Python技术栈性能测试工具Locust入门
Locust是一款Python技术栈的开源的性能测试工具。Locust直译为蝗虫,寓意着它能产生蝗虫般成千上万的并发用户:

Locust并不小众,从它Github的Star数量就可见一斑:
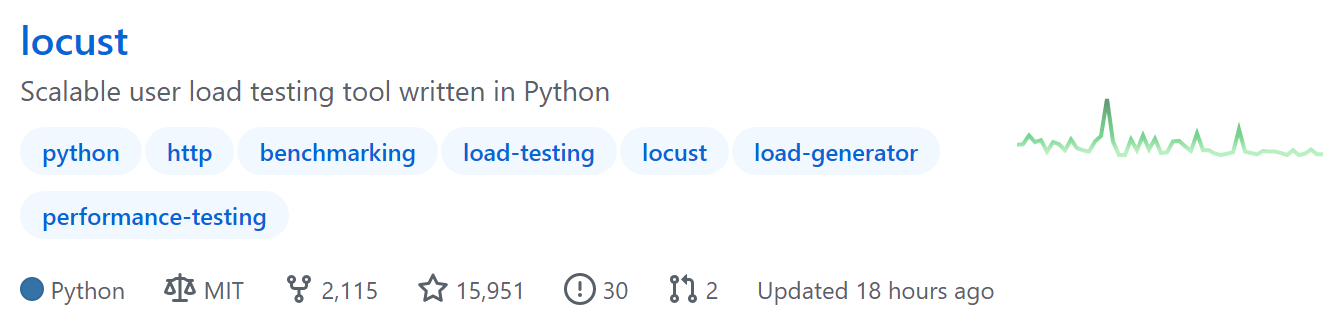
截止文章写作时,一共15951Star。
Locust生态良好,它已在多家外企(包括世界500强)投入使用:

如此看来,Locust是非常值得学习和掌握的一款工具。
Python的魔力在于化繁为简,基于Python的Locust也能给仍然困惑于性能测试的我们带来启发。
Locust特点
- 以纯Python方式编写用户脚本,提供极大自由度。
- 用户脚本可以串行方式编写,Locust会通过轻量级进程/协程产生并发,无需自己做并发编程。
- 并发量大,借助于gevent库,Locust能产生成千上万并发请求。
- 开销小,Locust用户运行时开销很小。
- 良好的Web UI对性能结果实时监测。
- 能测任何系统任何协议,只需要写个client即可。
- 开放REST API,尽情发挥。
安装Locust
需要Python版本3.6及以上。
执行pip命令:
$ pip install locust
验证安装成功:
$ locust -V
安装时会一并安装依赖库:
Installing collected packages: Werkzeug, pywin32, zope.event, greenlet, gevent, geventhttpclient, itsdangerous, flask, Flask-BasicAuth, ConfigArgParse, pyzmq, psutil, locust
能看出来flask为Locust提供了Web功能。
快速上手
使用Locust一般按照以下步骤进行:
- 编写Python用户脚本。
- 使用
locust命令执行性能测试。 - (可选)通过Web界面监测结果。
示例代码如下,新建locustfile.py文件:
import time
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
class QuickstartUser(HttpUser):
wait_time = between(1, 2.5)
@task
def hello_world(self):
self.client.get("/hello")
self.client.get("/world")
@task(3)
def view_items(self):
for item_id in range(10):
self.client.get(f"/item?id={item_id}", name="/item")
time.sleep(1)
def on_start(self):
self.client.post("/login", json={"username":"foo", "password":"bar"})
路径切换到locustfile.py文件所在目录,执行命令:
$ locust
也可以通过
-f指定某个目录文件:$ locust -f locust_files/my_locust_file.py
运行后,打开http://127.0.0.1:8089看到Web界面:
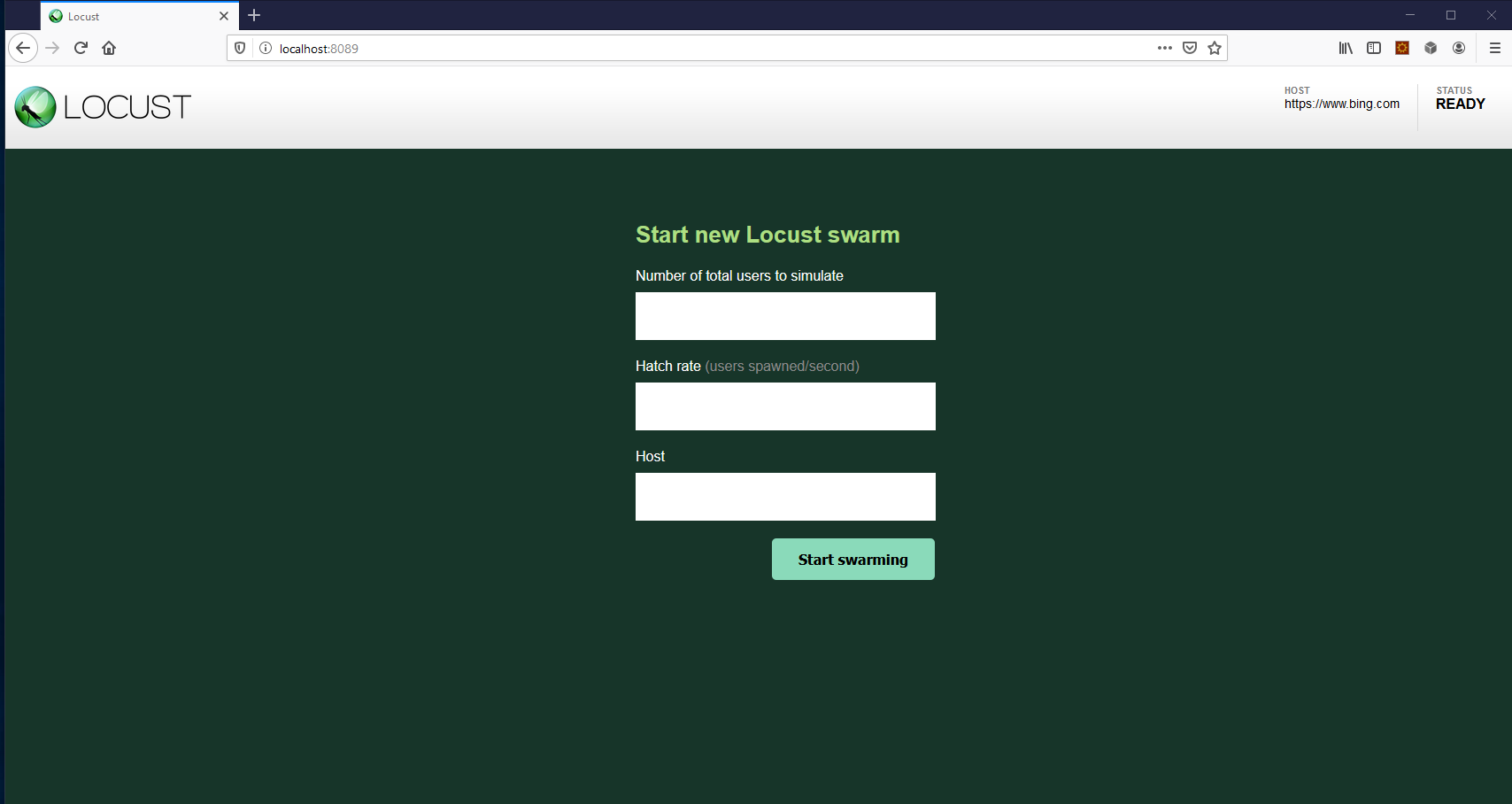
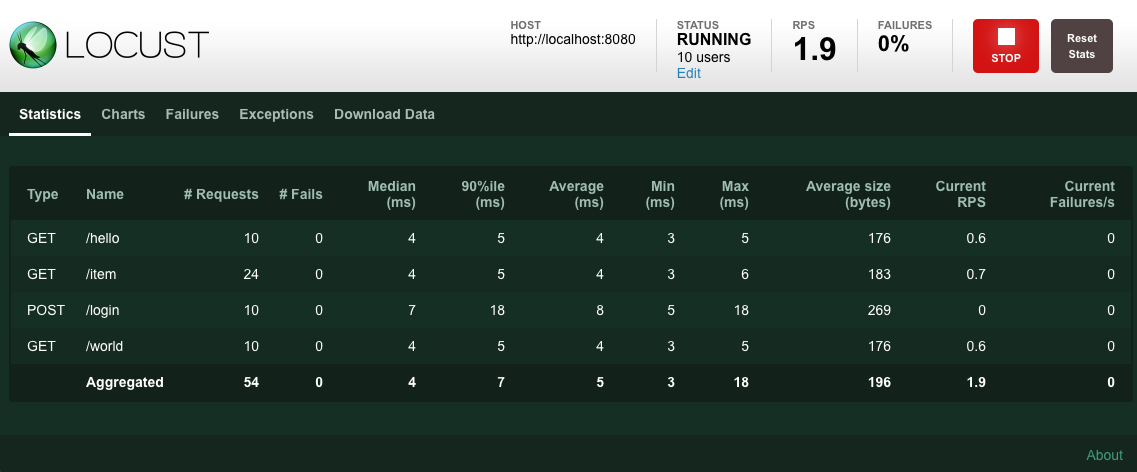
填写信息后,就能开始压测了。Web界面提供了结果统计数据:
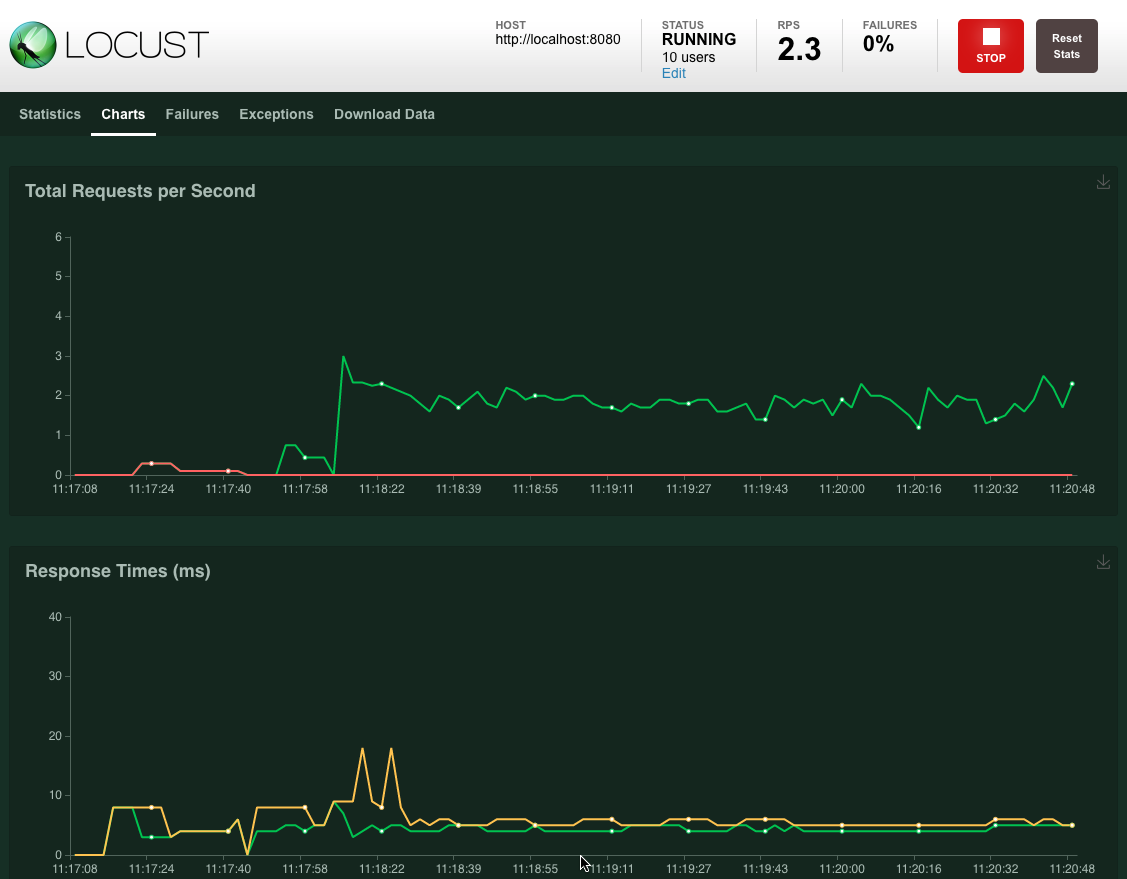
和性能指标走势图:
脚本解析
示例脚本解析如下:
# Locust用户脚本就是Python模块
import time
from locust import HttpUser, task, between
# 类继承自HttpUser
class QuickstartUser(HttpUser):
# 每个模拟用户等待1~2.5秒
wait_time = between(1, 2.5)
# 被@task装饰的才会并发执行
@task
def hello_world(self):
# client属性是HttpSession实例,用来发送HTTP请求
self.client.get("/hello")
self.client.get("/world")
# 每个类只会有一个task被选中执行
# 3代表weight权重
# 权重越大越容易被选中执行
# view_items比hello_wolrd多3倍概率被选中执行
@task(3)
def view_items(self):
for item_id in range(10):
# name参数作用是把统计结果按同一名称进行分组
# 这里防止URL参数不同会产生10个不同记录不便于观察
# 把10个汇总成1个"/item"记录
self.client.get(f"/item?id={item_id}", name="/item")
time.sleep(1)
# 每个模拟用户开始运行时都会执行
def on_start(self):
self.client.post("/login", json={"username":"foo", "password":"bar"})
小结
本文先了解了Locust的背景和生态,它是值得学习的,对于Python技术栈来说更加如此。接着介绍了使用pip命令安装Locust,其中发现顺带安装了flask,Locust的Web功能是flask提供的。然后给出了一段示例代码,按照步骤上手Locust。最后对示例代码进行了解析,浅尝辄止。locustfile实际上该怎么写呢?
参考资料:
所有文章公众号【测试开发刚哥】首发!
版权申明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请保留原文链接及作者。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号