【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(二)
前言:在【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(一)文末中已经提出loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory)的重要性,本文将以此为切入点继续分析。
AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory)
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory. 3 // 创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象 4 XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory); 5 6 // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's 7 // resource loading environment. 8 // 对XmlBeanDefinitionReader进行环境变量的设置 9 beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment()); 10 beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this); 11 beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this)); 12 13 // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader, 14 // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. 15 // 对XmlBeanDefinitionReader进行设置,可以进行覆盖 16 initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader); 17 // 从Resource中加载BeanDefinition 18 loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader); 19 }
分析:
- 首先创建一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象,因为我们需要解析xml文件,然后将其封装成BeanDefinition。
- 设置XmlBeanDefinitionReader对象的相关属性,这里着重关注ResourceLoader,这里引申出Resource/ResourceLoader体系。
- 从Resource中加载BeanDefinition。
Resource体系
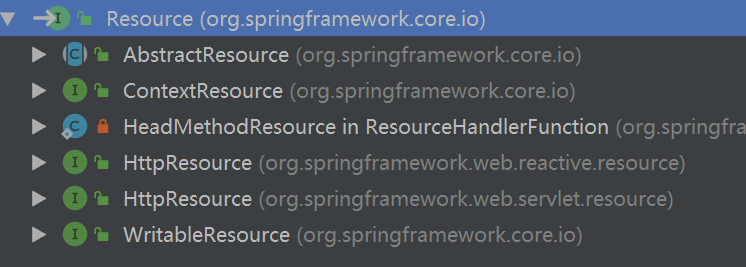
Resource继承InputStreamSource,为spring框架所有资源的访问提供抽象接口,子类AbstractResource提供Resource接口的默认实现。
ResourceLoader体系
ResourceLoader为spring资源加载的统一抽象,主要应用于根据给定的资源文件地址返回相应的Resource对象,其具体的实现由相应子类去负责。
这里列出笔者认为的几个比较重要ResourceLoader的实现类。

- DefaultResourceLoader是ResourceLoader的默认实现
- PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver,该类比较常用,除了支持"classpath*:"格式,还支持Ant风格的路径匹配模式
接下来进入AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions方法
1 protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException { 2 // 从配置文件Resource中,加载BeanDefinition 3 Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources(); 4 if (configResources != null) { 5 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources); 6 } 7 // 从配置文件地址中,加载BeanDefinition 8 String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations(); 9 if (configLocations != null) { 10 reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations); 11 } 12 }
分析:
看到这里是否很熟悉因为我们在【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(一)中已经设置了资源文件的路径(setConfigLocations)方法,因此这里会直接走到第9行处,然后调用AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions方法:
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null"); 3 int count = 0; 4 for (String location : locations) { 5 count += loadBeanDefinitions(location); 6 } 7 return count; 8 }
分析:
这里会遍历locations,并返回最终加载bean的个数,函数最终切入点:AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources):
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 // 获取ResourceLoader对象 3 ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader(); 4 // 资源加载器为null,抛出异常 5 if (resourceLoader == null) { 6 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 7 "Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available"); 8 } 9 10 // 如果当前ResourceLoader为匹配模式形式的[支持一个location返回Resource[]数组形式] 11 if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) { 12 // Resource pattern matching available. 13 try { 14 // 通过location返回Resource[]数组,通过匹配模式形式,可能存在多个Resource 15 Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location); 16 // 加载BeanDefinition,返回BeanDefinition加载的个数 17 int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources); 18 // 将Resource[] 添加到actualResources中 19 if (actualResources != null) { 20 Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources); 21 } 22 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 23 logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]"); 24 } 25 // 返回BeanDefinition加载的个数 26 return count; 27 } catch (IOException ex) { 28 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 29 "Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex); 30 } 31 // ResourceLoader为默认资源加载器,一个location返回一个Resource 32 } else { 33 // Can only load single resources by absolute URL. 34 Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location); 35 // 加载BeanDefinition,并返回加载BeanDefinition的个数 36 int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 37 // 将Resource添加到actualResources中 38 if (actualResources != null) { 39 actualResources.add(resource); 40 } 41 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 42 logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]"); 43 } 44 // 返回BeanDefinition加载的个数 45 return count; 46 } 47 }
分析:
- 首先获取ResourceLoader,ResourceLoader的赋值在创建XmlBeanDefinitionReader的过程中,如果未指定则会创建一个PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver对象。
- 然后根据对应的ResourceLoader返回的Resource对象。
关注第15行代码,getResources(String)方法,这里会直接委托给PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#getResources(String)进行处理:
1 public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { 2 Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null"); 3 4 // 以"classpath*:"开头的location 5 if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) { 6 // a class path resource (multiple resources for same name possible) 7 8 // #1.isPattern函数的入参为路径 9 // #2.所以这里判断路径是否包含通配符 如com.develop.resource.* 10 if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) { 11 // a class path resource pattern 12 // 这里通过通配符返回Resource[] 13 return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern); 14 // 路径不包含通配符 15 } else { 16 // all class path resources with the given name 17 // 通过给定的路径,找到所有匹配的资源 18 return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length())); 19 } 20 // 不以"classpath*:" 21 } else { 22 // Generally only look for a pattern after a prefix here, 23 // and on Tomcat only after the "*/" separator for its "war:" protocol. 24 // 通常在这里只是通过前缀后面进行查找,并且在tomcat中只有在"*/"分隔符之后才是其"war:"协议 25 // #1.如果是以"war:"开头,定位其前缀位置 26 // #2.如果不是以"war:"开头,则prefixEnd=0 27 int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 : 28 locationPattern.indexOf(':') + 1); 29 // 判断路径中是否含有通配符否含有通配符 30 if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) { 31 // a file pattern 32 // 通过通配符返回返回Resource[] 33 return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern); 34 // 路径不包含通配符 35 } else { 36 // a single resource with the given name 37 // 通过给定的location返回一个Resource,封装成数组形式 38 // 获取Resource的过程都是通过委托给相应的ResourceLoader实现 39 return new Resource[]{getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)}; 40 } 41 } 42 }
分析:
首先两大分支:根据资源路径是否包含"classpath*:"进行处理。
#1."classpath*:"分支:
- 首先判断路径中是否含有通配符"*"或"?",然后执行findPathMatchingResources函数。
- 如果不包含通配符,则根据路径找到所有匹配的资源,执行findAllClassPathResources函数。
#2.路径中不含"classpath*:"分支,与上述过程一样,同样按分支含有通配符与不含通配符进行处理。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#findPathMatchingResources(String)
1 protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException { 2 // 确定根路径与子路径 3 String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern); 4 String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length()); 5 // 得到根路径下的资源 6 Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath); 7 Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16); 8 // 遍历获取资源 9 for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) { 10 // 解析根路径资源 11 rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource); 12 URL rootDirUrl = rootDirResource.getURL(); 13 // bundle类型资源 14 if (equinoxResolveMethod != null && rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) { 15 URL resolvedUrl = (URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null, rootDirUrl); 16 if (resolvedUrl != null) { 17 rootDirUrl = resolvedUrl; 18 } 19 rootDirResource = new UrlResource(rootDirUrl); 20 } 21 // vfs类型资源 22 if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) { 23 result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirUrl, subPattern, getPathMatcher())); 24 // jar类型资源 25 } else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) { 26 result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirUrl, subPattern)); 27 // 其他类型资源 28 } else { 29 result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern)); 30 } 31 } 32 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 33 logger.debug("Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result); 34 } 35 // 将结果封装成数组形式 注意该转换形式 36 return result.toArray(new Resource[0]); 37 }
分析:
函数的整体处理逻辑比较简单,根据不同的资源类型,将资源最终转换为Resource数组。
特别分析:
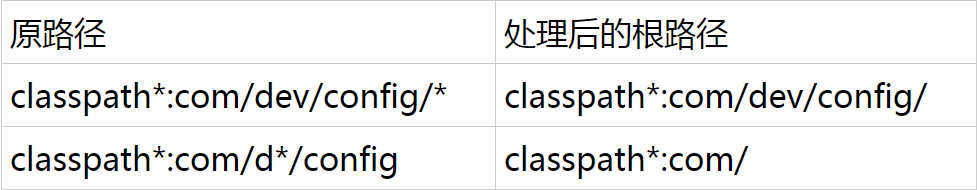
determineRootDir(String)
1 protected String determineRootDir(String location) { 2 // 确定":"的后一位,如果":"不存在,则prefixEnd=0 3 int prefixEnd = location.indexOf(':') + 1; 4 // location的长度 5 int rootDirEnd = location.length(); 6 // 从location的":"开始(可能不存在)一直到location结束,判断是否包含通配符,如果存在,则截取最后一个"/"分割的部分 7 /** 8 * 截取过程: 9 * classpath*:com/dev/config/* 10 * prefixEnd=11 11 * subString(prefixEnd,rootDirEnd)=com/dev/config/* 12 * 第一次循环rootDirEnd=26,也就是最后一个"/" 13 * subString(prefixEnd,rootDirEnd)=com/dev/config/ 14 * 第二次循环已经不包含通配符了,跳出循环 15 * 所以根路径为classpath*:com/dev/config/ 16 */ 17 while (rootDirEnd > prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) { 18 // 确定最后一个"/"位置的后一位,注意这里rootDirEnd-2是为了缩小搜索范围,提升速度 19 rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/', rootDirEnd - 2) + 1; 20 } 21 // 如果查找完后rootDirEnd=0,则将prefixEnd赋值给rootDirEnd,也就是冒号的后一位 22 if (rootDirEnd == 0) { 23 rootDirEnd = prefixEnd; 24 } 25 // 截取根目录 26 return location.substring(0, rootDirEnd); 27 }
分析:
该函数有点绕,整体思想就是决定出给定资源路径的根路径,代码中已经给出了详细注释,处理效果如下实例:
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#findAllClassPathResources(String)
1 protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException { 2 String path = location; 3 // location是否已"/"开头 4 if (path.startsWith("/")) { 5 path = path.substring(1); 6 } 7 // 真正加载location下所有classpath下的资源 8 Set<Resource> result = doFindAllClassPathResources(path); 9 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 10 logger.debug("Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result); 11 } 12 return result.toArray(new Resource[0]); 13 }
分析:
该函数会查找路径下的所有资源,核心函数doFindAllClassPathResources(String):
1 protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException { 2 Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<>(16); 3 ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader(); 4 // 根据ClassLoader来加载资源 5 // 如果PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver在初始化时,设置了ClassLoader,就用该ClassLoader的getResouce方法 6 // 否则调用ClassLoader的getSystemResource方法 7 Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path)); 8 // 遍历集合将集合转换成UrlResource形式 9 // 如果path为空,这里就会返回项目中classes的路径,通过addAllClassLoaderJarRoots方法进行加载 10 while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) { 11 URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement(); 12 result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url)); 13 } 14 // 如果path为空,则加载路径下的所有jar 15 if ("".equals(path)) { 16 // The above result is likely to be incomplete, i.e. only containing file system references. 17 // We need to have pointers to each of the jar files on the classpath as well... 18 // 加载所有jar 19 addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result); 20 } 21 return result; 22 }
分析:该函数的主要功能就是将搜索配置文件路径下的所有资源,然后封装成Resource集合返回,供加载BeanDefinition使用。
不含"classpath*:"分支的逻辑与上述分析差不多,这里不再做过多赘述。
Resource资源准备就绪后,再次回到loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources)函数中,在第17行代码处进入正式加载BeanDefinition过程。
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources)
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource... resources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(resources, "Resource array must not be null"); 3 int count = 0; 4 // 通过循环的形式单个加载BeanDefinition 5 for (Resource resource : resources) { 6 count += loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 7 } 8 return count; 9 }
在循环过程中会落入XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource)
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 // 这里会将Resource封装成EncodeResource,主要主要为了内容读取的正确性 3 return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource)); 4 }
该函数将Resource封装成EncodeResource,主要是为了内容读取的正确性,然后进入加载BeanDefinition的核心函数XmlBeanDefinitionReader#loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource)
1 public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 2 Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null"); 3 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 4 logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource()); 5 } 6 7 // 获取已经加载过的资源 8 Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get(); 9 // 表示当前没有资源加载 10 if (currentResources == null) { 11 currentResources = new HashSet<>(4); 12 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources); 13 } 14 // 将当前资源加入记录中,如果已经存在,则抛出异常,因为currentResource为Set集合 15 // 这里主要为了避免一个EncodeResource还没加载完成时,又加载本身,造成死循环(Detected cyclic loading of) 16 if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) { 17 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 18 "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!"); 19 } 20 try { 21 // 从封装的encodeResource中获取resource,并取得其输入流,通过流对资源进行操作 22 InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream(); 23 try { 24 // 将流封装成InputSource 25 InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream); 26 // 设置InputSource的编码 27 if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) { 28 inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding()); 29 } 30 // 核心逻辑,实现BeanDefinition的加载 31 return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource()); 32 } finally { 33 inputStream.close(); 34 } 35 } catch (IOException ex) { 36 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 37 "IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex); 38 } finally { 39 // 最后从缓存中清除资源 40 currentResources.remove(encodedResource); 41 // 如果当前资源集合为空,则从EncodeResource集合中移除当前资源的集合 42 if (currentResources.isEmpty()) { 43 this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove(); 44 } 45 } 46 }
分析:
- 首先判断缓存中是否已经存在当前资源,如果存在则抛出异常,这里是为了避免循环加载。
- 然后取出文件流封装成InputSource,进入加载BeanDefinition的核心函数doLoadBeanDefinitions。
1 protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) 2 throws BeanDefinitionStoreException { 3 try { 4 // #1.获取XML的Document实例 5 Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); 6 // #2.根据Document注册bean,并返回注册的bean的个数 7 return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); 8 } catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) { 9 throw ex; 10 } catch (SAXParseException ex) { 11 throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 12 "Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); 13 } catch (SAXException ex) { 14 throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 15 "XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex); 16 } catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) { 17 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 18 "Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex); 19 } catch (IOException ex) { 20 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 21 "IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); 22 } catch (Throwable ex) { 23 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(), 24 "Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex); 25 } 26 }
分析:
- 首先获取XML配置文件的Document实例。
- 根据Document注册Bean,并返回注册Bean的个数。
XmlBeanDefinitionReader#doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception { return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware()); }
分析:
这里是委派给DefaultDocumentLoader#loadDocument函数来实现。
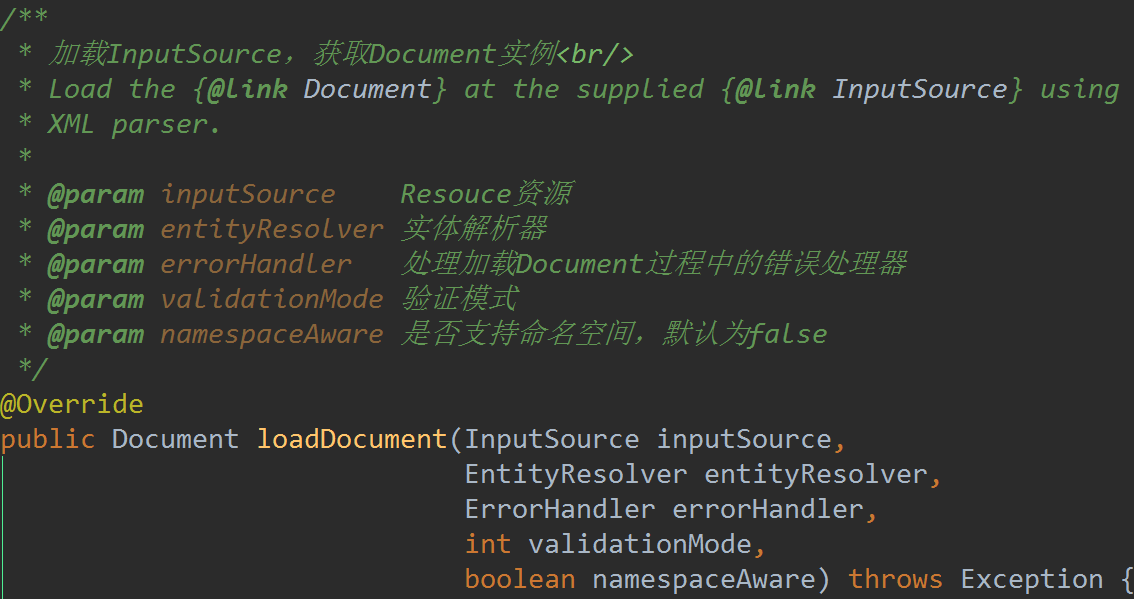
这里有一个验证模式的入参,从getValidationModeForResource函数而来:
1 protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) { 2 // 获取指定的验证模式,默认为自动模式 3 int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode(); 4 // #1.如果验证模式不为自动验证模式,则表示进行了设置,则直接返回验证模式即可 5 if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) { 6 return validationModeToUse; 7 } 8 // #2.到这里表示使用了自动验证模式,再次检测Resource使用的验证模式 9 int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource); 10 if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) { 11 return detectedMode; 12 } 13 // 最后使用默认的VALIDATION_XSD验证模式 14 // Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD, 15 // since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until 16 // detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag). 17 return VALIDATION_XSD; 18 }
分析:
- 首先获取当前的验证模式,默认为自动验证模式。
- 如果当前验证模式不为自动验证模式,则表示进行了设置,则直接返回当前验证模式即可。
- 如果使用了自动验证模式,则需再次检测Resource使用的验证模式
- 最后,如果还是自动验证模式,则返回XSD验证模式。
这里要科普一下DTD与XSD
DTD(Document Type Definition),即文档类型定义,为 XML 文件的验证机制,属于 XML 文件中组成的一部分。DTD 是一种保证 XML 文档格式正确的有效验证方式,它定义了相关 XML 文档的元素、属性、排列方式、元素的内容类型以及元素的层次结构。其实 DTD 就相当于 XML 中的 “词汇”和“语法”,我们可以通过比较 XML 文件和 DTD 文件 来看文档是否符合规范,元素和标签使用是否正确。
但是DTD存在着一些缺陷:
- 它没有使用 XML 格式,而是自己定义了一套格式,相对解析器的重用性较差;而且 DTD 的构建和访问没有标准的编程接口,因而解析器很难简单的解析 DTD 文档。
- DTD 对元素的类型限制较少;同时其他的约束力也叫弱。
- DTD 扩展能力较差。
- 基于正则表达式的 DTD 文档的描述能力有限。
针对 DTD 的缺陷,W3C 在 2001 年推出 XSD。XSD(XML Schemas Definition)即 XML Schema 语言。XML Schema 本身就是一个 XML文档,使用的是 XML 语法,因此可以很方便的解析 XSD 文档。相对于 DTD,XSD 具有如下优势:
- XML Schema 基于 XML ,没有专门的语法。
- XML Schema 可以象其他 XML 文件一样解析和处理。
- XML Schema 比 DTD 提供了更丰富的数据类型。
- XML Schema 提供可扩充的数据模型。
- XML Schema 支持综合命名空间。
- XML Schema 支持属性组。
spring中定义了一些验证模式:
/** * Indicates that the validation should be disabled. 禁用验证模式 */ public static final int VALIDATION_NONE = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE; /** * Indicates that the validation mode should be detected automatically. 自动获取验证模式 */ public static final int VALIDATION_AUTO = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_AUTO; /** * Indicates that DTD validation should be used. DTD验证模式 */ public static final int VALIDATION_DTD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_DTD; /** * Indicates that XSD validation should be used. XSD验证模式 */ public static final int VALIDATION_XSD = XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD;
XmlBeanDefinitionReader#detectValidationMode(Resource resource)函数是检测资源文件的验证模式的:
1 protected int detectValidationMode(Resource resource) { 2 // 如果资源已经被打开,则直接抛出异常 3 if (resource.isOpen()) { 4 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 5 "Passed-in Resource [" + resource + "] contains an open stream: " + 6 "cannot determine validation mode automatically. Either pass in a Resource " + 7 "that is able to create fresh streams, or explicitly specify the validationMode " + 8 "on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance."); 9 } 10 11 // 打开InputStream流 12 InputStream inputStream; 13 try { 14 inputStream = resource.getInputStream(); 15 } catch (IOException ex) { 16 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( 17 "Unable to determine validation mode for [" + resource + "]: cannot open InputStream. " + 18 "Did you attempt to load directly from a SAX InputSource without specifying the " + 19 "validationMode on your XmlBeanDefinitionReader instance?", ex); 20 } 21 22 try { 23 // 检测InputStream到底使用哪一种验证模式 24 // 核心逻辑 25 return this.validationModeDetector.detectValidationMode(inputStream); 26 } catch (IOException ex) { 27 throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Unable to determine validation mode for [" + 28 resource + "]: an error occurred whilst reading from the InputStream.", ex); 29 } 30 }
其核心功能:检测资源文件的验证模式是委托给XmlValidationModeDetector#detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream)
1 public int detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException { 2 // 将InputStream进行包装,便于读取 3 // Peek into the file to look for DOCTYPE. 4 BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream)); 5 try { 6 // 是否为DTD验证模式,默认为false,即不是DTD验证模式,那就是XSD验证模式 7 boolean isDtdValidated = false; 8 String content; 9 // 循环读取xml资源的内容 10 while ((content = reader.readLine()) != null) { 11 // 消费注释内容,返回有用信息 12 content = consumeCommentTokens(content); 13 // 如果为注释,或者为空,则继续循环 14 if (this.inComment || !StringUtils.hasText(content)) { 15 continue; 16 } 17 // #1.如果包含"DOCTYPE",则为DTD验证模式 18 if (hasDoctype(content)) { 19 isDtdValidated = true; 20 break; 21 } 22 // #2.该方法会校验,内容中是否有"<",并且"<"后面还跟着字母,如果是则返回true 23 // 如果为true,最终就是XSD模式 24 if (hasOpeningTag(content)) { 25 // End of meaningful data... 26 break; 27 } 28 } 29 // 返回DTD模式或XSD模式 30 return (isDtdValidated ? VALIDATION_DTD : VALIDATION_XSD); 31 } catch (CharConversionException ex) { 32 // Choked on some character encoding... 33 // Leave the decision up to the caller. 34 // 如果发生异常,则返回自动验证模式 35 return VALIDATION_AUTO; 36 } finally { 37 reader.close(); 38 } 39 }
分析:
这里会遍历资源的内容进行文件验证模式的判断
- consumeCommentTokens(String line)
1 /** 2 * 注释开始标志 <br/> 3 * The token that indicates the start of an XML comment. 4 */ 5 private static final String START_COMMENT = "<!--"; 6 7 /** 8 * 注释结束标志"-->" <br/> 9 * The token that indicates the end of an XML comment. 10 */ 11 private static final String END_COMMENT = "-->"; 12 13 private String consumeCommentTokens(String line) { 14 // 非注释,即为有用信息 15 if (!line.contains(START_COMMENT) && !line.contains(END_COMMENT)) { 16 return line; 17 } 18 String currLine = line; 19 // 消耗注释内容,使循环跳向下一行 20 while ((currLine = consume(currLine)) != null) { 21 // 当inComment标志位更新,并且返回信息不是以注释开始标志开始就返回currLine 22 if (!this.inComment && !currLine.trim().startsWith(START_COMMENT)) { 23 return currLine; 24 } 25 } 26 // 如果没有有用信息,则返回null 27 return null; 28 }
分析:
- 如果当前行不是注释,则直接返回。
- consume函数的主要作用是消耗注释内容,继续循环下一行的内容。
1 private String consume(String line) { 2 // 如果inComment:true,则走endComent函数;false,则走startComment函数,初始时为false 3 // 因此这里会走startComment,返回注释位置的index[注释位置+1的index] 4 int index = (this.inComment ? endComment(line) : startComment(line)); 5 // 如果index=-1,则表示没有注释信息,否则返回注释信息 6 return (index == -1 ? null : line.substring(index)); 7 } 8 9 private int startComment(String line) { 10 // 返回注释开始标志的位置信息 11 return commentToken(line, START_COMMENT, true); 12 } 13 14 private int endComment(String line) { 15 return commentToken(line, END_COMMENT, false); 16 } 17 18 private int commentToken(String line, String token, boolean inCommentIfPresent) { 19 // 查找注释标志的开始位置[<!--或-->] 20 int index = line.indexOf(token); 21 // index>-1表示存在注释开始标志,并将inComment更新为inCommentIfPresent 22 // [默认在startComment为true,endComment为false] 23 if (index > -1) { 24 this.inComment = inCommentIfPresent; 25 } 26 // 如果index=-1,则返回注释标志的后一个位置信息index+token.length() 27 return (index == -1 ? index : index + token.length()); 28 }
分析:
- consume函数意在消费注释信息,继续循环下一行的内容。
- inComment用来标记当前内容是否为注释,初始时为false,所以刚开始碰到一个注释语句,会执行startComment(line),将inComment置为true,然后返回"<!--"后面的内容,此时inComment为true,则会继续循环,此时会执行endComment(line),将inComment置为false,然后会返回"",在detectValidationMode函数中由于content="",此时会继续循环,从而跳过注释内容。
消费注释信息这里稍微有点绕,通过下面流程图可更好的理解:

文件验证模式代码分析完成,这里回到DefaultDocumentLoader#loadDocument:
1 public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, 2 EntityResolver entityResolver, 3 ErrorHandler errorHandler, 4 int validationMode, 5 boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception { 6 // 创建DocumentBuilderFactory 7 DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware); 8 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 9 logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]"); 10 } 11 // 创建DocumentBuilder对象 12 DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler); 13 // 通过DocumentBuilder解析InputSource,返回Document对象 14 // 解析xml文件的具体过程都是通过jdk内置的类进行解析的--DOMParser为其入口 15 return builder.parse(inputSource); 16 }
分析:
- 首先根据验证模式和是否支持命名空间创建DocumentBuilderFactory。
- 然后创建DocumentBuilder对象。
- 最后进行XML文件的解析,具体解析过程是利用jdk内置的DOMParser解析器进行解析。
DefaultDocumentLoader#createDocumentBuilderFactory:
1 protected DocumentBuilderFactory createDocumentBuilderFactory(int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) 2 throws ParserConfigurationException { 3 // 创建DocumentBuilderFactory实例 4 DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); 5 // 设置是否支持命名空间 6 factory.setNamespaceAware(namespaceAware); 7 // 是否有校验模式 8 if (validationMode != XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_NONE) { 9 // 开启校验模式 10 factory.setValidating(true); 11 // XSD模式下设置factory的属性 12 if (validationMode == XmlValidationModeDetector.VALIDATION_XSD) { 13 // Enforce namespace aware for XSD... 14 // 如果为XSD模式,强制开启命名空间支持 15 factory.setNamespaceAware(true); 16 try { 17 // 设置SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE属性为XSD 18 factory.setAttribute(SCHEMA_LANGUAGE_ATTRIBUTE, XSD_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE); 19 } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 20 ParserConfigurationException pcex = new ParserConfigurationException( 21 "Unable to validate using XSD: Your JAXP provider [" + factory + 22 "] does not support XML Schema. Are you running on Java 1.4 with Apache Crimson? " + 23 "Upgrade to Apache Xerces (or Java 1.5) for full XSD support."); 24 pcex.initCause(ex); 25 throw pcex; 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 30 return factory; 31 }
分析:这里逻辑就非常简单了,主要创建DocumentBuilderFactory对象,然后设置校验模式等相关属性。
DefaultDocumentLoader#createDocumentBuilder:
1 protected DocumentBuilder createDocumentBuilder(DocumentBuilderFactory factory, 2 @Nullable EntityResolver entityResolver, @Nullable ErrorHandler errorHandler) 3 throws ParserConfigurationException { 4 // 创建DocumentBuilder对象 5 DocumentBuilder docBuilder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); 6 // 设置实体解析器 7 if (entityResolver != null) { 8 docBuilder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver); 9 } 10 // 设置错误处理器 11 if (errorHandler != null) { 12 docBuilder.setErrorHandler(errorHandler); 13 } 14 return docBuilder; 15 }
分析:根据DocumentBuilderFactory工厂创建DocumentBuilder对象,并设置实体解析器与错误处理器。
XML文件的具体解析利用了jdk内置的DOMParser类进行,这里就不在深入了。
到这里就得到了XML配置文件的Document实例,介于篇幅原因,注册bean的过程将后面进行分析。
总结
这里总结下本文的重点:
- Resource体系与ResourceLoader体系,加载资源这里比较重要,因为有了资源才能进行后面的BeanDefinition加载。
- 检测配置文件是如何确定文件的验证模式,确定验证模式这里做的比较巧妙,着重如何消费注释信息继续下一次循环。
by Shawn Chen,2018.12.5日,下午。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号