软件开发工程师谈测试金字塔实践
测试金字塔是对测试的分层描述,在不同层次做不同类型的测试。测试金字塔如何运用到工程实践,是一件困难的事情。原文作者是一位德国Thoughtworks的软件开发工程师,本文将回顾传统的测试金字塔,并结合实例,进行一次有深度的探秘实践。

自动化测试的重要性
软件上线前都是要经过测试的,随着测试技术发展,相比于传统的手工测试,如今的自动化测试越来越重要,它能够将成天上周的测试工作缩减到分钟秒级,提高测试效率,更快发现缺陷。尤其是在敏捷开发、持续交付、DevOps文化中,自动化已经成为了对测试的基本要求。比如持续交付,使用build pipeline自动测试和部署,随时能发包到测试环境和生产环境。

测试金字塔
测试金字塔是Mike Cohn在他的书籍《Succeeding with Agile》中提出的概念:

测试金字塔描绘了不同层次的测试,以及应该在各个层次投入多少测试。由底向上包括3层:
-
Unit Tests
-
Service Tests
-
User Interface Tests
这是最原始的测试金字塔,从现代视角来看,这个金字塔显得过于简单了,并且可能造成误导。比如service test不太能定义清楚。比如在react, angular, ember.js等单页应用中,UI测试并不一定在最顶层,而是可以写单元测试来测试UI。
但它有2点启示:
-
编写不同粒度的测试
-
层次越高,测试投入越少
实践使用的工具和库
-
JUnit:单元测试
-
Mockito:mock依赖
-
Wiremock:stub外部服务
-
Pact:编写CDC测试
-
Selenium:编写UI自动化
-
REST-assured:编写REST接口自动化
一个简单的应用
作者在GitHub上传了开源项目(795star):
https://github.com/hamvocke/spring-testing
包含了遵循测试金字塔的分层测试的SpringBoot微服务应用。
功能
它提供了3个接口:
GET /hello 返回”Hello World“
GET /hello/{lastname} 返回"Hello {Firstname} {Lastname}"
GET /weather 返回德国柏林的天气(作者住在这)
整体结构
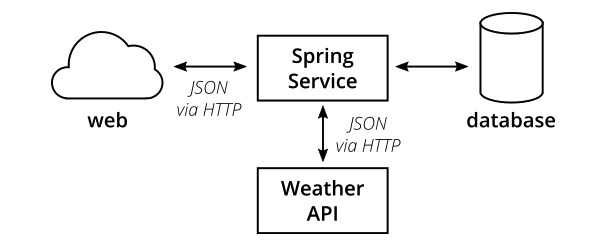
Spring Service从数据库取数据,对外提供API返回JSON数据,非常标准的简单应用。
内部结构
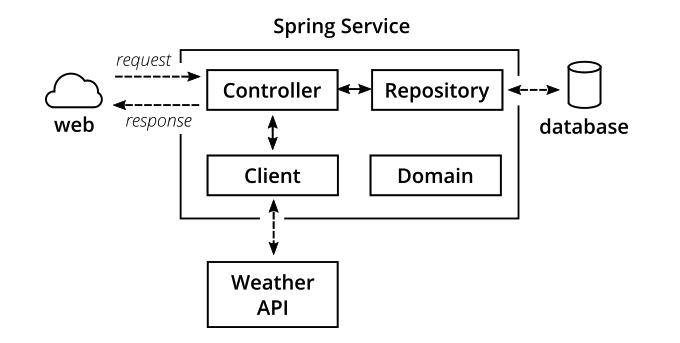
-
Controller提供REST接口,并处理HTTP请求和响应;
-
Repository跟数据库交互,负责持久化存储的数据读写;
-
Client访问外部API,比如这里访问了darksky.net的Weather API获取天气;
-
Domain定义领域模型,比如请求响应的结构体,也叫做POJO;
该应用支持CRUD,使用Spring Data访问数据库,数据库用的也是内存数据库,并且设计上省略掉了Service层,一切都为了简单,方便测试。
单元测试
什么是单元?
不同人对单元有不同理解,所谓单元,通常指某个函数,单元测试就是使用不同参数来调用函数,验证是否满足预期结果。在面向对象语言中,单元,可以是单个方法,也可以是整个类。
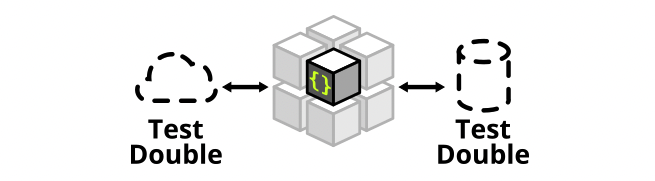
Mock和Stub
Test Double是“测试复制品“的意思,用来统称模拟真实对象的假对象:
Mock和Stub都是用来模拟的,它们的区别在于:
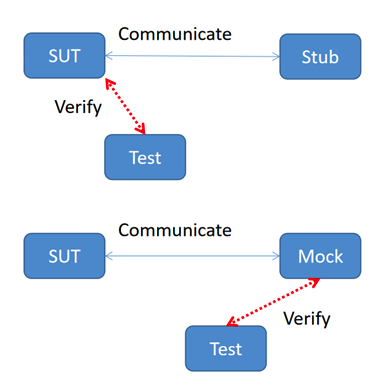
Stub只负责模拟,Mock还包括了验证。
以上是晦涩难懂且无关紧要的理论概念。实际点的,拿本文用到的Mockito和WireMock来说,Mockito用于单元测试mock依赖,WireMock用于集成测试stub外部服务,本质上都是模拟。
测什么
单元测试什么都能测,这就是单元测试的好处。
编写单元测试要遵循原则:一个production class对应一个test class。public要尽可能覆盖,private无法覆盖,protected或者package-private可覆盖可不覆盖,建议别覆盖。并且要保证分支覆盖,包括正常分支和边界场景。
但是并不是所有的public都需要编写单元测试,而是要避免琐碎的测试,比如getters或setters就不要测了,比如一些没有任何逻辑条件的也不需要测。
测试结构
-
初始化测试数据;
-
调用测试方法;
-
断言预期结果;
这是所有测试的良好结构设计,不只是单元测试。这三步还有其他叫法:"Arrange, Act, Assert",或者"given", "when", "then"。
实现单元测试
对于以下ExampleController:
@RestController
public class ExampleController {
private final PersonRepository personRepo;
@Autowired
public ExampleController(final PersonRepository personRepo) {
this.personRepo = personRepo;
}
@GetMapping("/hello/{lastName}")
public String hello(@PathVariable final String lastName) {
Optional<Person> foundPerson = personRepo.findByLastName(lastName);
return foundPerson
.map(person -> String.format("Hello %s %s!",
person.getFirstName(),
person.getLastName()))
.orElse(String.format("Who is this '%s' you're talking about?",
lastName));
}
}
编写单元测试:
public class ExampleControllerTest {
private ExampleController subject;
@Mock
private PersonRepository personRepo;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
initMocks(this);
subject = new ExampleController(personRepo);
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnFullNameOfAPerson() throws Exception {
Person peter = new Person("Peter", "Pan");
// Mockito模拟输入输出
given(personRepo.findByLastName("Pan"))
.willReturn(Optional.of(peter));
String greeting = subject.hello("Pan");
assertThat(greeting, is("Hello Peter Pan!"));
}
@Test
public void shouldTellIfPersonIsUnknown() throws Exception {
// Mockito模拟输入输出
given(personRepo.findByLastName(anyString()))
.willReturn(Optional.empty());
String greeting = subject.hello("Pan");
assertThat(greeting, is("Who is this 'Pan' you're talking about?"));
}
}
单元测试使用了JUnit,PersonRepository使用了Mockito模拟数据。第一个测试是验证入参存在的名字会返回Hello。第二个测试是验证入参不存在的名字会返回Who。
集成测试
单元测试是模块内测试,针对模块之间,就要做集成测试。还有其他部分,比如数据库、文件系统、远程调用其他应用等,这些在单元测试中会忽略或者mock掉,也都需要做集成测试。集成测试也有多种理解,可以理解为全部集成的测试。而作者的想法是单独集成,一次只集成一个,比如集成测试数据库,那么其他部分仍然使用mock:

-
启动数据库;
-
应用连接数据库;
-
调用方法往数据库写数据;
-
从数据库读数据,验证数据是刚才写入的;
比如集成测试其他服务:
-
启动应用;
-
启动其他服务的实例(或者模拟服务);
-
调用方法从其他服务的接口读数据;
-
验证当前应用能正确解析响应结果;
实现数据库集成
PersonRepository:
public interface PersonRepository extends CrudRepository<Person, String> {
Optional<Person> findByLastName(String lastName);
}
PersonRepository继承了CrudRepository,借助于Spring Data自动实现了增删改查,比如findOne, findAll, save, update, delete等方法,对于findByLastName方法,Spring Data也会根据返回类型、方法名称自动判断进行适配处理。
示例,保存Person到数据库中,并根据lastName查询:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@DataJpaTest
public class PersonRepositoryIntegrationTest {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository subject;
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
// 清理测试数据
subject.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void shouldSaveAndFetchPerson() throws Exception {
Person peter = new Person("Peter", "Pan");
subject.save(peter);
Optional<Person> maybePeter = subject.findByLastName("Pan");
assertThat(maybePeter, is(Optional.of(peter)));
}
}
实现独立服务集成
使用Wiremock模拟darksky.net服务:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class WeatherClientIntegrationTest {
@Autowired
private WeatherClient subject;
@Rule
public WireMockRule wireMockRule = new WireMockRule(8089);
@Test
public void shouldCallWeatherService() throws Exception {
wireMockRule.stubFor(get(urlPathEqualTo("/some-test-api-key/53.5511,9.9937"))
.willReturn(aResponse()
.withBody(FileLoader.read("classpath:weatherApiResponse.json"))
.withHeader(CONTENT_TYPE, MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)
.withStatus(200)));
Optional<WeatherResponse> weatherResponse = subject.fetchWeather();
Optional<WeatherResponse> expectedResponse = Optional.of(new WeatherResponse("Rain"));
assertThat(weatherResponse, is(expectedResponse));
}
}
怎么才能访问mock的这个服务呢?答案是在application.properties文件中配置:
weather.url = http://localhost:8089
以及WeatherClient实现:
@Autowired
public WeatherClient(final RestTemplate restTemplate,
@Value("${weather.url}") final String weatherServiceUrl,
@Value("${weather.api_key}") final String weatherServiceApiKey) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
this.weatherServiceUrl = weatherServiceUrl;
this.weatherServiceApiKey = weatherServiceApiKey;
}
在集成测试darksky.net服务时,采用的是Wiremock,mock了darksky.net服务,如何验证mock的服务和真实的服务之间有无差异呢,就要进行契约测试。
契约测试
在微服务架构体系中,应用被拆分成了多个独立的松耦合的服务,彼此之间通过接口通信:
-
HTTPS
-
RPC
-
消息队列
每个接口包含2部分:provider和consumer:

比如在HTTPS中,provider提供接口,consumer调用接口;比如在消息队列中,provider发布消息,consumer订阅消息。
所谓契约,就是接口之间相互约定好的定义。传统的契约过程是这样的:
-
编写详尽的接口定义(契约);
-
根据契约实现provider;
-
把契约同步给consumer;
-
consumer根据契约实现;
-
运行起来手动验证契约是否达成一致;
-
希望双方都不要随意变更契约;
而在CDC(Consumer-Driven Contract tests)中,第5、6步已经被自动化测试取代:
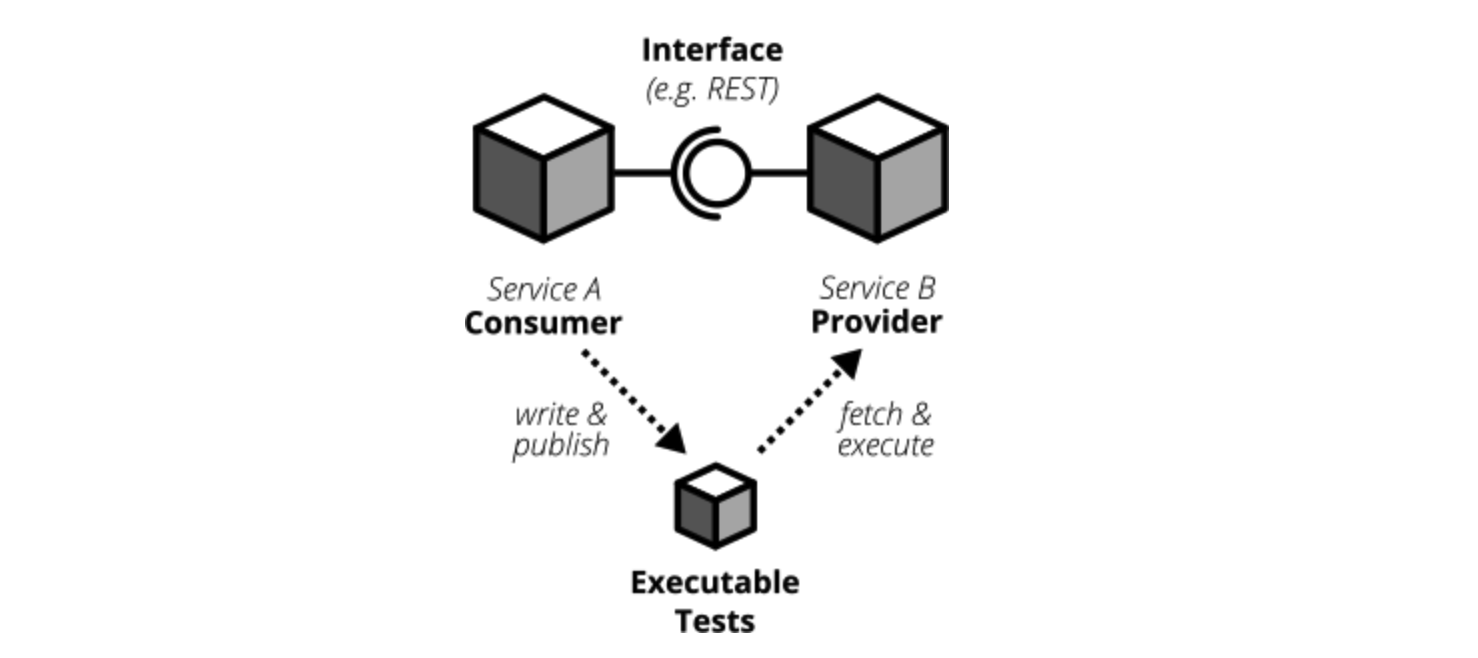
consumer编写并发布契约测试,provider获取并执行契约测试,当provider把所有契约测试都实现以后,自然就满足consumer了。provider会把契约测试放入持续集成中,确保所有契约测试都能始终保持通过,假如consumer发布了新的契约,契约测试就会失败,从而提醒provider更新实现。
Consumer Test
使用Pact工具实现契约测试。
build.gradle:
testCompile('au.com.dius:pact-jvm-consumer-junit_2.11:3.5.5')
WeatherClientConsumerTest:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class WeatherClientConsumerTest {
@Autowired
private WeatherClient weatherClient;
@Rule
public PactProviderRuleMk2 weatherProvider =
new PactProviderRuleMk2("weather_provider", "localhost", 8089, this);
@Pact(consumer="test_consumer")
public RequestResponsePact createPact(PactDslWithProvider builder) throws IOException {
return builder
.given("weather forecast data")
.uponReceiving("a request for a weather request for Hamburg")
.path("/some-test-api-key/53.5511,9.9937")
.method("GET")
.willRespondWith()
.status(200)
.body(FileLoader.read("classpath:weatherApiResponse.json"),
ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.toPact();
}
@Test
@PactVerification("weather_provider")
public void shouldFetchWeatherInformation() throws Exception {
Optional<WeatherResponse> weatherResponse = weatherClient.fetchWeather();
assertThat(weatherResponse.isPresent(), is(true));
assertThat(weatherResponse.get().getSummary(), is("Rain"));
}
}
每次运行都会生成一个pact文件,target/pacts/&pact-name>.json,这个文件就可以拿给provider实现契约,通常做法是让provider在仓库中取最新版本文件。
Provider Test
provider加载pact文件并实现契约:
@RunWith(RestPactRunner.class)
@Provider("weather_provider") // same as the "provider_name" in our clientConsumerTest
@PactFolder("target/pacts") // tells pact where to load the pact files from
public class WeatherProviderTest {
@InjectMocks
private ForecastController forecastController = new ForecastController();
@Mock
private ForecastService forecastService;
@TestTarget
public final MockMvcTarget target = new MockMvcTarget();
@Before
public void before() {
initMocks(this);
target.setControllers(forecastController);
}
@State("weather forecast data") // same as the "given()" in our clientConsumerTest
public void weatherForecastData() {
when(forecastService.fetchForecastFor(any(String.class), any(String.class)))
.thenReturn(weatherForecast("Rain"));
}
}
UI测试
UI测试主要验证应用界面是否正确:

用户输入,触发程序,数据展示给用户,状态变更正确。
UI自动化主要基于Selenium来做,由于前端变化大、控件识别难等问题,导致UI自动化失败率比较高,可以考虑采用截图的方式,把前后截图进行对比,来做断言,当然Selenium已经支持截图对比了。
端到端测试
端到端测试,通常是指从用户界面进行测试:

如果没有用户界面,也可以指对接口进行测试。
UI端到端测试
使用Selenium和WebDriver实现:
build.gradle
testCompile('org.seleniumhq.selenium:selenium-chrome-driver:2.53.1')
testCompile('io.github.bonigarcia:webdrivermanager:1.7.2')
HelloE2ESeleniumTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class HelloE2ESeleniumTest {
private WebDriver driver;
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@BeforeClass
public static void setUpClass() throws Exception {
ChromeDriverManager.getInstance().setup();
}
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
driver = new ChromeDriver();
}
@After
public void tearDown() {
driver.close();
}
@Test
public void helloPageHasTextHelloWorld() {
driver.get(String.format("http://127.0.0.1:%s/hello", port));
assertThat(driver.findElement(By.tagName("body")).getText(), containsString("Hello World!"));
}
}
接口端到端测试
使用REST-assured实现:
build.gradle
testCompile('io.rest-assured:rest-assured:3.0.3')
HelloE2ERestTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class HelloE2ERestTest {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepository;
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
personRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void shouldReturnGreeting() throws Exception {
Person peter = new Person("Peter", "Pan");
personRepository.save(peter);
when()
.get(String.format("http://localhost:%s/hello/Pan", port))
.then()
.statusCode(is(200))
.body(containsString("Hello Peter Pan!"));
}
}
验收测试
在测试金字塔的位置越高,就越会站在用户角度进行测试。验收测试就是完全从用户角度出发,看系统是否能满足用户需求。
简单示例:
def test_add_to_basket():
# given
user = a_user_with_empty_basket()
user.login()
bicycle = article(name="bicycle", price=100)
# when
article_page.add_to_.basket(bicycle)
# then
assert user.basket.contains(bicycle)
探索测试
探索测试是一种手工测试方法,充分发挥了测试人员的自由和创造力。
探索测试发现缺陷以后,可以补充到自动化测试中,以避免将来出现这个问题。
不要执着于测试术语
单元测试、集成测试、端到端测试、验收测试,每个人都有自己的不同理解,现在的软件测试行业,也没有统一的测试术语,将这些测试类型的边界明确区分开来。只要我们在公司内部、团队内部,能对术语达成一致,顺畅沟通就可以了。
参考资料:
Thoughtworks研发博客 https://martinfowler.com/articles/practical-test-pyramid.html
Test Double http://xunitpatterns.com/Test Double.html
WireMock和Mockito区别 https://geek-docs.com/mockito/mockito-ask-answer/wiremock-vs-mockito.html
Pact官方文档 https://docs.pact.io/
所有文章公众号【测试开发刚哥】首发!
版权申明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请保留原文链接及作者。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号