进程间通信实验
实验三 进程间通信
一、实验目的
通过 Linux 系统中线程和管道通信机制的实验,加深对于线程控制和管道通信概
念的理解,观察和体验并发进/线程间的通信和协作的效果 ,练习利用无名管道进行
进/线程间通信的编程和调试技术。
二、实验内容
设有二元函数 f(x,y) = f(x) + f(y)
其中:
f(x) = f(x-1) * x
(x >1)
f(x)=1
(x=1)
f(y) = f(y-1) + f(y-2)
(y> 2)
f(y)=1
(y=1,2)
请编程建立 3 个并发协作进程,它们分别完成 f(x,y)、f(x)、f(y)
三、实验要求
根据示例实验程序和独立实验程序观察和记录的调试和运行的信息,说明它们
反映出操作系统教材中讲解的进程协作和进程通信概念的哪些特征和功能?在真实
的操作系统中它是怎样实现和反映出教材中进程通信概念的。你对于进程协作和进
程通信的概念和实现有哪些新的理解和认识?管道机制的机理是什么?怎样利用管
道完成进程间的协作和通信?根据实验程序、调试过程和结果分析写出实验报告
四、实验步骤
1) 打开一终端命令行窗体,新建一个文件夹,在该文件夹中建立以下名为suanshu.c的C语言程序,该程序皆为头文件,该程序代码为:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#define READ 0
#define WRITE 1
int fx(int x);
int fy(int y);
int main()
{
pid_t pid1, pid2;
int pipe11[2], pipe12[2], pipe21[2], pipe22[2];
int x, y;
if (pipe(pipe11) < 0)
{
perror("管程创建失败\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pipe(pipe12) < 0)
{
perror("管程创建失败\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pipe(pipe21) < 0)
{
perror("管程创建失败\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pipe(pipe22) < 0)
{
perror("管程创建失败\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
pid1 = fork();
if (pid1 < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "child1 fork failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if (pid1 == 0)
{
int x, X;
//子进程1
close(pipe11[WRITE]);
close(pipe12[READ]);
//wait parent write to child1
read(pipe11[READ], &x, sizeof(int));
X = fx(x);
//write to parent
write(pipe12[WRITE], &X, sizeof(int));
close(pipe11[READ]);
close(pipe12[WRITE]);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else
{
pid2 = fork();
if (pid2 < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "child2 fork failed\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
else if (pid2 == 0)
{
int y, Y;
//子进程2
close(pipe21[WRITE]);
close(pipe22[READ]);
//wait parent write to child2
read(pipe21[READ], &y, sizeof(int));
Y = fy(y);
//write to parent
write(pipe22[WRITE], &Y, sizeof(int));
close(pipe21[READ]);
close(pipe22[WRITE]);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
else
{
int x, y, X, Y, XY;
//父进程
//输入x
printf("请输入x = \n");
scanf("%d", &x);
//输入y
printf("请输入y = \n");
scanf("%d", &y);
close(pipe11[READ]);
close(pipe12[WRITE]);
close(pipe21[READ]);
close(pipe22[WRITE]);
//write to child1 x
write(pipe11[WRITE], &x, sizeof(int));
//write to child2 y
write(pipe21[WRITE], &y, sizeof(int));
//read XYwer X of child1
read(pipe12[READ], &X, sizeof(int));
//read XYwerY of child2
read(pipe22[READ], &Y, sizeof(int));
//calculate
XY = X + Y;
printf("f(x) = %d\n", X);
printf("f(y) = %d\n", Y);
printf("f(x,y) = %d\n", XY);
}
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
//f(x)递归程序
int fx(int x)
{
if (x <= 1)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return fx(x - 1) * x;
}
}
//f(y)递归程序
int fy(int y)
{
if (y <= 2)
{
return 1;
}
else
{
return fy(y - 1) + fy(y - 2);
}
2) 输入gcc -c suanshu.c -o suanshu.o命令生成suanshu.o文件

3) 出现错误截图如下:
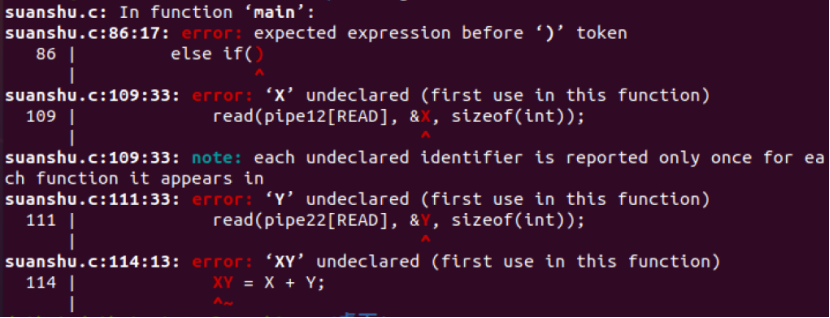
五、实验结果
1)排除error更改代码,出现error的原因是因为if语句出现错误,画蛇添足没有必要用到它,以及一些变量的使用未经过声明,改正后再输入gcc -c suanshu.c -o suanshu.o命令生成suanshu.o文件

2)输入gcc suanshu.o -o suanshu生成suanshu执行文件

3)输入./suanshu再按照提示输入做运算的x与y的值
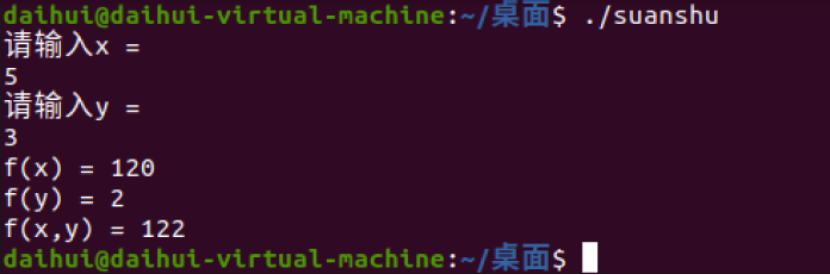
六、实验小结
在这次实验中我通过 Linux 系统中线程和管道通信机制的实验,加深对于线程控制和管道通信概念的理解,首先是设计实验代码方面先创建进程,每个子进程的执行代码段实现对应函数功能。再建立父进程与子进程间的通信,因为他们是同步并发问题所以可以利用两个管道pipe1和pipe2来实现,f(x)通过pipe1向父进程中写入f(x)的值,f(y)通过pipe2向进程中写入f(y)的值。通过实验充分的了解了线程间通信和协作的过程。

