PLT hook笔记
1. hook技术概述
hook技术是一种拦截用户函数调用的技术。通过hook技术可以实现统计用户对某些函数的调用次数,对函数注入新的功能的目标。在Linux平台,Hook技术可以分成用户和内核两个层面,每个类比中都存在不同的hook技术。本文主要介绍针对动态链接技术的PLT hook。
2. 代码实例
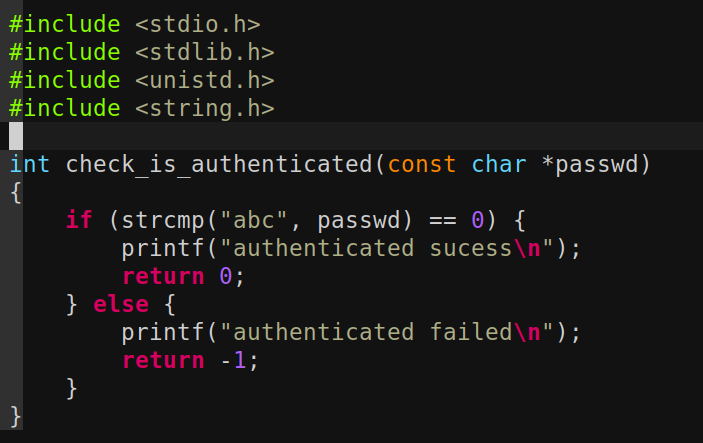
其次编写我们的main.c 该函数实现了将要替换strcmp函数的my_strcmp,和使hook生效的hook函数。代码的具体细节
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #include <inttypes.h> 6 #include <execinfo.h> 7 #include <sys/user.h> 8 #include <sys/mman.h> 9 #include "passwd.h" 10 11 #define PAGE_SHIFT 12 12 #define PAGE_SIZE (_AC(1,UL) << PAGE_SHIFT) 13 #define PAGE_MASK (~(PAGE_SIZE-1)) 14 15 #define __AC(X,Y) (X##Y) 16 #define _AC(X,Y) __AC(X,Y) 17 18 #define PAGE_START(addr) ((addr) & PAGE_MASK) 19 #define PAGE_END(addr) (PAGE_START(addr) + PAGE_SIZE) 20 21 int my_strcmp(const char *s1, const char *s2) 22 { 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 uintptr_t get_base_addr(char *libname) 27 { 28 FILE *fp; 29 char line[1024]; 30 //char base_addr[1024]; 31 uintptr_t base_addr = 0; 32 33 if (NULL == (fp = fopen("/proc/self/maps", "r"))) { 34 perror("open err"); 35 return -1; 36 } 37 38 while (NULL != fgets(line, sizeof(line), fp)) { 39 if (NULL != strstr(line, libname)) { 40 sscanf(line, "%"PRIxPTR"-%*lx %*4s 00000000", &base_addr); 41 printf("line2:%s, base_addr:%"PRIxPTR"\n", line, base_addr); 42 break; 43 } 44 } 45 fclose(fp); 46 47 return base_addr; 48 } 49 50 void hook() { 51 uintptr_t base_addr; 52 uintptr_t addr; 53 //1. get the base addr of libpasswd.so 54 base_addr = get_base_addr("libpasswd"); 55 if (0 == base_addr) return; 56 addr = base_addr + 0x201020; 57 //2. add the write permisson 58 mprotect((void *)PAGE_START(addr), PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE); 59 //3. replace our hook func my_strcmp 60 *(void **)addr = my_strcmp; 61 //4. clear the cache 62 __builtin___clear_cache((void *)PAGE_START(addr), 63 (void *)PAGE_END(addr)); 64 } 65 66 int main() 67 { 68 hook(); 69 check_is_authenticated("abcd"); 70 return 0; 71 }

在将libpasswd.so放置到/usr/lib/目录中之后,使用以下命令编译main.c

运行之后我们 可以看到验证结果始终是正确的,说明我们对于libpasswd.so中的strcmp函数的Hook已经生效。

怎么样,是不是很神奇呀!下面我们就来看看plt hook到底是怎么实现的。
3. PLT hook原理

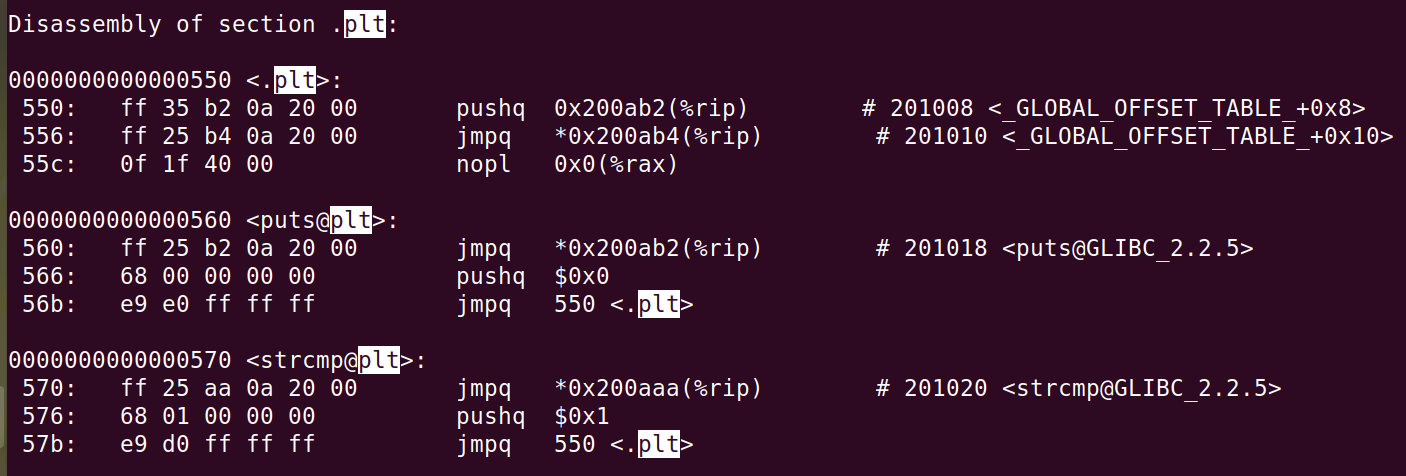
以上就是第一次调用strcmp函数的流程,可以看出开销还是不小的。在后续的调用中,首先还是跳转到strcmp的plt条目中,然后执行jmpq *0x200aaa(%rip)指令,不同的是这是strcmp对应的GOT条目已经被写入了strcmp的运行时地址,所以这条jmp指令直接将程序的执行跳转到strcmp函数中。那么是不是只要在strcmp对应的GOT条目中写入我们自己的函数的地址,就可以将控制跳转到自己实现的函数中了嘛。本着这样的思路我们来看看开始时的代码。
4. 代码分析
- 第一步我们要获取libpasswd在进程中的首地址,时刻记住我们拦截的是动态库中的函数,将来要替换的GOT[strcmp]也属于libpasswd。
-
第二步就是获取libpasswd中调用strcmp对应的GOT条目的地址,为什么是addr = base_addr + 0x201020呢?我们回到上文的libpasswd的plt段,可以看到strcmp的plt条目的第一条指令已经写出了相应的GOT条目的地址就是0x201020。又因为我们拦截的动态库的strcmp函数,所以必须加上libpasswd在main中的首地址。

3. 因为我们要写入目标进程的数据段,所以必须给相应的页增加写权限,这里使用mprotect函数来调整相应页的权限。
1 void hook() { 2 uintptr_t base_addr; 3 uintptr_t addr; 4 //1. get the base addr of libpasswd.so 5 base_addr = get_base_addr("libpasswd"); 6 if (0 == base_addr) return; 7 addr = base_addr + 0x201020; 8 //2. add the write permisson 9 mprotect((void *)PAGE_START(addr), PAGE_SIZE, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE); 10 //3. replace our hook func my_strcmp 11 *(void **)addr = my_strcmp; 12 //4. clear the cache 13 __builtin___clear_cache((void *)PAGE_START(addr), 14 (void *)PAGE_END(addr)); 15 }

