gcc编译过程简述
在linux系统上,从源文件到目标文件的转化是由编译器完成的。以hello.c程序的编译为例,如下:
dfcao@linux: gcc -o hello hello.c
在这里,gcc编译器读取源文件hello.c,并把它翻译成一个可执行文件 hello。
这个翻译过程可分为四个阶段逐步完成:预处理,编译,汇编,链接,如下图所示。
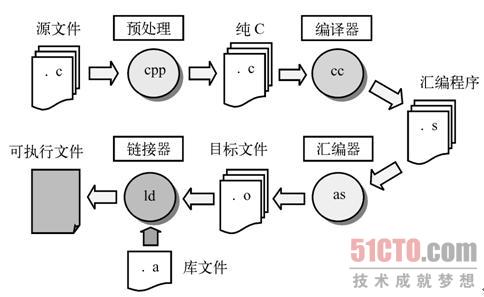
逐步做下简单分析:
在未编译前,hello.c 的源代码如下
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}
第一步、预处理阶段
执行命令: gcc -o hello.i -E hello.c
或者 cpp -o hello.i hello.c (这里cpp不是值c plus plus,而是预处理器the C Preprocessor)
预处理器cpp根据以字符开头#开头的命令,修改原始C程序。比如hello.c中的第一行为 #include <stdio.h>,预处理器便将stdio.h的内容直接插入到程序中。
预处理之后得到文本文件hello.i,打开如下
# 1 "hello.c"
# 1 "<built-in>"
# 1 "<命令行>"
# 1 "hello.c"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4
...
...
...
extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 940 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 2 "hello.c" 2
int main()
{
printf("hello, world\n");
}
在源代码的前面插入了stdio.h,整个hello.i 的行数由hello.c的6行变到了855行!
第二步、编译阶段
执行命令: gcc -o hello.s -S hello.i
或者 ccl -o hello.s hello.i
编译器ccl 将文本文件hello.i 翻译为hello.s,这个文件里面包含一个汇编程序,如下
.file "hello.c"
.section .rodata
.LC0:
.string "hello, world"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB0:
.cfi_startproc
pushl %ebp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 8
.cfi_offset 5, -8
movl %esp, %ebp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 5
andl $-16, %esp
subl $16, %esp
movl $.LC0, (%esp)
call puts
leave
.cfi_restore 5
.cfi_def_cfa 4, 4
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE0:
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (Ubuntu/Linaro 4.6.3-1ubuntu5) 4.6.3"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
汇编语言是非常有用的,因为它将不同高级语言的不同编译器提供了通用的输出语言。例如,C和Fortran 的在此步编译产生的输出文件都是一样的汇编语言。
第三步、汇编阶段
执行命令: gcc -o hello.o -c hello.s
或者 as -o hello.o hello.s
汇编器as 将hello.s 翻译成机器语言保存在hello.o 中。这是个二进制文件,用命令hexdump hello.o 打开如下
0000000 457f 464c 0101 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000010 0001 0003 0001 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
0000020 011c 0000 0000 0000 0034 0000 0000 0028
0000030 000d 000a 8955 83e5 f0e4 ec83 c710 2404
0000040 0000 0000 fce8 ffff c9ff 00c3 6568 6c6c
0000050 2c6f 7720 726f 646c 0000 4347 3a43 2820
0000060 6255 6e75 7574 4c2f 6e69 7261 206f 2e34
0000070 2e36 2d33 7531 7562 746e 3575 2029 2e34
0000080 2e36 0033 0014 0000 0000 0000 7a01 0052
0000090 7c01 0108 0c1b 0404 0188 0000 001c 0000
00000a0 001c 0000 0000 0000 0017 0000 4100 080e
00000b0 0285 0d42 5305 0cc5 0404 0000 2e00 7973
00000c0 746d 6261 2e00 7473 7472 6261 2e00 6873
00000d0 7473 7472 6261 2e00 6572 2e6c 6574 7478
00000e0 2e00 6164 6174 2e00 7362 0073 722e 646f
00000f0 7461 0061 632e 6d6f 656d 746e 2e00 6f6e
0000100 6574 472e 554e 732d 6174 6b63 2e00 6572
0000110 2e6c 6865 665f 6172 656d 0000 0000 0000
0000120 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
*
0000140 0000 0000 001f 0000 0001 0000 0006 0000
0000150 0000 0000 0034 0000 0017 0000 0000 0000
0000160 0000 0000 0004 0000 0000 0000 001b 0000
0000170 0009 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 03e8 0000
0000180 0010 0000 000b 0000 0001 0000 0004 0000
0000190 0008 0000 0025 0000 0001 0000 0003 0000
00001a0 0000 0000 004c 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000
第四步、链接阶段
执行命令: gcc -o hello hello.o
或者 ld -o hello hello.o
注意!hello程序调用了printf 函数,这个函数是标准C库中的一个函数,他保存在一个名为printf.o 的文件中,这个文件必须以某种方式合并到我们的hello.o的程序中。
链接器ld 负责处理这种合并。结果得到hello 可执行文件,可以被加载到内存中由系统执行。
./hello
总结
编译器的编译过程:
源文件-->预处理-->编译/优化-->汇编-->链接-->可执行文件。
平常用的最多、看起来一句命令就搞定的一次编译背后其实非常不简单。此博作简单记录,能力到了之后再做深入分析。
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------#
参考文献
《Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective》 by Randal Bryant.
“编译过程” by itwilliamlee, http://www.lisdn.com/html/95/n-15195.html



