.left); return balance(h); }
// Assuming that h is red and both h.left and h.left.left
// are black, make h.left or one of its children red.
private Node moveRedLeft(Node h) {
// assert (h != null);
// assert isRed(h) && !isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left);
flipColors(h); //这一行把父结点和左子结点拉到一行。
if (isRed(h.right.left)) {
h.right = rotateRight(h.right);
h = rotateLeft(h);
flipColors(h); //算法4书少了这一行。网站有。这一行代表借了一个节点之后,再还一个给父节点。否则我们就连着兄弟节点一起变成一个大节点了。
}
return h;
}
// restore red-black tree invariant
private Node balance(Node h) {
// assert (h != null);
//if (isRed(h.right)) h = rotateLeft(h); 这句在书里有,但代码网站并没有这一行。
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);
h.size = size(h.left) + size(h.right) + 1;
return h;
}
其中balance()函数就是在返回的时候解开临时的4节点,使整个树再次平衡。

删除最大值
删除最大值和删除最小值类似,但是因为红链接都是左链接,所以代码有所不同。
/**
* Removes the largest key and associated value from the symbol table.
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the symbol table is empty
*/
public void deleteMax() {
if (isEmpty()) throw new NoSuchElementException("BST underflow");
// if both children of root are black, set root to red
if (!isRed(root.left) && !isRed(root.right))
root.color = RED;
root = deleteMax(root);
if (!isEmpty()) root.color = BLACK;
// assert check();
}
// delete the key-value pair with the maximum key rooted at h
private Node deleteMax(Node h) {
if (isRed(h.left))
h = rotateRight(h);
if (h.right == null)
return null;
if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left))
h = moveRedRight(h);
h.right = deleteMax(h.right);
return balance(h);
}
// Assuming that h is red and both h.right and h.right.left
// are black, make h.right or one of its children red.
private Node moveRedRight(Node h) {
// assert (h != null);
// assert isRed(h) && !isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left);
flipColors(h);
if (isRed(h.left.left)) {
h = rotateRight(h);
flipColors(h);
}
return h;
}
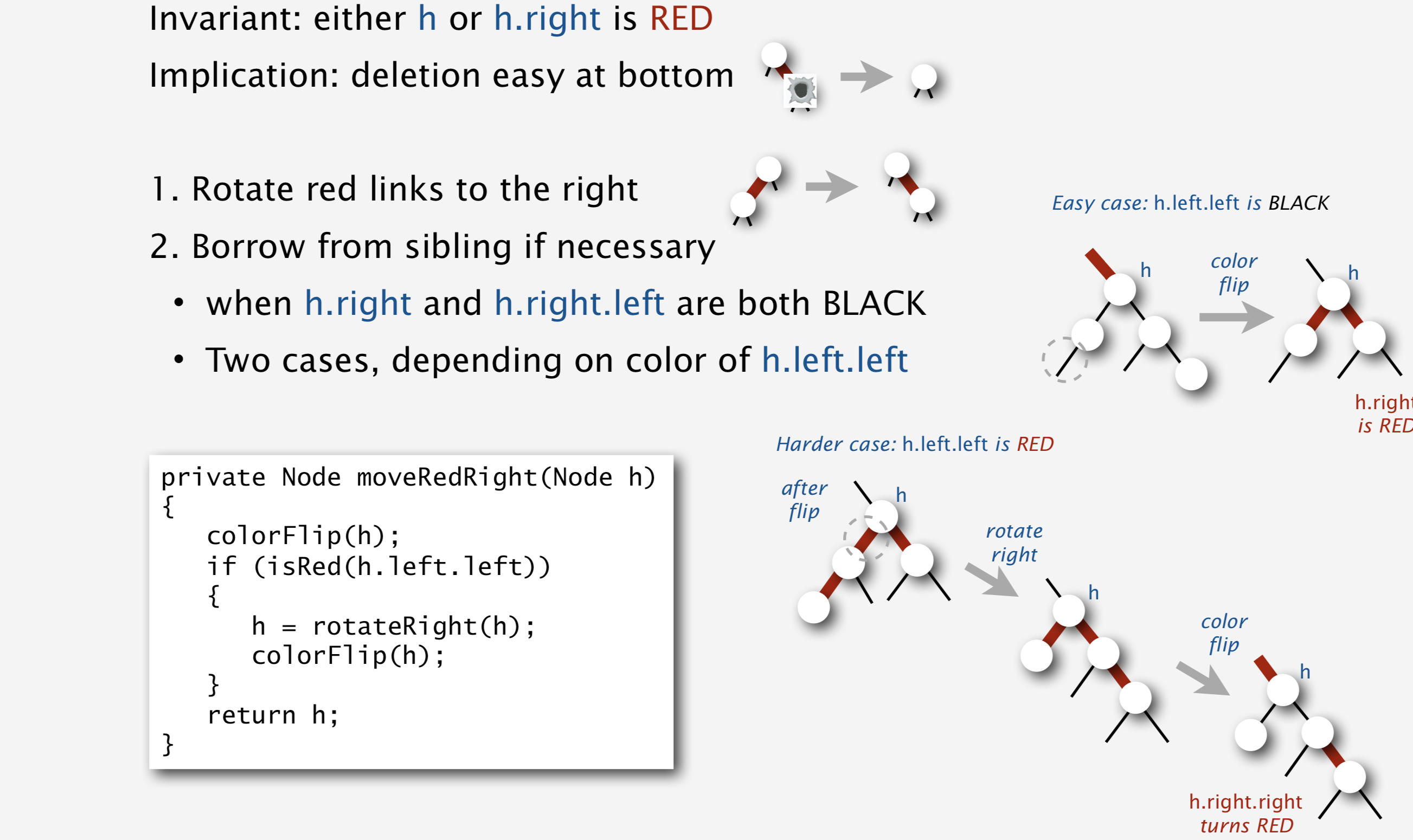
真正的删除函数就用到了delMin()函数
// delete the key-value pair with the given key rooted at h
private Node delete(Node h, Key key) {
// assert get(h, key) != null;
if (key.compareTo(h.key) < 0) {
if (!isRed(h.left) && !isRed(h.left.left))
h = moveRedLeft(h);
h.left = delete(h.left, key);
}
else {
if (isRed(h.left))
h = rotateRight(h);
if (key.compareTo(h.key) == 0 && (h.right == null))
return null;
if (!isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.right.left))
h = moveRedRight(h);
if (key.compareTo(h.key) == 0) {
Node x = min(h.right);
h.key = x.key;
h.val = x.val;
// h.val = get(h.right, min(h.right).key);
// h.key = min(h.right).key;
h.right = deleteMin(h.right);
}
else h.right = delete(h.right, key);
}
return balance(h);
}
参考资料:
《算法4》
https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/33balanced/
https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/33balanced/RedBlackBST.java.html
https://blog.csdn.net/leonliu1995/article/details/78374492
https://www.cs.princeton.edu/~rs/talks/LLRB/RedBlack.pdf
https://www.cs.princeton.edu/~rs/talks/LLRB/LLRB.pdf


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号