Netty基础01-NIO-ByteBuffer
2、ByteBuffer
简单案例
- pom
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.netty</groupId>
<artifactId>netty-all</artifactId>
<version>4.1.39.Final</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId>
<artifactId>gson</artifactId>
<version>2.8.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>19.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- code
// 读取data.txt文件中的内容
@Slf4j
public class ChannelAndBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、FileChannel
// 输入输出流 RadomAccessFile
try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("data.txt").getChannel()) {
//2、准备缓冲区 10个字节
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
while (true) {
// 3、从channel 读取数据 也就是想buffer写入数据
int len = channel.read(buffer);
// len == -1表示没有数据
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
log.debug("--->{}", "读取的字节数:" + len);
// 4、切换buffer模式为度模式
buffer.flip();
// 5、检查buffer中是否还有剩余数据
while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {
byte b = buffer.get();
log.debug("--->{}", "读出的字节:" + (char) b);
}
// 6、切换为写模式
buffer.clear();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
- 日志
2021-04-10 14:18:12.648 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读取的字节数:10
2021-04-10 14:18:12.652 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:1
2021-04-10 14:18:12.652 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:2
2021-04-10 14:18:12.652 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:3
2021-04-10 14:18:12.652 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:4
2021-04-10 14:18:12.652 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:5
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:6
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:7
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:8
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:9
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:0
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读取的字节数:3
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:a
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:b
2021-04-10 14:18:12.653 [main] DEBUG com.riest.netty.ChannelAndBuffer: --->读出的字节:c
正确使用姿势
- 向buffer写入数据。例如调用channel.read(buffer)
- 调用flip() 切换至读模式
- 从buffer读取数据,例如调用buffer.get()
- 调用clear()或者compacy()切换至写模式
- 重复上述步骤
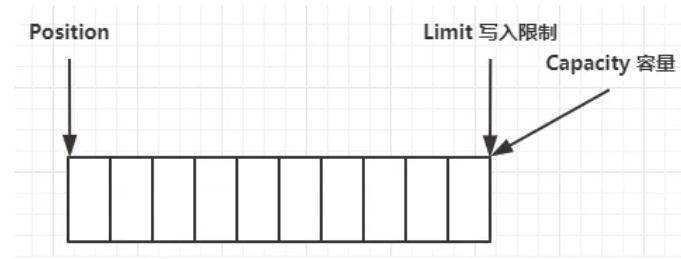
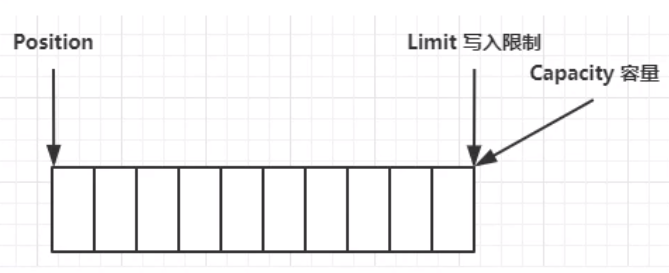
结构
- limit:写入限制
- Capacity:容量
- Position:位置(指针)
一开始:
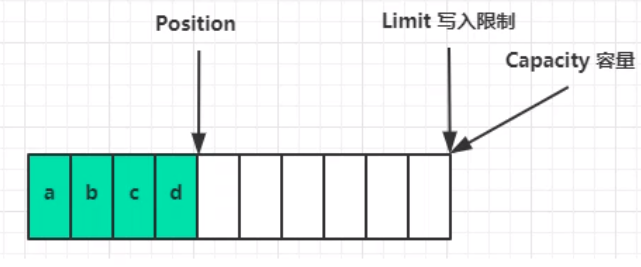
写模式下:position是写入位置,limit等于容量,下图表示写入了4个字节后的状态
flip()动作发生后:position切换为读取位置,limit切换为读取限制
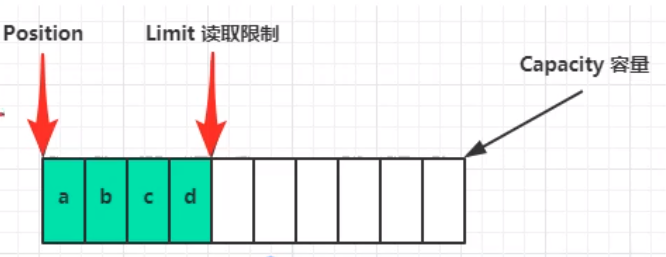
读取四个字节后,状态

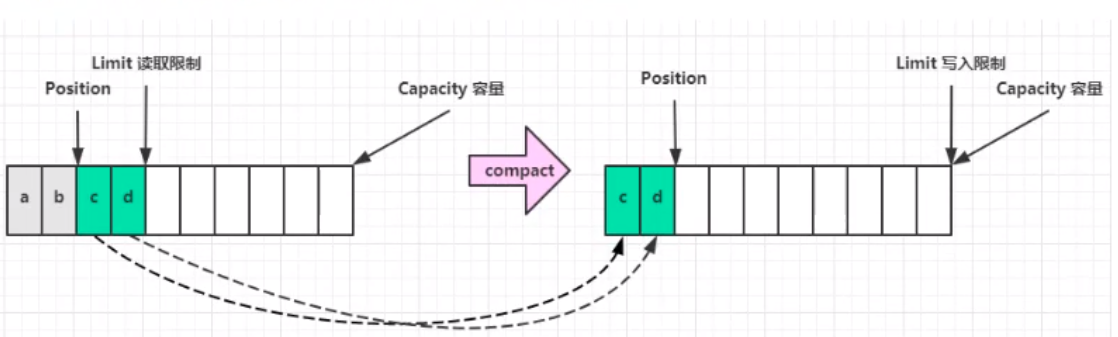
clear()发生后,状态:
comapct()方法,将未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式
常用方法
-
分配内存方法
// 1、分配内存的方法 ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(16); ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(16); // class java.nio.HeapByteBuffer java 堆内存,读写效率低,收到GC影响 System.out.println(allocate.getClass()); // class java.nio.DirectByteBuffer 系统内存 ,读写效率高(少一次拷贝),不受GC影响,分配效率低 System.out.println(byteBuffer.getClass()); -
写入方法
// 2、写入方法 try (FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("").getChannel()) { ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); // channel channel.read(buffer); // buffer buffer.put((byte)'a'); //...... } catch (IOException e) { } -
读取方法
//3、读取方法 ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); // 写 allocate.put(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}); // 切换至读模式 allocate.flip(); allocate.get(new byte[4]); debugAll(allocate); // 从头开始读 allocate.rewind(); debugAll(allocate); // get 方法会让position的指针往后移动,如果向重复读取数据 // 可以将rewind方法将position重新置为0 // 或者调用get(int i)方法获取索引的 i 的内容,它不会移动指针
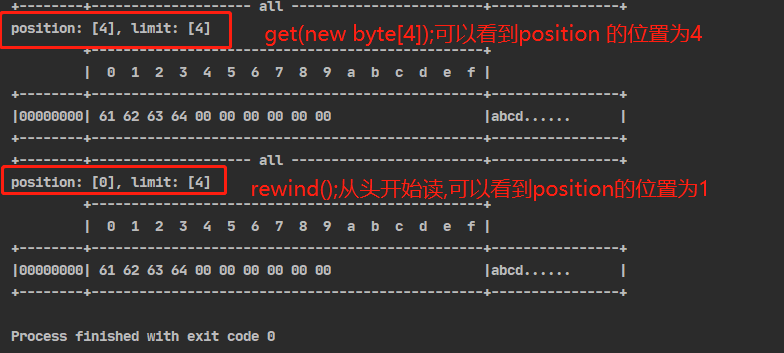
-
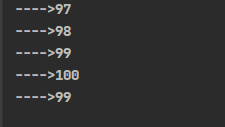
mark & reset
mark 做一个标记,记录position的位置
reset将position重置到position的位置
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); allocate.put(new byte[]{'a', 'b', 'c', 'd'}); allocate.flip(); System.out.println("---->"+allocate.get()); System.out.println("---->"+allocate.get()); // 标记position的位置 allocate.mark(); System.out.println("---->"+allocate.get()); System.out.println("---->"+allocate.get()); // 将position 重置到 postion 索引为2 的位置 allocate.reset(); System.out.println("---->"+allocate.get());
-
String 和 ByteBuffer相互转换
// 1、字符串转ByteBuffer ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(16); buffer1.put("hello".getBytes()); debugAll(buffer1); // 该方法会自动切换至读模式 ByteBuffer buffer2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("hello"); debugAll(buffer2); // 该方法会自动切换至读模式 ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.wrap("hello".getBytes()); debugAll(buffer3); // 2、ByteBuffer 转字符串 String str1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer2).toString(); System.out.println("---->"+str1); // buffer1切换读模式 buffer1.flip(); String str2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.decode(buffer1).toString(); System.out.println("---->"+str2);
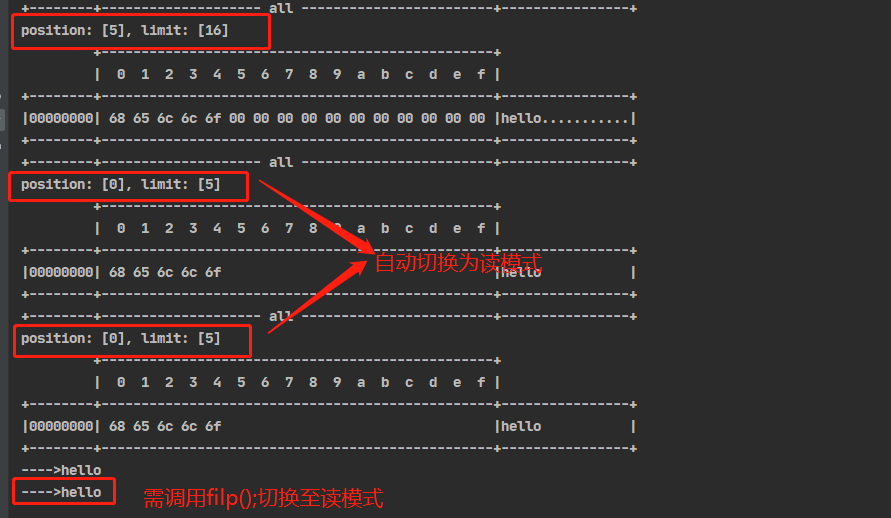
分散读取Scattered Read
/**
* 分散读取
*/
public static void scatteringRead(){
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("word1.txt","r").getChannel()) {
ByteBuffer buffer1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(4);
ByteBuffer buffer2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
ByteBuffer buffer3 = ByteBuffer.allocate(6);
channel.read(new ByteBuffer[]{buffer1,buffer2,buffer3});
buffer1.flip();
buffer2.flip();
buffer3.flip();
debugAll(buffer1);
debugAll(buffer2);
debugAll(buffer3);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
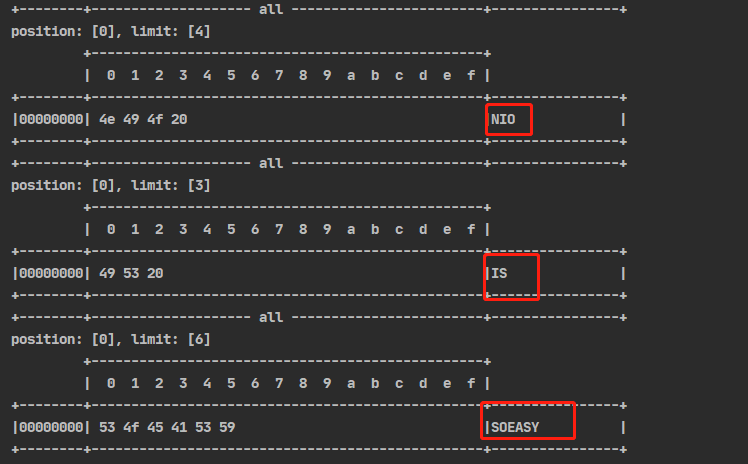
集中写 Gather Write
/**
* 集中写
*/
public static void gatherWrite(){
ByteBuffer b1 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("NIO ");
ByteBuffer b2 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("IS ");
ByteBuffer b3 = StandardCharsets.UTF_8.encode("SOEASY");
try (FileChannel channel = new RandomAccessFile("word2.txt", "rw").getChannel()) {
channel.write(new ByteBuffer[]{b1,b2,b3});
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
练习
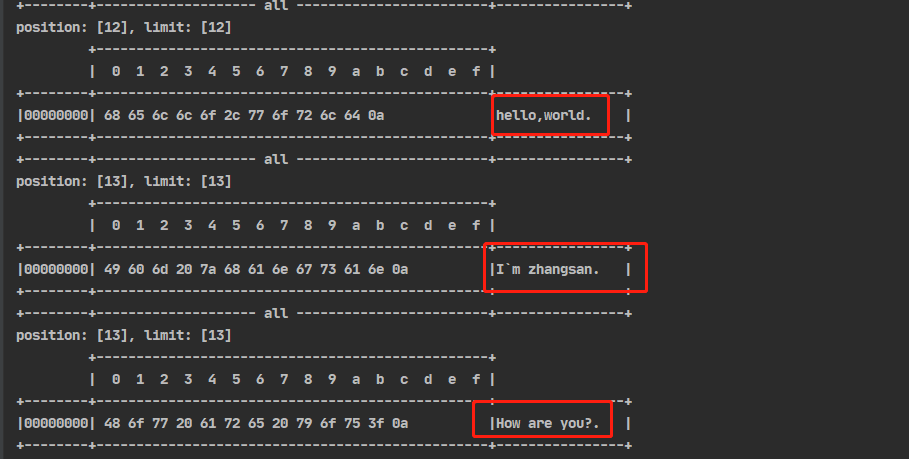
网络上有很多条数据发送给服务器,数据之间使用 \n 进行分隔 ,但由于某种原有导致这些数据在接收是,被进行了重新组合,例如原始数据有三条,分别为
Hello,world\n
I`m zhangsan\n
How are you?\n
变成了下面的两个ByeBuffer(黏包、半包)
Hello,world\nI`m zhangsan\nHo
w are you?\n
现在要求你编写code,将错乱的数据恢复成原始的按照 \n分隔的数据
code 如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "hello,world\nI`m zhangsan\nHo";
String str2 = "w are you?\n";
ByteBuffer b1 = ByteBuffer.allocate(30);
b1.put(str1.getBytes());
dispose(b1);
b1.put(str2.getBytes());
dispose(b1);
}
public static void dispose(ByteBuffer buffer) {
// 切换成读模式
buffer.flip();
for (int i = 0; i < buffer.limit(); i++) {
if (buffer.get(i) == '\n') {
// \n 的位置
int len = i + 1 - buffer.position();
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(len);
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
allocate.put(buffer.get());
}
debugAll(allocate);
}
}
//将未读完的部分向前压缩,然后切换至写模式
buffer.compact();
}