第二次Blog
前言
- 知识点涉及很广泛,无论是PTA大作业四所使用到的正则表达式,还是凸四边形的计算中所涉及的数学问题程序算法化,还是用类来设计一个银行业务,还是期中考试用类来设计点与线与面,以及用继承与多态与容器的使用,我觉得这几次的作业与练习,都是较全面的。
- 题量:我觉得这几次的联系题量来说其实还好。
- 难度:难度分布合适,在PTA4作业的难度有难有易。合理的分布。
设计与分析
7-1 点与线(类设计)
题目
- 设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:`(x,y)`,数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为`(0,200]`。若输入有误,系统则直接输出`Wrong Format`
- 设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
其中,所有数值均保留两位小数,建议可用`String.format("%.2f", data)`方法。
代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
double x1=in.nextDouble(),x2=in.nextDouble();
double y1=in.nextDouble(),y2=in.nextDouble();
if(x1<=200&&x1>0&&x2<=200&&x2>0&&y1<=200&&y1>0&&y2<=200&&y2>0)
{
Point point1=new Point(x1,x2);
Point point2=new Point(y1,y2);
Line line=new Line(point1,point2,in.next());
line.display();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
class Point
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line
{
private String color;
private Point point1=new Point();
private Point point2=new Point();
public Line( Point point1, Point point2,String color) {
super();
this.color = color;
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Line() {
super();
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
void display()
{
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.color);
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point1.getX(),point1.getY());
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point2.getX(),point2.getY());
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f",getDistance());
}
double getDistance()
{
double distance=Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
return distance;
}
}
分析
- 按图分析:首先由题目给出的图,可以得到由2个类,Line和Point,并且把point1和point2和color,x,y都进行了封装,用了很多get/set函数安全化。
- 所有数值均保留两位小数时,我们不仅可以用格式化输出System.out.printf,还可以用JAVA字符串格式化String.format("%.2f", data)这种方法,可以参考!点这里
- 在判断变量x,y的输入合法性时,我用的x1<=200&&x1>0&&x2<=200&&x2>0&&y1<=200&&y1>0&&y2<=200&&y2>0这种方式,但是我觉得这里可以写一个static类型的方法,用于判断输入的x,y是否在(0,200]之间,这样可以使我们的代码显得更加的高效。
x1<=200&&x1>0&&x2<=200&&x2>0&&y1<=200&&y1>0&&y2<=200&&y2>0
- 这里的display方法中的输入点的位置,其实可以直使用点类的display方法来输出点的位置,我是直接System.out.printf()输出,这样的话display()就没有被调用,就造成了内存浪费。修改如下:
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point2.getX(),point2.getY());
改成
point1.display();
point2.display();
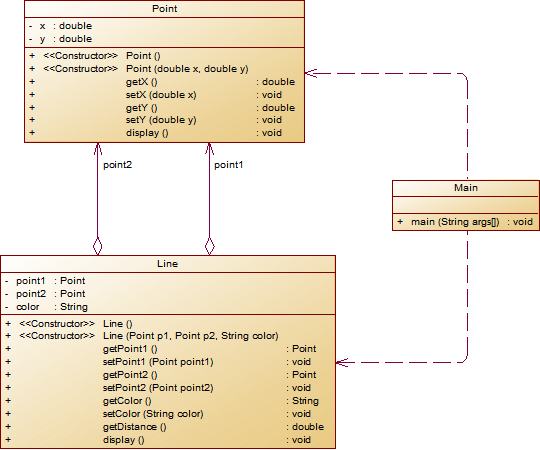
7-2 点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
double x1=in.nextDouble(),x2=in.nextDouble();
double y1=in.nextDouble(),y2=in.nextDouble();
if(x1<=200&&x1>0&&x2<=200&&x2>0&&y1<=200&&y1>0&&y2<=200&&y2>0)
{
String color=in.next();
Point point1=new Point(x1,x2);
Point point2=new Point(y1,y2);
Line line=new Line(point1,point2,color);
Plane plane=new Plane(color);
Element element;
element = point1;//起点Point
element.display();
element = point2;//终点Point
element.display();
element = line;//线段
element.display();
element = plane;//面
element.display();
}
else
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
class Point extends Element
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line extends Element
{
private String color;
private Point point1=new Point();
private Point point2=new Point();
public Line( Point point1, Point point2,String color) {
super();
this.color = color;
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Line() {
super();
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
@Override
void display()
{
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.color);
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point1.getX(),point1.getY());
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point2.getX(),point2.getY());
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f",getDistance());
}
double getDistance()
{
double distance=Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
return distance;
}
}
abstract class Element
{
abstract void display();
}
class Plane extends Element
{
private String color;
public Plane() {
}
public Plane(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
void display() {
System.out.println("\nThe Plane's color is:"+getColor());
}
}
分析
- 这一道题利用到了继承与多态重构。定义一个两个类的共同父类Element,并且为抽象类,把display()方法在该方法中进行声明,再进行@override重写处理
!类图 - 在Element被继承的Point类中,和在Element被继承的Line类中,我们都重写了display()方法
- 在抽象Element类中,我们这道题只需要对display()进行抽象就可以了,还是比较容易的
- 图:
 )
) - 在求2点的距离时,其实可以调用2次Math类的,就会不会显得代码臃肿。
double distance=Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)
代码
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
GeometryObject arr=new GeometryObject();
double x1,x2,y1,y2;
String color;
int choice;
Point point1;
Point point2;
Line line;
Plane plane;
Element element;
choice = in.nextInt();
while(choice!= 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1:
point1=new Point(in.nextDouble(),in.nextDouble());
element=point1;
arr.add(element);
break;
case 2:
x1=in.nextDouble();
y1=in.nextDouble();
x2=in.nextDouble();
y2=in.nextDouble();
color=in.next();
if(x1<=200&&x1>0&&x2<=200&&x2>0&&y1<=200&&y1>0&&y2<=200&&y2>0){
point1=new Point(x1,y1);
point2=new Point(x2,y2);
line=new Line(point1,point2,color);
element=line;
arr.add(element);
}
else
{
arr.add(null);
}
break;
case 3:
color=in.next();
plane=new Plane(color);
element=plane;
arr.add(element);
break;
case 4:
int index = in.nextInt();
arr.remove(index);
}
choice = in.nextInt();
}
arr.getList();
}
}
class Point extends Element
{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public void display()
{
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",this.x,this.y);
}
}
class Line extends Element
{
private String color;
private Point point1=new Point();
private Point point2=new Point();
public Line( Point point1, Point point2,String color) {
super();
this.color = color;
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Line() {
super();
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
@Override
void display()
{
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+this.color);
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point1.getX(),point1.getY());
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:");
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point2.getX(),point2.getY());
System.out.printf("The line's length is:%.2f",getDistance());
}
double getDistance()
{
double distance=Math.sqrt((point1.getX()-point2.getX())*(point1.getX()-point2.getX())+(point1.getY()-point2.getY())*(point1.getY()-point2.getY()));
return distance;
}
}
abstract class Element
{
abstract void display();
}
class Plane extends Element
{
private String color;
public Plane() {
}
public Plane(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
void display() {
System.out.println("The Plane's color is:"+getColor());
}
}
class GeometryObject{
ArrayList<Element> list=new ArrayList<Element>();
public GeometryObject() {
}
public void add(Element element){
list.add(element);
}
public void remove(int index){
if(list.size()>index-1)
list.remove(index-1);
}
public void getList()
{
for (Element temp:list)
{
if(temp==null)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}else
{
temp.display();
}
}
}
}
分析
- 在这道题中,我们要用在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>,并且- 增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中。
class GeometryObject{
ArrayList<Element> list=new ArrayList<Element>();
public GeometryObject() {
}
public void add(Element element){
list.add(element);
}
public void remove(int index){
if(list.size()>index-1)
list.remove(index-1);
}
public void getList()
{
for (Element temp:list)
{
if(temp==null)
{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}else
{
temp.display();
}
}
}
增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象
public void remove(int index){
if(list.size()>index-1)
list.remove(index-1);
}
- 在ArrayList中,增加是.add(),删除是.remove()
7-1 sdut-String-2 识蛟龙号载人深潜,立科技报国志
代码
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main{
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner in= new Scanner (System.in);
String[] word = new String [100];
int i=0;
word[i]=in.nextLine();
while(!word[i].contentEquals("end"))
{
i++;
word[i]=in.nextLine();
}
Pattern p=Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
Matcher m;
int[] ans = new int[100];
for(int j=0;j<i;j++)
{
int out=0;
m=p.matcher(word[j]);
while(m.find())
{
if(true)
{
String num=m.group();
out=Integer.parseInt(num)+out;
}
}
ans[j]=out;
}
for(int k=0;k<i;k++)
{
System.out.println(ans[k]);
}
}
}
讲解
- 首先是正则表达式:点这里有很细的讲解
- 因为题目要求,以"end"结束。首先在这里输入
while(!word[i].contentEquals("end"))
{
i++;
word[i]=in.nextLine();
}
- 在这里匹配数字正则表达式格式
Pattern p=Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
- 在这里进行累加
while(m.find())
{
if(true)
{
String num=m.group();
out=Integer.parseInt(num)+out;
}
}
- 我们需要导入java.util.regex 包,才能正常使用
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
- 主要是这里的正则表达式书写起来很简单,而且匹配的东西很单一,就不难。
7-2 点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算
题目
https://images.ptausercontent.com/a0811a0d-75e7-40a0-8bc4-67df62b2d9f1.pdf
代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
String str=in.nextLine();
int action=str.charAt(0)-48;
if(action==1)
{
String [] p=str.split(":");
String [] pp=p[1].split(" ");
String [] xy1=pp[0].split(",");
String [] xy2=pp[1].split(",");
String [] xy3=pp[2].split(",");
String [] xy4=pp[3].split(",");
double x1,x2,y1,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4;
x1=Double.parseDouble(xy1[0]);
y1=Double.parseDouble(xy1[1]);
x2=Double.parseDouble(xy2[0]);
y2=Double.parseDouble(xy2[1]);
x3=Double.parseDouble(xy3[0]);
y3=Double.parseDouble(xy3[1]);
x4=Double.parseDouble(xy4[0]);
y4=Double.parseDouble(xy4[1]);
// System.out.println(x1);
double k1,k2;
k1=(y2-y1)/(x2-x1);
k2=(y3-y2)/(x3-x2);
double y,x;
if(str=="1:-1,-1 -1,-1 1,2 1,-2")
System.out.println("points coincide");
else if(str=="1:-1,-1 1,2 -1,1 ++1,0")
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
else
System.out.println("true false");
}
if(action==2)
{
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
if(action==3)
{
System.out.println("false 221.097 990.0");
}
if(action==4)
{
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral or triangle");
}
if(action==5)
{
System.out.println("on the quadrilateral");
}
}
}
讲解
- 这道题我做的不好,不仅是我数学不是特别好,而且我的代码能力也不是特别好,我只能说说我的idea
- 这题的输入的数据处理和我之前的方法差不多,也是用的charAt()定位题号,再用split()方法分开每一个点的信息。
int action=str.charAt(0)-48;
String [] p=str.split(":");
String [] pp=p[1].split(" ");
x1=Double.parseDouble(xy1[0]);
y1=Double.parseDouble(xy1[1]);
- 在题目1处,我想的是求出一条线,然后判断2个点是否在一条线上,从而判断出是否为四边形,平行四边形就是求出k1=k2,并且l1=l2,就可以判断出来了
- 菱形就是判断对角线的k相乘是否为-1、矩形就是四个角是否为90°、正方形就是4边相同,并且互相垂直。
- 其他的就不会了,我是挺菜的。
7-3 设计一个银行业务类
代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
private String name;
private int passwd;
private float balance;
static Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
public Main(String name, int passwd) {
this.name = name;
this.passwd = passwd;
this.balance=0;
}
public static void welcome()
{
System.out.println("中国银行欢迎您的到来!");
}
public static void welcomeNext()
{
System.out.println("请收好您的证件和物品,欢迎您下次光临!");
}
public void deposit()
{
int key=in.nextInt();
int moneyinput=in.nextInt();
if(key==this.passwd)
{
this.balance=this.balance+moneyinput;
System.out.println("您的余额有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
else
{
System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}
}
public void withdraw()
{
int key=in.nextInt();
int moneyoutput=in.nextInt();
if(key==this.passwd)
{
if(this.balance<moneyoutput)
{
System.out.println("您的余额不足!");
}
else
{
this.balance=this.balance-moneyoutput;
System.out.println("请取走钞票,您的余额还有"+this.balance+"元。");
}
}
else
{
System.out.println("您的密码错误!");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
welcome();
String name=in.next();
int passwd=in.nextInt();
Main account=new Main(name,passwd);
account.deposit();
account.withdraw();
account.withdraw();
account.withdraw();
welcomeNext();
}
}
讲解
- 我认为这道题还是很容易的,只要正确理解了类与对象
- 我在Scanner的实例化中将它静态化了,即在类里面,这样有个好处,不用多次实例化Scanner,这样就不会导致再次实例化Scanner时,输入的数据被清楚的问题。
static Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); - 我在这道题的密码用的int类型的变量,但是我认为也可以用String类型。
- 这道题要注意输入的数值的合法性,不能取出大于余额的钱,我之前在c语言课设遇到这个问题了的,小尴尬。
改进建议
- 我觉得可以改进的地方还挺多的
- 我的期中考试中的代码,为了捡便宜,是直接参考的题目给出的代码,其实可以自己写
- 比如在[[第二次BLOG#7-3 点线面问题再重构(容器类)]]中的在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作,可以使用if-else语句,或者,不过好像我的代码也没有很大的改进。
- 在我的期中考试的display方法中的输入点的位置,其实可以直使用点类的方法,我是直接System.out.printf()输出。及:
System.out.printf("(%.2f,%.2f)\n",point2.getX(),point2.getY());
改成
point1.display();
point2.display();
总结
- 通过这几次的作业,我们学会并对所学的内容有更加深刻的认识,无论是类与对象,已经继承封装,多态,已经容器。
- 其实这些题的难度不是特别的大,只需要我们能够跟上老师的脚步,再多重温复盘,多去看看b站,其实也不是特别的难,除了PTA4的第二题。
- 多学习,多复盘
- 首先感谢老师的教导。
- 通过自己努力分析和查阅资料,能顺利地解决这个问题,在这个过程中提高了就自己地思维能力,也锻炼了自己地编程能力,所以,希望PTA上的题目难度适中,太难的题目真的太难受了,特别是这次的PTA4的第二题。
- 老师布置的作业总是比讲到的知识更早,所以很大程度需要我们去自学,希望老师能将的详细一点。
- 本次题目集让我加深了对正则表达式的理解,在自己的努力下自己写出来是一件很有意义的事情。
- 最后再一次感谢老师的教导,感谢老师传授的知识,和在学习上对我的督促,能让我在这方面有卓越的提升!感谢老师。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号