文件系统
Linux文件系统结构与Windows有些不同。Linux在文件系统的基础上没有物理驱动器(例如C:驱动器),
而是使用逻辑文件系统。在文件系统结构的最顶层是/,它通常被称为文件系统的根,就好像它是一个倒置
树。请记住,这与 root 用户不同。这些术语起初可能看起来令人困惑,但是一旦习惯了 Linux,
它们就会变得更容易区分。
文件系统的根(/)位于文件系统目录树的顶部,以下是要了解的最重要的子目录:
- /root root 用户的主目录
- /etc 通常包含 Linux 配置文件 - 控制程序启动时间和方式的文件
- /home 用户的主目录
- /mnt 将其他文件系统附加或安装到文件系统的位置
- /media CD 和 USB 设备通常连接或安装到文件系统的位置
- /bin 其中包含应用程序二进制文件(相当于 Microsoft Windows 中的可执行文件)
- /lib lib 库文件(与 Windows DLL 类似的共享程序)
在执行例行任务时不应该以 root 用户身份登录也很重要,因为当你以 root 身份登录时,任何攻击你的系统的人(是的,黑客有时会被黑客入侵)会立即获得 root 权限,从而“拥有”你的系统。在启动常规应用程序,浏览 Web,运行 Wireshark 等工具时以常规用户身份登录。
LINUX 基本命令
用 pwd 查看当前目录
┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ pwd
/home/kali
创建一个工作目录 并 用cd 导航文件系统 ls查看
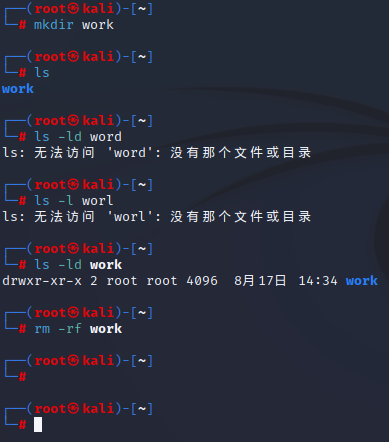
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# mkdir work
──(root㉿kali)-[~] 查看当前目录本身的权限与属性信息
└─# ls -ld work
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:34 work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~] 删除目录
└─# rm -rf work
──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# mkdir work/doc
mkdir: 无法创建目录 "work/doc": 没有那个文件或目录
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# mkdir -p work/doc
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# ls
work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# ls work
doc
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# mkdir --help
用法:mkdir [选项]... 目录...
若 <目录> 不存在,则创建 <目录>。
长选项的必选参数对于短选项也是必选的。
-m, --mode=模式 设置文件模式(格式同 chmod),而不是 a=rwx - umask
-p, --parents 需要时创建目标目录的父目录,但即使这些目录已存在
也不视为错误,且其文件模式也不受 -m 选项影响。
-v, --verbose 每次创建新目录时,打印一条消息
-Z 将每个创建的目录的 SELinux 安全上下文设置为默认类型
--context[=上下文] 类似 -Z,但如果指定了 <上下文>,则将 SELinux
或 SMACK 安全上下文设置为 <上下文>
--help 显示此帮助信息并退出
--version 显示版本信息并退出
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# mkdir -pv work/{doc,app,bak,script}
mkdir: 已创建目录 'work/app'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'work/bak'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'work/script'
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# ls work
app bak doc exam script
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# cd work/exam
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─#
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# mkdir -p test/{1..100}
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ls test
1 13 18 22 27 31 36 40 45 5 54 59 63 68 72 77 81 86 90 95
10 14 19 23 28 32 37 41 46 50 55 6 64 69 73 78 82 87 91 96
100 15 2 24 29 33 38 42 47 51 56 60 65 7 74 79 83 88 92 97
11 16 20 25 3 34 39 43 48 52 57 61 66 70 75 8 84 89 93 98
12 17 21 26 30 35 4 44 49 53 58 62 67 71 76 80 85 9 94 99
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# rm -rf test
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# mkdir -pv test/user{1..10}
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user1'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user2'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user3'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user4'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user5'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user6'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user7'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user8'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user9'
mkdir: 已创建目录 'test/user10'
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# rm -rf test
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# mkdir {a..d}
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam]
└─# ls
a b c d
cd 命令
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work/exam] 返回根目录
└─# cd
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~] 查看
└─# ls
work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~] 切换到work
└─# cd work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work] 查看当前所在目录
└─# pwd
/root/work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work] 返回上一级目录
└─# cd ..
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# cd /etc
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/etc]
└─# cd /etc/network
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/etc/network] 返回根
└─# cd ../..
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/] 返回上一次目录
└─# cd -
/etc/network
┌──(root㉿kali)-[/etc/network] 返回根
└─# cd ~
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~] 切换到对应目录
└─# cd ~ work
~/work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─# cd ~/test
cd: 没有那个文件或目录: /root/test
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─# cd ~/etc
cd: 没有那个文件或目录: /root/etc
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─# cd -
~
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~]
└─# cd ~/work
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─#
ls 命令
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work] 长格式显示
└─# ls -l
总计 20 d :文件类型 rwxr-xr-x :操作权限 root :所属 4096:大小 8月17日 14:42:时间
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 app
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 bak
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:40 doc
drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 8月17日 14:53 exam
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 script
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─# ls -l -a
总计 28
drwxr-xr-x 7 root root 4096 8月17日 14:43 .
drwx------ 8 root root 4096 8月17日 14:40 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 app
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 bak
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:40 doc
drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 8月17日 14:53 exam
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 script
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work] 与上同理查看隐藏文件
└─# ls -la
总计 28
drwxr-xr-x 7 root root 4096 8月17日 14:43 .
drwx------ 8 root root 4096 8月17日 14:40 ..
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 app
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 bak
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:40 doc
drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 8月17日 14:53 exam
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 8月17日 14:42 script
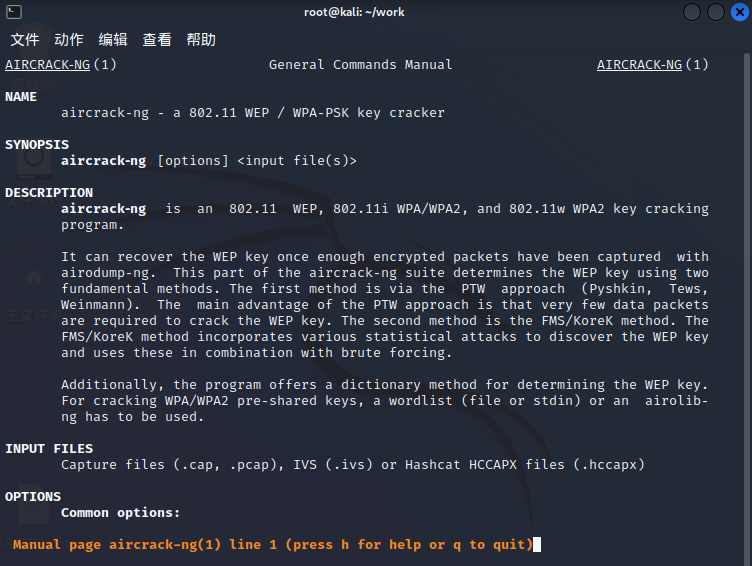
获取帮助 --help or -h
┌──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─# aircrack-ng --help
Aircrack-ng 1.7 - (C) 2006-2022 Thomas d'Otreppe
https://www.aircrack-ng.org
usage: aircrack-ng [options] <input file(s)>
Common options:
-a <amode> : force attack mode (1/WEP, 2/WPA-PSK)
-e <essid> : target selection: network identifier
-b <bssid> : target selection: access point's MAC
-p <nbcpu> : # of CPU to use (default: all CPUs)
-q : enable quiet mode (no status output)
-C <macs> : merge the given APs to a virtual one
-l <file> : write key to file. Overwrites file.
Static WEP cracking options:
-c : search alpha-numeric characters only
-t : search binary coded decimal chr only
-h : search the numeric key for Fritz!BOX
-d <mask> : use masking of the key (A1:XX:CF:YY)
-m <maddr> : MAC address to filter usable packets
-n <nbits> : WEP key length : 64/128/152/256/512
-i <index> : WEP key index (1 to 4), default: any
-f <fudge> : bruteforce fudge factor, default: 2
-k <korek> : disable one attack method (1 to 17)
-x or -x0 : disable bruteforce for last keybytes
-x1 : last keybyte bruteforcing (default)
-x2 : enable last 2 keybytes bruteforcing
-y : experimental single bruteforce mode
-K : use only old KoreK attacks (pre-PTW)
-s : show the key in ASCII while cracking
-M <num> : specify maximum number of IVs to use
-D : WEP decloak, skips broken keystreams
-P <num> : PTW debug: 1: disable Klein, 2: PTW
-1 : run only 1 try to crack key with PTW
-V : run in visual inspection mode
WEP and WPA-PSK cracking options:
-w <words> : path to wordlist(s) filename(s)
-N <file> : path to new session filename
-R <file> : path to existing session filename
WPA-PSK options:
-E <file> : create EWSA Project file v3
-I <str> : PMKID string (hashcat -m 16800)
-j <file> : create Hashcat v3.6+ file (HCCAPX)
-J <file> : create Hashcat file (HCCAP)
-S : WPA cracking speed test
-Z <sec> : WPA cracking speed test length of
execution.
-r <DB> : path to airolib-ng database
(Cannot be used with -w)
SIMD selection:
--simd-list : Show a list of the available
SIMD architectures, for this
machine.
--simd=<option> : Use specific SIMD architecture.
<option> may be one of the following, depending on
your platform:
generic
avx512
avx2
avx
sse2
altivec
power8
asimd
neon
Other options:
-u : Displays # of CPUs & SIMD support
--help : Displays this usage screen
──(root㉿kali)-[~/work]
└─# nmap -h
Nmap 7.94 ( https://nmap.org )
Usage: nmap [Scan Type(s)] [Options] {target specification}
TARGET SPECIFICATION:
Can pass hostnames, IP addresses, networks, etc.
Ex: scanme.nmap.org, microsoft.com/24, 192.168.0.1; 10.0.0-255.1-254
-iL <inputfilename>: Input from list of hosts/networks
-iR <num hosts>: Choose random targets
--exclude <host1[,host2][,host3],...>: Exclude hosts/networks
--excludefile <exclude_file>: Exclude list from file
HOST DISCOVERY:
-sL: List Scan - simply list targets to scan
-sn: Ping Scan - disable port scan
-Pn: Treat all hosts as online -- skip host discovery
-PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: TCP SYN/ACK, UDP or SCTP discovery to given ports
-PE/PP/PM: ICMP echo, timestamp, and netmask request discovery probes
-PO[protocol list]: IP Protocol Ping
-n/-R: Never do DNS resolution/Always resolve [default: sometimes]
--dns-servers <serv1[,serv2],...>: Specify custom DNS servers
--system-dns: Use OS's DNS resolver
--traceroute: Trace hop path to each host
SCAN TECHNIQUES:
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM: TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans
-sU: UDP Scan
-sN/sF/sX: TCP Null, FIN, and Xmas scans
--scanflags <flags>: Customize TCP scan flags
-sI <zombie host[:probeport]>: Idle scan
-sY/sZ: SCTP INIT/COOKIE-ECHO scans
-sO: IP protocol scan
-b <FTP relay host>: FTP bounce scan
PORT SPECIFICATION AND SCAN ORDER:
-p <port ranges>: Only scan specified ports
Ex: -p22; -p1-65535; -p U:53,111,137,T:21-25,80,139,8080,S:9
--exclude-ports <port ranges>: Exclude the specified ports from scanning
-F: Fast mode - Scan fewer ports than the default scan
-r: Scan ports sequentially - don't randomize
--top-ports <number>: Scan <number> most common ports
--port-ratio <ratio>: Scan ports more common than <ratio>
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
--version-intensity <level>: Set from 0 (light) to 9 (try all probes)
--version-light: Limit to most likely probes (intensity 2)
--version-all: Try every single probe (intensity 9)
--version-trace: Show detailed version scan activity (for debugging)
SCRIPT SCAN:
-sC: equivalent to --script=default
--script=<Lua scripts>: <Lua scripts> is a comma separated list of
directories, script-files or script-categories
--script-args=<n1=v1,[n2=v2,...]>: provide arguments to scripts
--script-args-file=filename: provide NSE script args in a file
--script-trace: Show all data sent and received
--script-updatedb: Update the script database.
--script-help=<Lua scripts>: Show help about scripts.
<Lua scripts> is a comma-separated list of script-files or
script-categories.
OS DETECTION:
-O: Enable OS detection
--osscan-limit: Limit OS detection to promising targets
--osscan-guess: Guess OS more aggressively
TIMING AND PERFORMANCE:
Options which take <time> are in seconds, or append 'ms' (milliseconds),
's' (seconds), 'm' (minutes), or 'h' (hours) to the value (e.g. 30m).
-T<0-5>: Set timing template (higher is faster)
--min-hostgroup/max-hostgroup <size>: Parallel host scan group sizes
--min-parallelism/max-parallelism <numprobes>: Probe parallelization
--min-rtt-timeout/max-rtt-timeout/initial-rtt-timeout <time>: Specifies
probe round trip time.
--max-retries <tries>: Caps number of port scan probe retransmissions.
--host-timeout <time>: Give up on target after this long
--scan-delay/--max-scan-delay <time>: Adjust delay between probes
--min-rate <number>: Send packets no slower than <number> per second
--max-rate <number>: Send packets no faster than <number> per second
FIREWALL/IDS EVASION AND SPOOFING:
-f; --mtu <val>: fragment packets (optionally w/given MTU)
-D <decoy1,decoy2[,ME],...>: Cloak a scan with decoys
-S <IP_Address>: Spoof source address
-e <iface>: Use specified interface
-g/--source-port <portnum>: Use given port number
--proxies <url1,[url2],...>: Relay connections through HTTP/SOCKS4 proxies
--data <hex string>: Append a custom payload to sent packets
--data-string <string>: Append a custom ASCII string to sent packets
--data-length <num>: Append random data to sent packets
--ip-options <options>: Send packets with specified ip options
--ttl <val>: Set IP time-to-live field
--spoof-mac <mac address/prefix/vendor name>: Spoof your MAC address
--badsum: Send packets with a bogus TCP/UDP/SCTP checksum
OUTPUT:
-oN/-oX/-oS/-oG <file>: Output scan in normal, XML, s|<rIpt kIddi3,
and Grepable format, respectively, to the given filename.
-oA <basename>: Output in the three major formats at once
-v: Increase verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect)
-d: Increase debugging level (use -dd or more for greater effect)
--reason: Display the reason a port is in a particular state
--open: Only show open (or possibly open) ports
--packet-trace: Show all packets sent and received
--iflist: Print host interfaces and routes (for debugging)
--append-output: Append to rather than clobber specified output files
--resume <filename>: Resume an aborted scan
--noninteractive: Disable runtime interactions via keyboard
--stylesheet <path/URL>: XSL stylesheet to transform XML output to HTML
--webxml: Reference stylesheet from Nmap.Org for more portable XML
--no-stylesheet: Prevent associating of XSL stylesheet w/XML output
MISC:
-6: Enable IPv6 scanning
-A: Enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute
--datadir <dirname>: Specify custom Nmap data file location
--send-eth/--send-ip: Send using raw ethernet frames or IP packets
--privileged: Assume that the user is fully privileged
--unprivileged: Assume the user lacks raw socket privileges
-V: Print version number
-h: Print this help summary page.
EXAMPLES:
nmap -v -A scanme.nmap.org
nmap -v -sn 192.168.0.0/16 10.0.0.0/8
nmap -v -iR 10000 -Pn -p 80
SEE THE MAN PAGE (https://nmap.org/book/man.html) FOR MORE OPTIONS AND EXAMPLES
man 查看联机属性
manual 快捷
G 回到手册最后一行
gg 回到手册第一行
/关键字 根据关键字向下搜索 如:EXAMPLS(例子)
tg: shell常用快捷键
- ctrl + w :删除光标左侧单词
- ctrl + a :回到行首
- ctrl + e :回到行尾
本文来自博客园,作者:depressiom,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/depressiom/p/16748540.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)