20192317邓子彦 实验四 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验报告
20192317邓子彦 实验四 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验报告
学号 2019-2020 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验四报告
课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
班级: 1923
姓名: 邓子彦
学号:20192317
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2020年10月22日
必修/选修: 必修
- 1.实验内容
(一)Java Socket编程
1.学习蓝墨云上教材《Java和Android编程》“第16章 输入/输出 ”和“第22章 网络”,学习JavaSocket编程
2.结对编程。结对伙伴A编写客户端SocketClient.java,结对伙伴B编写服务器端。
3.截图加学号水印上传蓝墨云,代码push到码云,并撰写实验报告。
(二)Java和密码学
参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6683948.html
以结对的方式完成Java密码学相关内容的学习(帖子中所有代码和相关知识点需要学习)。提交学习成果码云链接和代表性成果截图,要有学号水印。
(三)编写有理数/复数计算器
结对编程,结对伙伴A编写有理数计算器。结对伙伴B编写复数计算器。截图加水印上传蓝墨云,代码push码云。
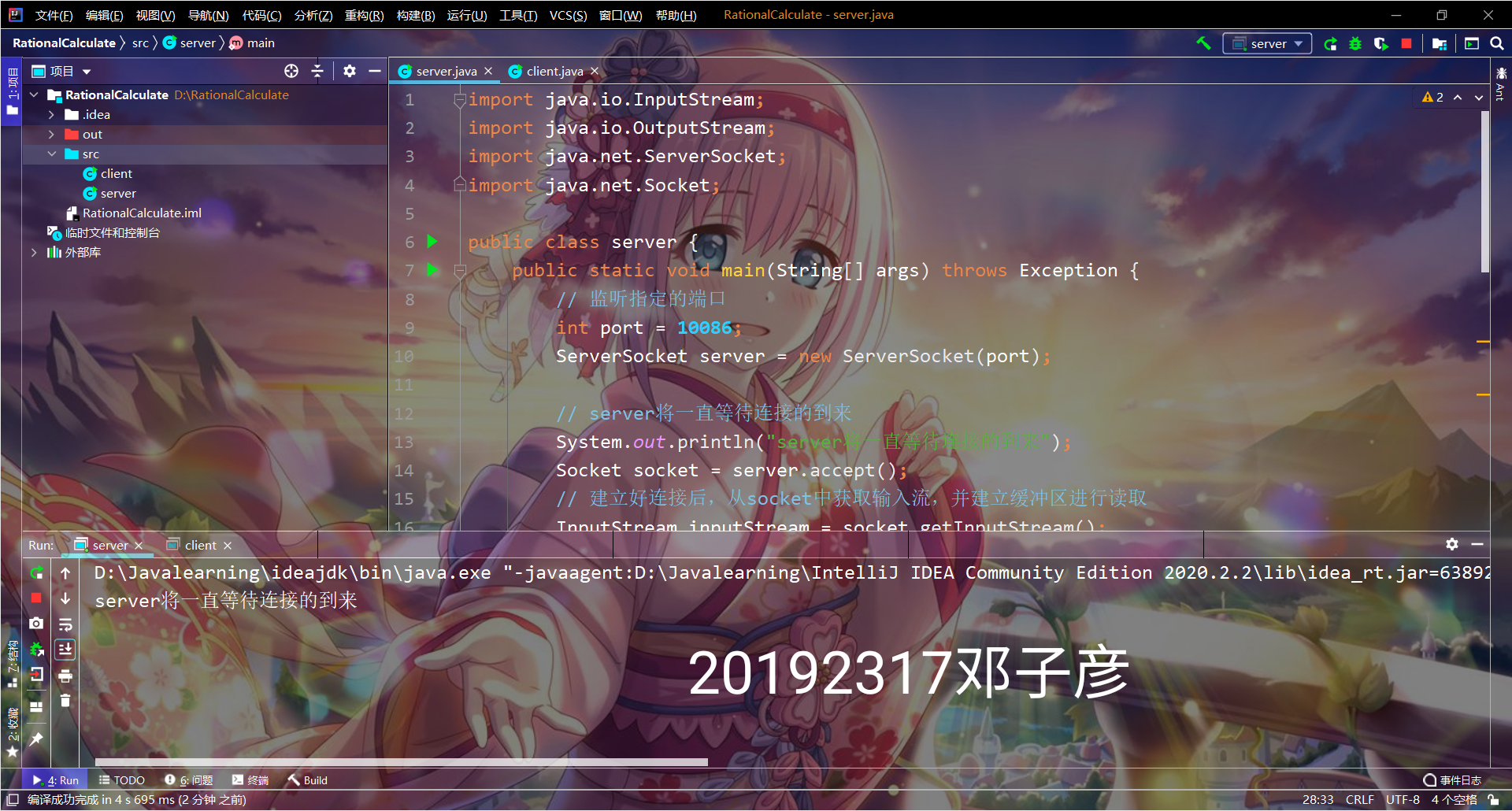
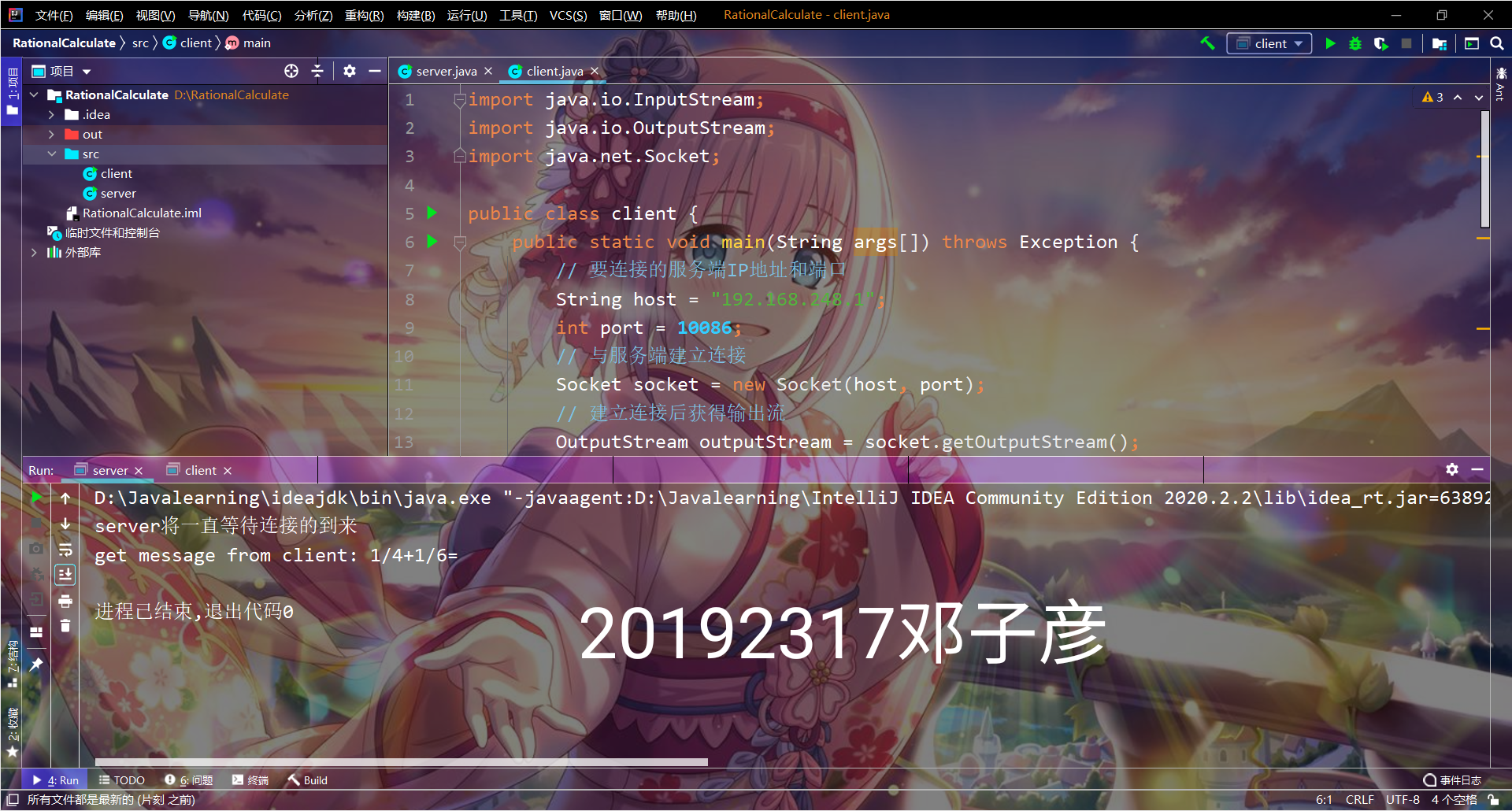
(四)远程有理数计算器
结对编程,结对伙伴A编程实现客户端,结果伙伴B实现服务器端。
客户端通过键盘输入一个有理数计算的公式(例如:1/4 + 1/6 = ),并把该公式以字符串的形式发送给伙伴B(服务器端),服务器端根据字符串计算出结果为5/12,并把结果返回给客户端A,A收到结果后输出结果。截图加水印上传蓝墨云,代码push码云。
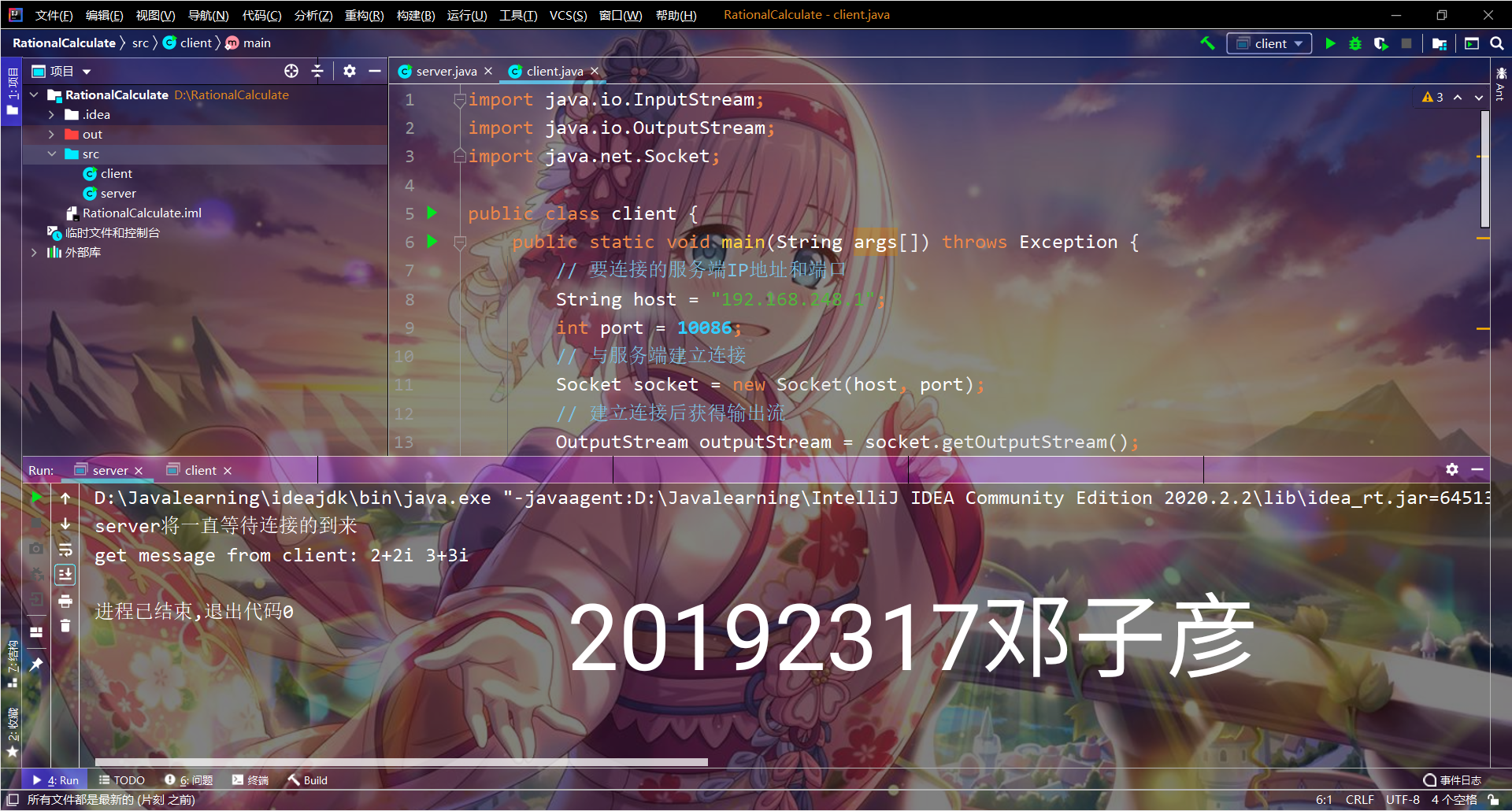
(五)远程复数计算器
结对编程,结对伙伴B编程实现客户端,结果伙伴A实现服务器端。
客户端通过键盘输入一个有理数计算的公式(例如:1/4 + 1/6 = ),并把该公式以字符串的形式发送给伙伴A(服务器端),服务器端根据字符串计算出结果为5/12,并把结果返回给客户端B,B收到结果后输出结果。截图加水印上传蓝墨云,代码push码云。
- 2.实验结果
(一)Java Socket编程
- 1.一个人实现了客户端和服务器
- 实验代码
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
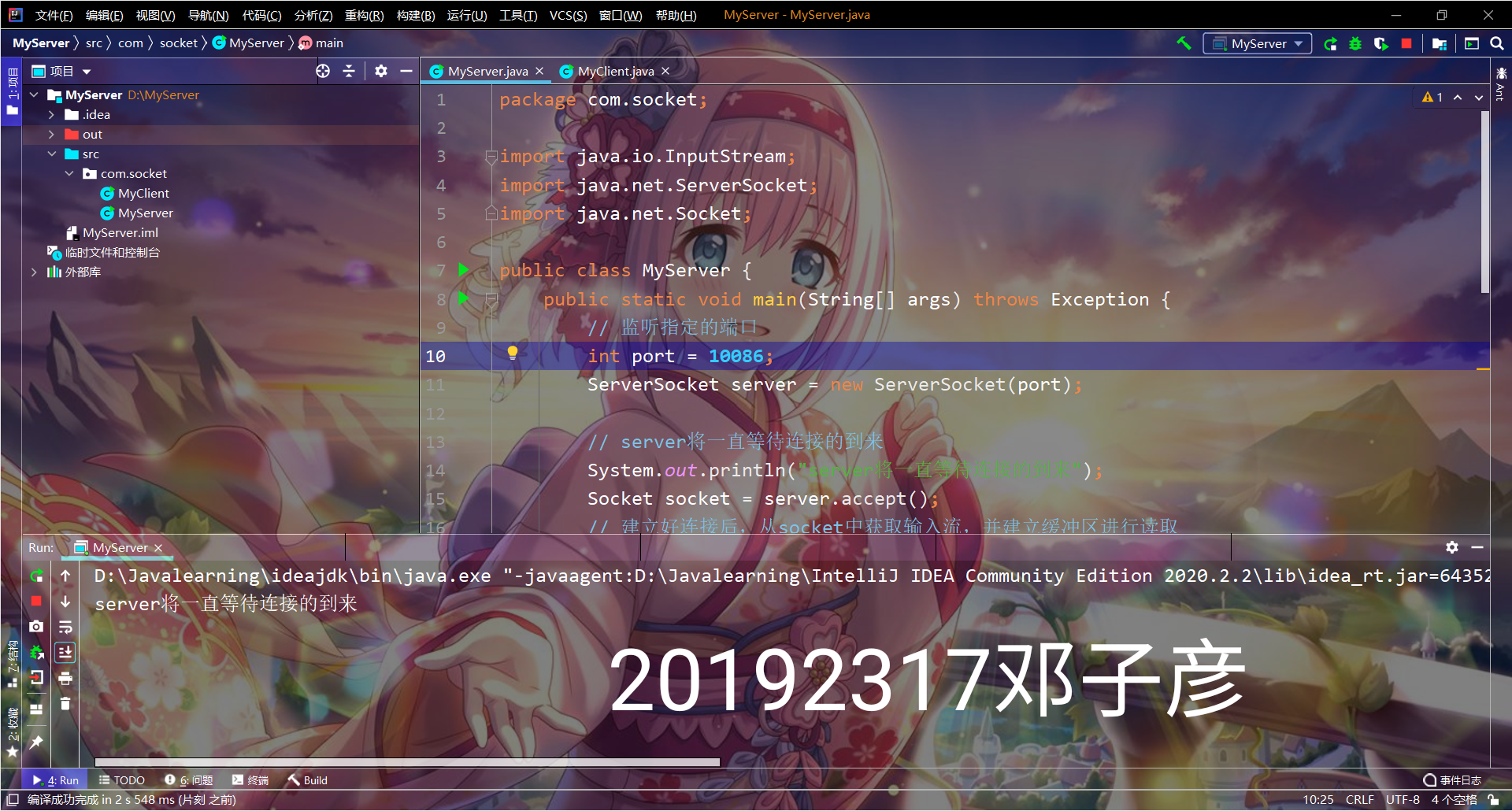
public class server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 监听指定的端口
int port = 10086;
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port);
// server将一直等待连接的到来
System.out.println("server将一直等待连接的到来");
Socket socket = server.accept();
// 建立好连接后,从socket中获取输入流,并建立缓冲区进行读取
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
//只有当客户端关闭它的输出流的时候,服务端才能取得结尾的-1
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
// 注意指定编码格式,发送方和接收方一定要统一,建议使用UTF-8
sb.append(new String(bytes, 0, len, "UTF-8"));
}
System.out.println("get message from client: " + sb);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
- 2
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
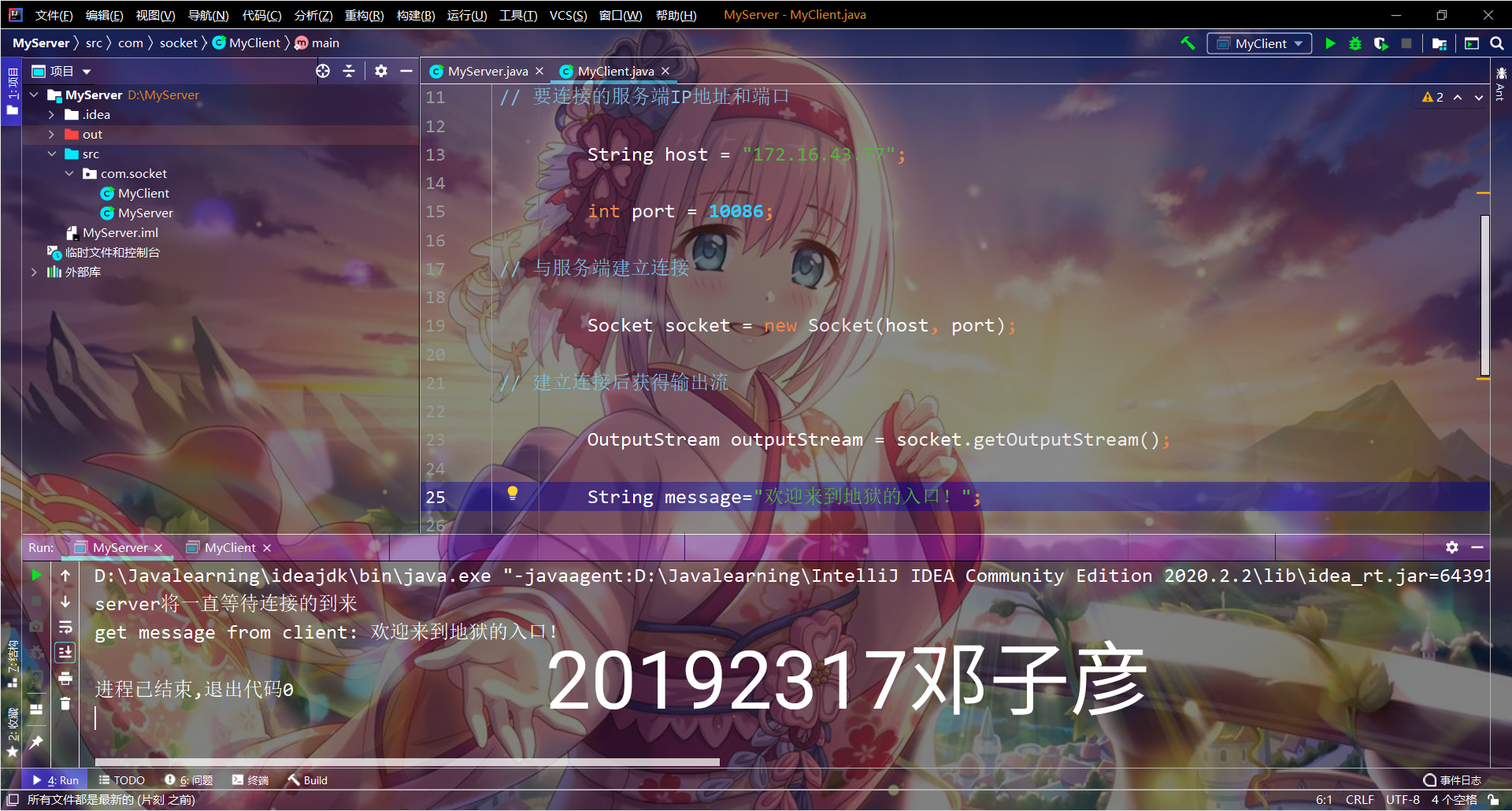
public class client {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
// 要连接的服务端IP地址和端口
String host = "192.168.248.1";
int port = 10086;
// 与服务端建立连接
Socket socket = new Socket(host, port);
// 建立连接后获得输出流
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
String message = "欢迎来到地狱的入口!";
socket.getOutputStream().write(message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
//通过shutdownOutput高速服务器已经发送完数据,后续只能接受数据
socket.shutdownOutput();
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while ((len = inputStream.read(bytes)) != -1) {
//注意指定编码格式,发送方和接收方一定要统一,建议使用UTF-8
sb.append(new String(bytes, 0, len,"UTF-8"));
}
System.out.println("get message from server: " + sb);
inputStream.close();
outputStream.close();
socket.close();
}
}
-
2.实验截图
-
(二)Java和密码学
-
实验代码
-
CasesarCode
package cryptology;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CaesarCode {
char ciphertext[]; // 密文
int key;
char plaintext[]; // 明文
StringBuffer plaintextStr = new StringBuffer("");
StringBuffer ciphertextStr = new StringBuffer("");
final int max = 500; // 最大字符
public static void main(String[] args) {
CaesarCode m = new CaesarCode();
m.setKey();
m.getPlaintext();
m.encryption();
m.deciphering();
m.display();
}
/**
* 设置密钥,返回偏移值
* @return
*/
int setKey() {
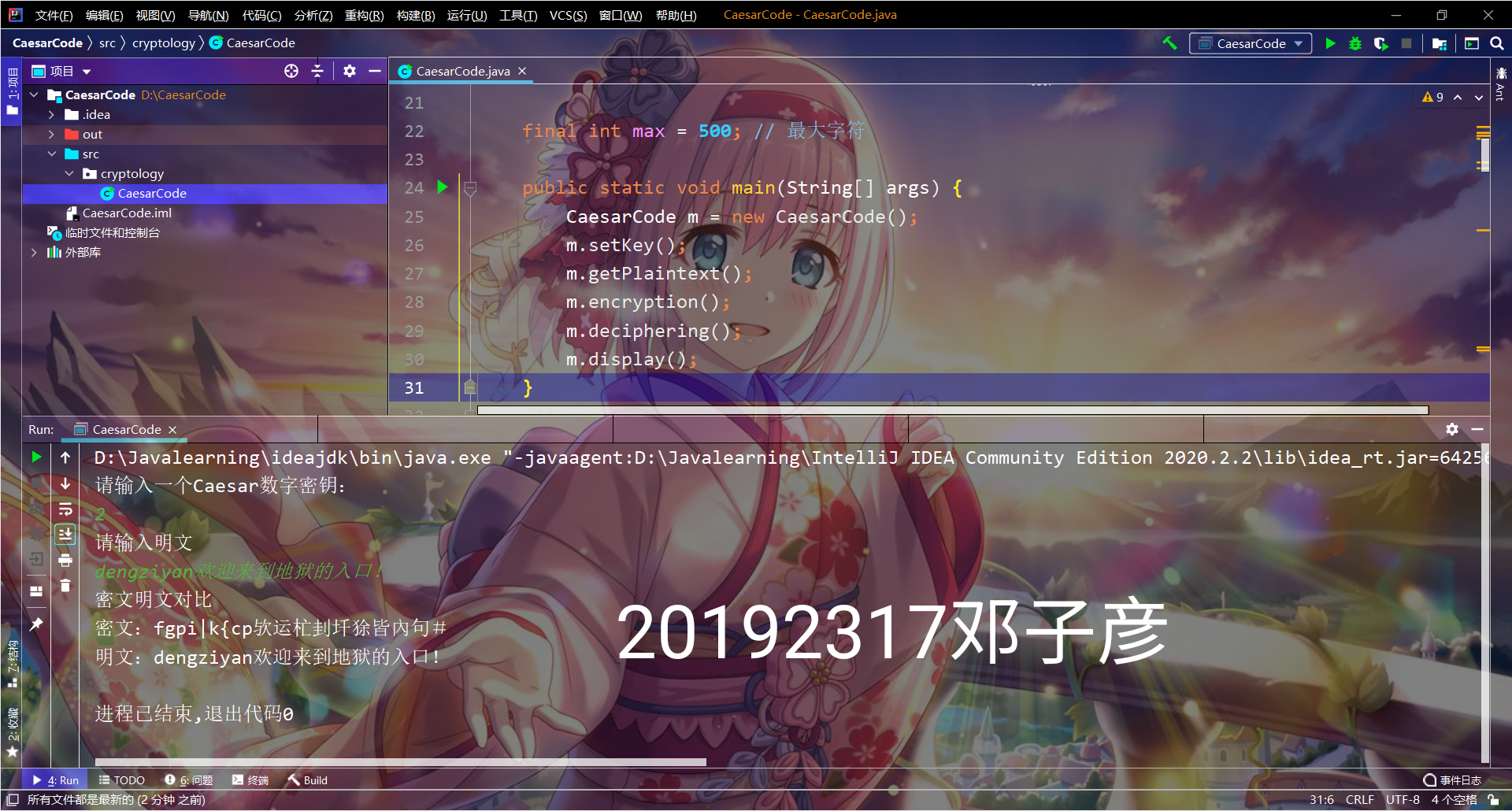
System.out.println("请输入一个Caesar数字密钥:");
while (true) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
try {
key = sc.nextInt() % 26; // %26的意义是获取密钥的偏移值
return key;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR__请重新输入整数密钥...");
}
}
}
/**
* 获得明文
*/
void getPlaintext() {
plaintext = new char[max];
for (int j = 0; j < max; j++) {
plaintext[j] = '★'; // 设置临时变量将数组填充,因明文中可存在' '空,所以需要填充判断
}
int i = 0;
char ch = ' ';
BufferedReader bf = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.println("请输入明文");
try {
ch = (char) bf.read(); // 获得字符
while (ch != '\r' && ch != '\n') { // 回车
plaintext[i] = ch;
i++;
try {
ch = (char) bf.read();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 加密
*/
void encryption() {
ciphertext = new char[max];
for (int j = 0; j < max; j++) {
ciphertext[j] = '★'; // 设置临时变量将数组填充,因明文中可存在' '空,所以需要填充判断
}
for (int i = 0; i < plaintext.length; i++) {
if (plaintext[i] != '★') {
int temp = plaintext[i] + key; // 偏移后的ASCII码
ciphertext[i]=(char)temp; // 加密符号
ciphertextStr.append(ciphertext[i]); // 拼接字符串
} else {
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 解密
*/
void deciphering() {
char c = ' ';
for (int i = 0; i < ciphertext.length; i++) {
if (ciphertext[i] != '★') {
int temp = ciphertext[i] - key;
c = (char) temp;
plaintextStr.append(c); // 拼接解密字符串
} else {
break;
}
}
}
/**
* 显示对比结果
*/
void display() {
System.out.println("密文明文对比");
System.out.println("密文:" + ciphertextStr);
System.out.println("明文:" + plaintextStr);
}
-
实验截图
-
DES
package com.journaldev.des;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.security.InvalidAlgorithmParameterException;
import java.security.InvalidKeyException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.spec.AlgorithmParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.CipherInputStream;
import javax.crypto.CipherOutputStream;
import javax.crypto.KeyGenerator;
import javax.crypto.NoSuchPaddingException;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
public class DES {
private static Cipher encryptCipher;
private static Cipher decryptCipher;
private static final byte[] iv = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 99, 88, 77, 66 };
public static void main(String[] args) {
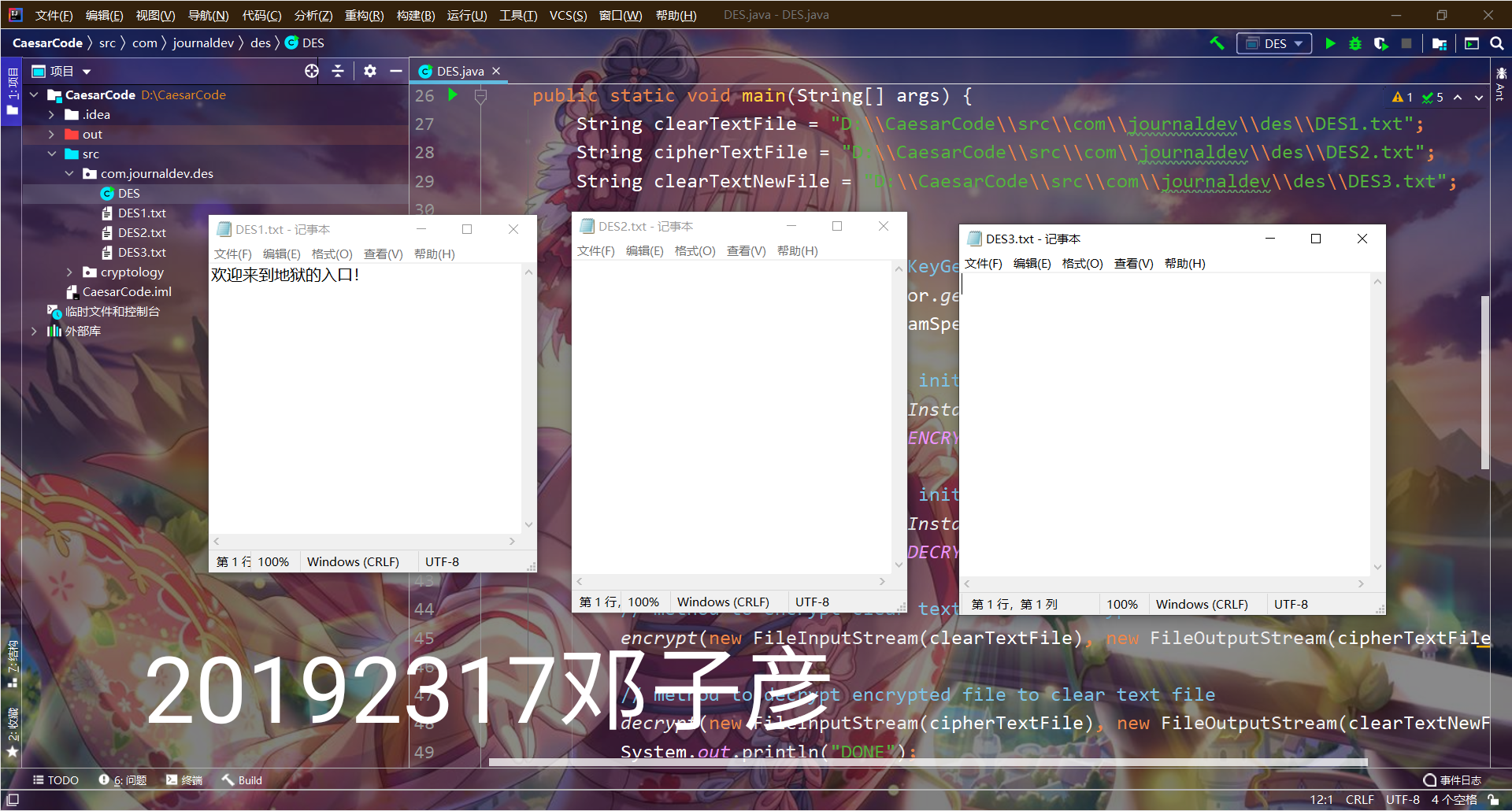
String clearTextFile = "D:\\CaesarCode\\src\\com\\journaldev\\des\\DES1.txt";
String cipherTextFile = "D:\\CaesarCode\\src\\com\\journaldev\\des\\DES2.txt";
String clearTextNewFile = "D:\\CaesarCode\\src\\com\\journaldev\\des\\DES3.txt";
try {
// create SecretKey using KeyGenerator
SecretKey key = KeyGenerator.getInstance("DES").generateKey();
AlgorithmParameterSpec paramSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv);
// get Cipher instance and initiate in encrypt mode
encryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
encryptCipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key, paramSpec);
// get Cipher instance and initiate in decrypt mode
decryptCipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
decryptCipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, paramSpec);
// method to encrypt clear text file to encrypted file
encrypt(new FileInputStream(clearTextFile), new FileOutputStream(cipherTextFile));
// method to decrypt encrypted file to clear text file
decrypt(new FileInputStream(cipherTextFile), new FileOutputStream(clearTextNewFile));
System.out.println("DONE");
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | NoSuchPaddingException | InvalidKeyException
| InvalidAlgorithmParameterException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static void encrypt(InputStream is, OutputStream os) throws IOException {
// create CipherOutputStream to encrypt the data using encryptCipher
os = new CipherOutputStream(os, encryptCipher);
writeData(is, os);
}
private static void decrypt(InputStream is, OutputStream os) throws IOException {
// create CipherOutputStream to decrypt the data using decryptCipher
is = new CipherInputStream(is, decryptCipher);
writeData(is, os);
}
// utility method to read data from input stream and write to output stream
private static void writeData(InputStream is, OutputStream os) throws IOException {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int numRead = 0;
// read and write operation
while ((numRead = is.read(buf)) >= 0) {
os.write(buf, 0, numRead);
}
os.close();
is.close();
}
}
-
实验截图

-
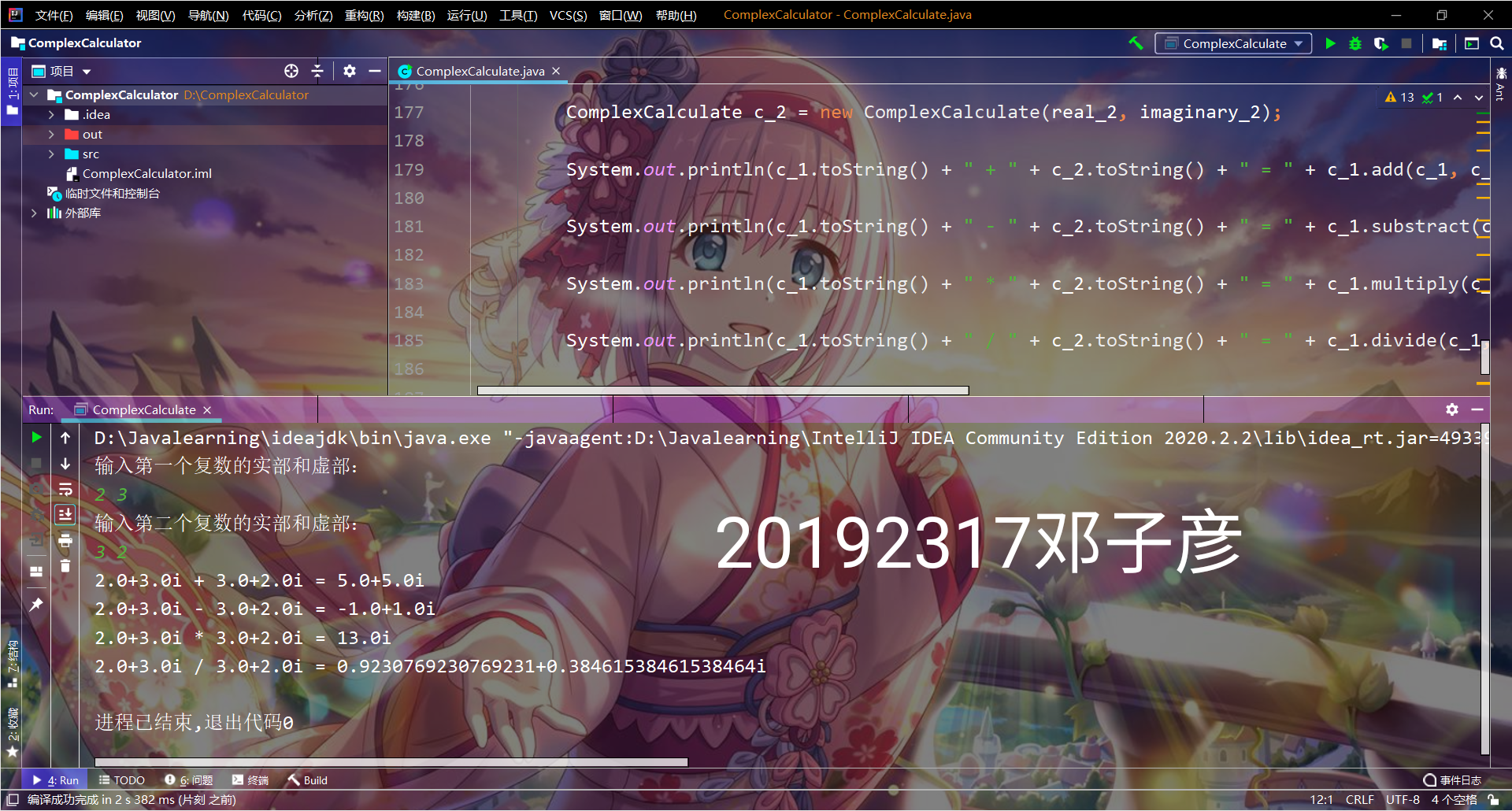
(三)编写有理数/复数计算器
-
有理数计算器
-
实验代码
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class youlishu{
public static void main(String[] args) throws NumberFormatException, IOException{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] strs=br.readLine().split(" ");
br.close();
numAdd(strs[0],strs[1]);
// numSub(strs[0],strs[1]);
// numMult(strs[0],strs[1]);
// numDivi(strs[0],strs[1]);
}
// 化简分数形式有理数
public static String numSimply(String str) {
String[] strs=str.split("/");
Long str1=Long.parseLong(strs[0]);//分子
Long str2=Long.parseLong(strs[1]);//分母
if(str2<0) {
str2=-str2;
str1=-str1;
}
Long num1=str1/str2;
Long num2=str1%str2;
if(num2<0) {
num2=-num2;
}
// 真分数
if(num1==0&&num2!=0) {
Long gcd=getGCD(str1,str2);
str=str1/gcd+"/"+str2/gcd;
// 判断str1是正数还是负数
if(str1>0) {
return str;
}else {
return "("+str+")";
}
}
// 整数
else if(num2==0&&num1!=0) {
String result=String.valueOf(num1);
// 判断str1是正数还是负数
if(str1>0) {
return result;
}else {
return "("+result+")";
}
}
// 为0
else if(num1==0&&num2==0) {
return "0";
}
// 假分数
else {
// 对假分数的真分数部分化简
String result1=num2+"/"+str2;
String result2=numSimply(result1);
// 判断num1是正数还是负数
if(num1>0) {
return num1+" "+result2;
}else {
return "("+num1+" "+result2+")";
}
}
}
// 利用辗转相除法求两个数的最大公约数
// 这个方法默认a<b,因为用于真分数的化简,分子一定小于分母
public static Long getGCD(Long a,Long b) {
while(b%a!=0) {
Long temp=b%a;
b=a;
a=temp;
}
// 如果最大公约数是负数,需要把它转换为正数
if(a<0) {
a=-a;
}
return a;
}
// 有理数加法
public static void numAdd(String str1,String str2) {
String[] strs1=str1.split("/");
String[] strs2=str2.split("/");
Long son1=Long.parseLong(strs1[0]);
Long mon1=Long.parseLong(strs1[1]);
Long son2=Long.parseLong(strs2[0]);
Long mon2=Long.parseLong(strs2[1]);
Long son3=son1*mon2+son2*mon1;
Long mon3=mon1*mon2;
String str3=son3+"/"+mon3;
String result1=numSimply(str1);
String result2=numSimply(str2);
String result3=numSimply(str3);
System.out.println(result1+" + "+result2+" = "+result3);
}
// 有理数减法
public static void numSub(String str1,String str2) {
String[] strs1=str1.split("/");
String[] strs2=str2.split("/");
Long son1=Long.parseLong(strs1[0]);
Long mon1=Long.parseLong(strs1[1]);
Long son2=Long.parseLong(strs2[0]);
Long mon2=Long.parseLong(strs2[1]);
Long son3=son1*mon2-son2*mon1;
Long mon3=mon1*mon2;
String str3=son3+"/"+mon3;
String result1=numSimply(str1);
String result2=numSimply(str2);
String result3=numSimply(str3);
System.out.println(result1+" - "+result2+" = "+result3);
}
// 有理数乘法
public static void numMult(String str1,String str2) {
String[] strs1=str1.split("/");
String[] strs2=str2.split("/");
Long son1=Long.parseLong(strs1[0]);
Long mon1=Long.parseLong(strs1[1]);
Long son2=Long.parseLong(strs2[0]);
Long mon2=Long.parseLong(strs2[1]);
Long son3=son1*son2;
Long mon3=mon1*mon2;
String str3=son3+"/"+mon3;
String result1=numSimply(str1);
String result2=numSimply(str2);
String result3=numSimply(str3);
System.out.println(result1+" * "+result2+" = "+result3);
}
// 有理数除法
public static void numDivi(String str1,String str2) {
String[] strs1=str1.split("/");
String[] strs2=str2.split("/");
Long son1=Long.parseLong(strs1[0]);
Long mon1=Long.parseLong(strs1[1]);
Long son2=Long.parseLong(strs2[0]);
Long mon2=Long.parseLong(strs2[1]);
String result1=numSimply(str1);
String result2=numSimply(str2);
if(result2.equals("0")) {
System.out.print(result1+" / "+result2+" = Inf");
}else {
Long son3=son1*mon2;
Long mon3=mon1*son2;
String str3=son3+"/"+mon3;
String result3=numSimply(str3);
System.out.print(result1+" / "+result2+" = "+result3);
}
}
}
-
实验截图
-
(四)远程有理数计算器
-
(五)远程复数计算器
-
实验截图


-
3.实验过程中遇到的问题及解决过程
问题1:刚开始按照教程走的时候,客户端和服务器不能连接,显示不出消息
解决:上CSDN查找教程,查怎么样实现客户端和服务器连接。得到的答案是要找到客户端的,需要在命令行中输入ipconfig找到自己电脑的ip地址,然后统一一个不被占用的端口(我选的是10086)
问题2:远程计算器不懂该怎么连接
解决:上CSDN找了很多教程,又询问了其他已经完成的同学,最后在大家帮助下完成了远程计算器的连接。
- 4.其他(感悟、思考等)
实验越来越难做,这次我选择独狼一人做完两个任务,导致工作量和需要学习的内容很多,一整周都在忙Java的学习,不过也让我感到充实,也提醒自己不能轻易地被困难击败。
- 5.参考资料
《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》
《Java程序设计与数据结构教程(第二版)》学习指导



