MapReduce
1. MAPREDUCE实践篇(1)
1.1 MAPREDUCE 示例编写及编程规范
1.1.1 编程规范
(1)用户编写的程序分成三个部分:Mapper,Reducer,Driver(提交运行mr程序的客户端)
(2)Mapper的输入数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
(3)Mapper的输出数据是KV对的形式(KV的类型可自定义)
(4)Mapper中的业务逻辑写在map()方法中
(5)map()方法(maptask进程)对每一个<K,V>调用一次
(6)Reducer的输入数据类型对应Mapper的输出数据类型,也是KV
(7)Reducer的业务逻辑写在reduce()方法中
(8)Reducetask进程对每一组相同k的<k,v>组调用一次reduce()方法
(9)用户自定义的Mapper和Reducer都要继承各自的父类
(10)整个程序需要一个Drvier来进行提交,提交的是一个描述了各种必要信息的job对象
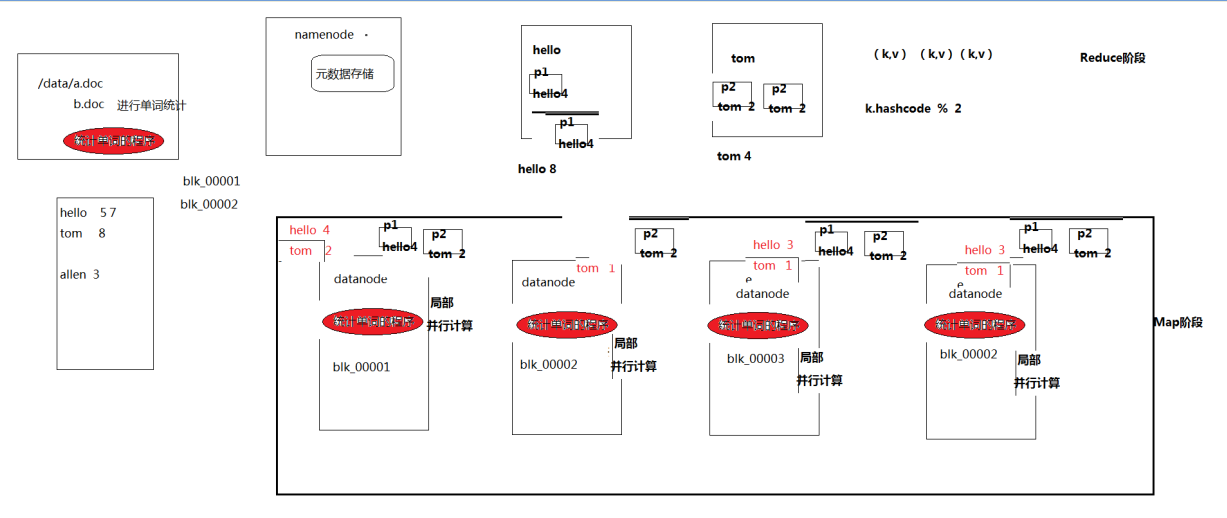
1.7.2 wordcount示例编写
需求:在一堆给定的文本文件中统计输出每一个单词出现的总次数
首先创建maven工程,在pom.xml文件中要导的包和打包插件
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId> <version>2.6.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-hdfs</artifactId> <version>2.6.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId> <version>2.6.4</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId> <artifactId>hadoop-mapreduce-client-core</artifactId> <version>2.6.4</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <!--打包插件--> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.4</version> <configuration> <archive> <manifest> <addClasspath>true</addClasspath> <classpathPrefix>lib/</classpathPrefix> <mainClass>cn.itcast.mapreduce.WordCountDriver</mainClass> </manifest> </archive> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build>
(1)定义一个mapper类
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; /** * * @author AllenWoon * * Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> * KEYIN:是指框架读取到的数据的key类型 * 在默认的读取数据组件InputFormat下,读取的key是一行文本的偏移量,所以key的类型是long类型的 * * VALUEIN指框架读取到的数据的value类型 * 在默认的读取数据组件InputFormat下,读到的value就是一行文本的内容,所以value的类型是String类型的 * * keyout是指用户自定义逻辑方法返回的数据中key的类型 这个是由用户业务逻辑决定的。 * 在我们的单词统计当中,我们输出的是单词作为key,所以类型是String * * VALUEOUT是指用户自定义逻辑方法返回的数据中value的类型 这个是由用户业务逻辑决定的。 * 在我们的单词统计当中,我们输出的是单词数量作为value,所以类型是Integer * * 但是,String ,Long都是jdk中自带的数据类型,在序列化的时候,效率比较低。hadoop为了提高序列化的效率,他就自己自定义了一套数据结构。 * * 所以说在我们的hadoop程序中,如果该数据需要进行序列化(写磁盘,或者网络传输),就一定要用实现了hadoop序列化框架的数据类型 * * * Long------->LongWritable * String----->Text * Integer---->IntWritable * null------->nullWritable * */ public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>{ /** * 这个map方法就是mapreduce程序中被主体程序MapTask所调用的用户业务逻辑方法 * * Maptask会驱动我们的读取数据组件InputFormat去读取数据(KEYIN,VALUEIN),每读取一个(k,v),他就会传入到这个用户写的map方法中去调用一次 * * 在默认的inputFormat实现中,此处的key就是一行的起始偏移量,value就是一行的内容 */ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //获取每一行的文本内容 String lines = value.toString(); String[] words = lines.split(" "); for (String word :words) { context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1)); } } }
(2)定义一个reducer类
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; /*** * * @author AllenWoon * * reducetask在调用我们的reduce方法 * * reducetask应该接收到map阶段(前一阶段)中所有maptask输出的数据中的一部分; * (key.hashcode% numReduceTask==本ReduceTask编号) * * reducetask将接收到的kv数据拿来处理时,是这样调用我们的reduce方法的: * * 先讲自己接收到的所有的kv对按照k分组(根据k是否相同) * * 然后将一组kv中的k传给我们的reduce方法的key变量,把这一组kv中的所有的v用一个迭代器传给reduce方法的变量values * */ public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{ @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int count =0; for(IntWritable v :values){ count += v.get(); } context.write(key, new IntWritable(count)); } }
(3)定义一个主类,用来描述job并提交job
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; /** * * @author AllenWoon * * 本类是客户端用来指定wordcount job程序运行时候所需要的很多参数 * * 比如:指定哪个类作为map阶段的业务逻辑类 哪个类作为reduce阶段的业务逻辑类 * 指定用哪个组件作为数据的读取组件 数据结果输出组件 * 指定这个wordcount jar包所在的路径 * * .... * 以及其他各种所需要的参数 */ public class WordCountDriver { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); conf.set("fs.defaultFS", "hdfs://mini1:9000"); // conf.set("mapreduce.framework.name", "yarn"); // conf.set("yarn.resourcemanager.hostname", "mini1"); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); //$JAVA_HOMEbin -cp hdfs-2.3.4.jar:mapreduce-2.0.6.4.jar; //告诉框架,我们的的程序所在jar包的位置 job.setJar("/root/wordcount.jar"); job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么 //TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/wordcount/input")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/wordcount/output")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
最后,maven-->update project; maven build--->clean package ,apply run进行打包
把包名改成和上面的一样,这里是wordcount.jar,并把包上传到指定路径/root/wordcount.jar
也可以:job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class);不用指定路径
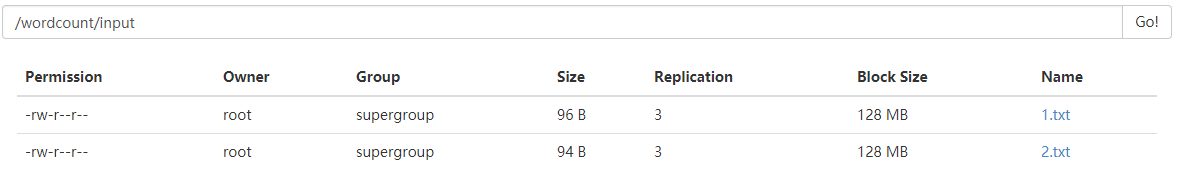
准备测试文件:
创目录:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop fs -mkdir -p /wordcount/input
vi 1.txt
allen hello allen allen hello hello hello
allen allen allen hello hello ello ello
allen allen
vi 2.txt
hello allen allen hello hello hello hello , allen allen
allne hello heool hello allen allen
上传到fdfs:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop fs -put 1.txt 2.txt /wordcount/output
通过http://mini1:50070/explorer.html#/wordcount/output查看是否上传成功
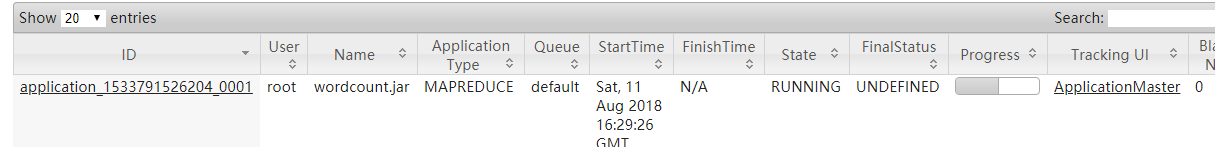
运行程序[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop jar wordcount.jar cn.itcast.mapreduce.WordCountDriver
通过http://mini1:8088/cluster查看程序运行情况
注:
1.集群时间要同步
2.运行过程中如果出现错误: INFO ipc.Client: Retrying connect to server: 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0:10020. Already tried 0 time(s); retry policy is RetryUpToMaximumCountWithFixedSleep(maxRetries=10, sleepTime=1000 MILLISECONDS)
原因:hadoop的historyserver服务没有启动。
解决方案:启动historyserver: mr-jobhistory-daemon.sh start historyserver
运行结束在http://mini1:50070/explorer.html#/wordcount/output可以看到
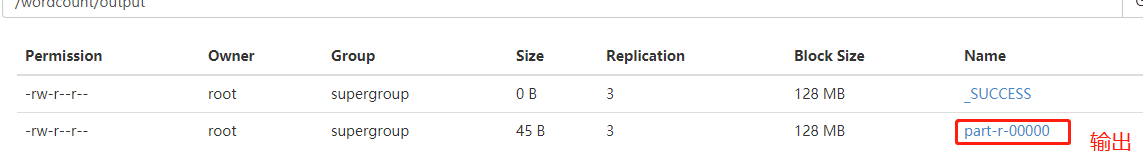
也可以通过命令查看:
[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop fs -cat /wordcount/output/part-r-00000
MAPREDUCE中的Combiner
(1)combiner是MR程序中Mapper和Reducer之外的一种组件
(2)combiner组件的父类就是Reducer
(3)combiner和reducer的区别在于运行的位置:
Combiner是在每一个maptask所在的节点运行
Reducer是接收全局所有Mapper的输出结果;
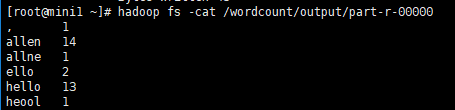
(4) combiner的意义就是对每一个maptask的输出进行局部汇总,以减小网络传输量
如图:

具体实现步骤:
1、 自定义一个combiner继承Reducer,重写reduce方法
2、 在job中设置: job.setCombinerClass(CustomCombiner.class)
(5) combiner能够应用的前提是不能影响最终的业务逻辑
而且,combiner的输出kv应该跟reducer的输入kv类型要对应起来
Combiner的使用要非常谨慎
因为combiner在mapreduce过程中可能调用也肯能不调用,可能调一次也可能调多次
所以:combiner使用的原则是:有或没有都不能影响业务逻辑
1.2 MAPREDUCE程序运行模式
1.2.1 本地运行模式
(1)mapreduce程序是被提交给LocalJobRunner在本地以单进程的形式运行
(2)而处理的数据及输出结果可以在本地文件系统,也可以在hdfs上
(3)怎样实现本地运行?写一个程序,不要带集群的配置文件(本质是你的mr程序的conf中是否有mapreduce.framework.name=local以及yarn.resourcemanager.hostname参数)
(4)本地模式非常便于进行业务逻辑的debug,只要在eclipse中打断点即可
如果在windows下想运行本地模式来测试程序逻辑,需要在windows中配置环境变量:
%HADOOP_HOME% = d:/hadoop-2.6.1
%PATH% = %HADOOP_HOME%\bin
并且要将d:/hadoop-2.6.1的lib和bin目录替换成windows平台编译的版本
1.2.2 集群运行模式
(1)将mapreduce程序提交给yarn集群resourcemanager,分发到很多的节点上并发执行
(2)处理的数据和输出结果应该位于hdfs文件系统
(3)提交集群的实现步骤:
A、将程序打成JAR包,然后在集群的任意一个节点上用hadoop命令启动
$ hadoop jar wordcount.jar cn.itcast.bigdata.mrsimple.WordCountDriver inputpath outputpath
B、直接在linux的eclipse中运行main方法
(项目中要带参数:mapreduce.framework.name=yarn以及yarn的两个基本配置)
C、如果要在windows的eclipse中提交job给集群,则要修改YarnRunner类
(1)创建同名的包和类
(2)修改YarnRunner类

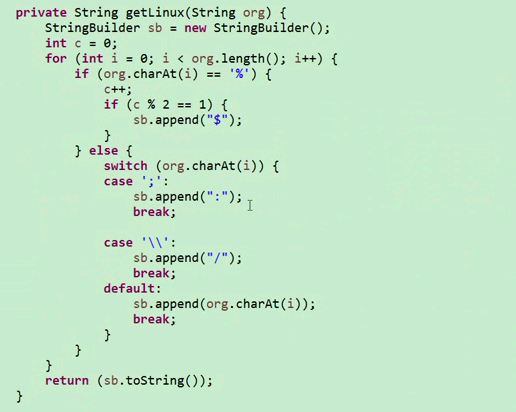
(3)测试
在测试类中要配置

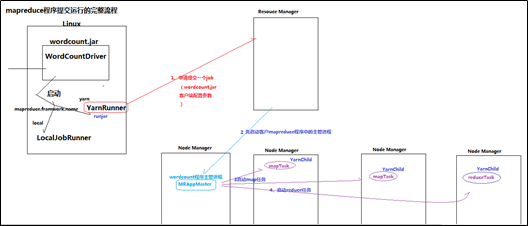
mapreduce程序在集群中运行时的大体流程:
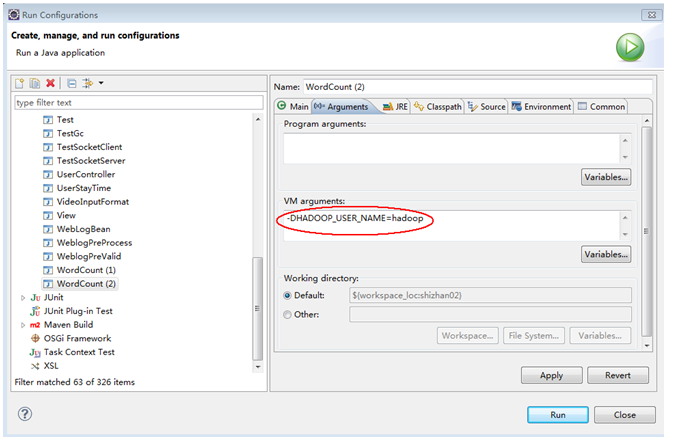
附:在windows平台上访问hadoop时改变自身身份标识的方法之二:
MapReduce运算框架主体工作流程
2. MAPREDUCE实践篇(2)
2.1. Mapreduce中的排序初步
2.1.1 需求
对日志数据中的上下行流量信息汇总,并输出按照总流量倒序排序的结果
数据如下:
1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157995052 13826544101 5C-0E-8B-C7-F1-E0:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 264 0 200 1363157991076 13926435656 20-10-7A-28-CC-0A:CMCC 120.196.100.99 2 4 132 1512 200 1363154400022 13926251106 5C-0E-8B-8B-B1-50:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 240 0 200 1363157993044 18211575961 94-71-AC-CD-E6-18:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 iface.qiyi.com 视频网站 15 12 1527 2106 200 1363157995074 84138413 5C-0E-8B-8C-E8-20:7DaysInn 120.197.40.4 122.72.52.12 20 16 4116 1432 200 1363157993055 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 18 15 1116 954 200 1363157995033 15920133257 5C-0E-8B-C7-BA-20:CMCC 120.197.40.4 sug.so.360.cn 信息安全 20 20 3156 2936 200 1363157983019 13719199419 68-A1-B7-03-07-B1:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.82 4 0 240 0 200 1363157984041 13660577991 5C-0E-8B-92-5C-20:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 s19.cnzz.com 站点统计 24 9 6960 690 200 1363157973098 15013685858 5C-0E-8B-C7-F7-90:CMCC 120.197.40.4 rank.ie.sogou.com 搜索引擎 28 27 3659 3538 200 1363157986029 15989002119 E8-99-C4-4E-93-E0:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 www.umeng.com 站点统计 3 3 1938 180 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200 1363157984040 13602846565 5C-0E-8B-8B-B6-00:CMCC 120.197.40.4 2052.flash2-http.qq.com 综合门户 15 12 1938 2910 200 1363157995093 13922314466 00-FD-07-A2-EC-BA:CMCC 120.196.100.82 img.qfc.cn 12 12 3008 3720 200 1363157982040 13502468823 5C-0A-5B-6A-0B-D4:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 y0.ifengimg.com 综合门户 57 102 7335 110349 200 1363157986072 18320173382 84-25-DB-4F-10-1A:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 input.shouji.sogou.com 搜索引擎 21 18 9531 2412 200 1363157990043 13925057413 00-1F-64-E1-E6-9A:CMCC 120.196.100.55 t3.baidu.com 搜索引擎 69 63 11058 48243 200 1363157988072 13760778710 00-FD-07-A4-7B-08:CMCC 120.196.100.82 2 2 120 120 200 1363157985066 13726238888 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200 1363157993055 13560436666 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 18 15 1116 954 200
2.1.2 分析
基本思路:实现自定义的bean来封装流量信息,并将bean作为map输出的key来传输
MR程序在处理数据的过程中会对数据排序(map输出的kv对传输到reduce之前,会排序),排序的依据是map输出的key
所以,我们如果要实现自己需要的排序规则,则可以考虑将排序因素放到key中,让key实现接口:WritableComparable
然后重写key的compareTo方法
2.1.3 第一步,得到要排序的数据
1、 自定义的bean
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean>{ private long upFlow; private long downFlow; private long sumFlow; //序列化框架在反序列化的时候创建对象的实例会去调用我们的无参构造函数 //如果空参构造函数被覆盖,一定要显示定义一下,否则在反序列时会抛异常 public FlowBean() { } public FlowBean(long upFlow, long downFlow, long sumFlow) { super(); this.upFlow = upFlow; this.downFlow = downFlow; this.sumFlow = sumFlow; } public FlowBean(long upFlow, long downFlow) { super(); this.upFlow = upFlow; this.downFlow = downFlow; this.sumFlow = upFlow+downFlow; } public void set(long upFlow, long downFlow) { this.upFlow = upFlow; this.downFlow = downFlow; this.sumFlow = upFlow+downFlow; } public long getUpFlow() { return upFlow; } public void setUpFlow(long upFlow) { this.upFlow = upFlow; } public long getDownFlow() { return downFlow; } public void setDownFlow(long downFlow) { this.downFlow = downFlow; } public long getSumFlow() { return sumFlow; } public void setSumFlow(long sumFlow) { this.sumFlow = sumFlow; } @Override public String toString() { return upFlow+"\t"+downFlow+"\t"+sumFlow; } //反序列化,从输入流中读取各个字段信息 @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { downFlow=in.readLong(); upFlow=in.readLong(); sumFlow=in.readLong(); } //序列化,将对象的字段信息写入输出流 @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeLong(downFlow); out.writeLong(upFlow); out.writeLong(sumFlow); } @Override public int compareTo(FlowBean o) { return 0; } }
2、 mapper 和 reducer
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; public class FlowSum { // 在kv中传输我们的自定义的对象是可以的 ,不过必须要实现hadoop的序列化机制 也就是implement Writable public static class FlowSumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, FlowBean> { Text k = new Text(); FlowBean v = new FlowBean(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 将读取到的每一行数据进行字段的切分 String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, "\t"); // 抽取我们业务所需要的字段 String phoneNum = fields[1]; long upFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 3]); long downFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 2]); k.set(phoneNum); v.set(upFlow, downFlow); context.write(k, v); } } public static class FlowSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, FlowBean, Text, FlowBean> { FlowBean value = new FlowBean(); // 这里reduce方法接收到的key就是某一组《a手机号,bean》《a手机号,bean》 // 《b手机号,bean》《b手机号,bean》当中的第一个手机号 // 这里reduce方法接收到的values就是这一组kv对中的所以bean的一个迭代器 @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { long upFlowCount = 0; long downFlowCount = 0; for (FlowBean bean : values) { upFlowCount += bean.getUpFlow(); downFlowCount += bean.getDownFlow(); } value.set(upFlowCount, downFlowCount); context.write(key, value); } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf=new Configuration(); Job job=Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(FlowSum.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(FlowSumMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(FlowSumReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型,如果mapper的输出类型与最后的输出类型一致,可省略 // job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); // job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); //告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么 //TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/flowsum/input")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/flowsum/output")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
在pom.xml中把mainClass修改为当前要执行的主函数类<mainClass>cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSum</mainClass>,然后打包上传到Linux服务器
注:修改pom.xml文件后通常会有异常,处理:maven--》update project ;并把jdk版本改为1.7
根据指定的文件路径创建文件: hadoop fs -mkdir -p /flowsum/input
创建要处理的文件:vi flow.txt 拷贝入日志数据,并把flow.txt文件上传到hdfs :hadoop fs -put flow.txt /flowsum/input
然后运行程序:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop jar FlowSum-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSum
2.1.4 第二步,按照总流量倒序排序:
首先在自定义的bean中实现compareTo(FlowBean o)方法
@Override public int compareTo(FlowBean o) { //自定义倒序比较规则 return sumFlow > o.getSumFlow() ? -1:1; }
编写排序的mapper和reducer
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; /** * 实现流量汇总并按照流量大小的倒序排序 前提:处理的数据是已经汇总的结果文件 * @author AllenWoon * */ public class FlowSumSort { public static class FlowSumSortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, FlowBean, Text>{ FlowBean k = new FlowBean(); Text v = new Text(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = line.split("\t"); String phoNum = fields[0]; long upFlowSum = Long.parseLong(fields[1]); long downFlowSum = Long.parseLong(fields[2]); k.set(upFlowSum, downFlowSum); v.set(phoNum); context.write(k, v); } } public static class FlowSumSortReducer extends Reducer<FlowBean, Text, Text, FlowBean>{ @Override protected void reduce(FlowBean bean, Iterable<Text> PhoneNum, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { context.write(PhoneNum.iterator().next(), bean); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(FlowSumSort.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(FlowSumSortMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(FlowSumSortReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(FlowBean.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); //告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么 //TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/flowsum/output")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/flowsum/outputsort")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
在pom.xml中把mainClass修改为当前要执行的主函数类<mainClass>cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumSort</mainClass>,然后打包上传到Linux服务器
然后运行程序:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop jar FlowSumSort-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumSort
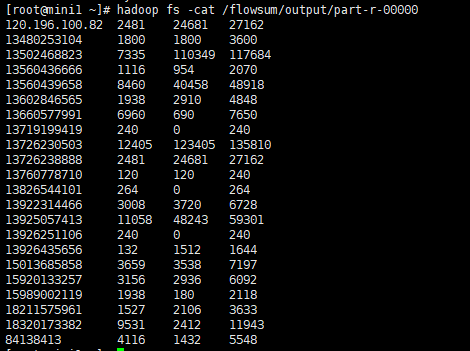
查看输出结果:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop fs -cat /flowsum/outputsort/part-r-00000
2.2 以上是两步实现排序,也可以一步实现排序,就是通过一个TreeMap先保存数据,进行排序,然后在提交:
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Set; import java.util.TreeMap; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; public class FlowSumOneStepSort { // 在kv中传输我们的自定义的对象是可以的 ,不过必须要实现hadoop的序列化机制 也就是implement Writable public static class OneStepFlowSumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, FlowBean> { Text k = new Text(); FlowBean v = new FlowBean(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 将读取到的每一行数据进行字段的切分 String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, "\t"); // 抽取我们业务所需要的字段 String phoneNum = fields[1]; long upFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 3]); long downFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 2]); k.set(phoneNum); v.set(upFlow, downFlow); context.write(k, v); } } public static class OneStepFlowSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, FlowBean, Text, FlowBean> { //这里进行reduce的缓存 TreeMap<FlowBean,Text> treeMap=new TreeMap<FlowBean,Text>(); // 这里reduce方法接收到的key就是某一组《a手机号,bean》《a手机号,bean》 // 《b手机号,bean》《b手机号,bean》当中的第一个手机号 // 这里reduce方法接收到的values就是这一组kv对中的所以bean的一个迭代器 @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { long upFlowCount = 0; long downFlowCount = 0; for (FlowBean bean : values) { upFlowCount += bean.getUpFlow(); downFlowCount += bean.getDownFlow(); } FlowBean value=new FlowBean(); value.set(upFlowCount, downFlowCount); Text text=new Text(key.toString()); treeMap.put(value, text); } //这里进行全局的最终输出 @Override protected void cleanup(Reducer<Text, FlowBean, Text, FlowBean>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { Set<Entry<FlowBean, Text>> entrys=treeMap.entrySet(); for(Entry<FlowBean, Text> entry : entrys){ context.write(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey()); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf=new Configuration(); Job job=Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(FlowSumOneStepSort.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(OneStepFlowSumMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(OneStepFlowSumReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型,如果mapper的输出类型与最后的输出类型一致,可省略 // job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); // job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); //告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么 //TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/flowsum/input")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("/flowsum/outputonestepsort")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
在pom.xml中把mainClass修改为当前要执行的主函数类<mainClass>cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumOneStepSort</mainClass>,然后打包上传到Linux服务器
注:修改pom.xml文件后通常会有异常,处理:maven--》update project ;并把jdk版本改为1.7
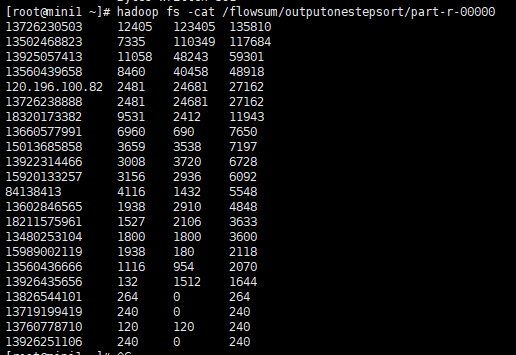
然后运行程序:[root@mini1 ~]# [root@mini1 ~]# hadoop jar FlowSumOneStep-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumOneStepSort
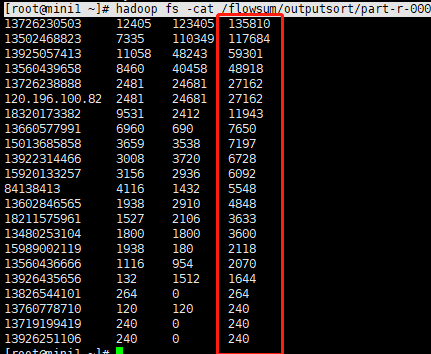
查看输出结果:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop jar FlowSumOneStep-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumOneStepSort
2.3 将流量汇总统计结果按照手机归属地不同省份输出到不同文件中
2.3.1 继承Partitioner类,重写getPartition(Text key, FlowBean value, int numPartitions)方法,实现分区的逻辑处理
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.util.HashMap; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; public class ProvivcePartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, FlowBean> { private static HashMap<String, Integer> provinceMap = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); static { provinceMap.put("135", 0); provinceMap.put("136", 1); provinceMap.put("137", 2); provinceMap.put("138", 3); provinceMap.put("139", 4); } @Override public int getPartition(Text key, FlowBean value, int numPartitions) { Integer code=provinceMap.get(key.toString().substring(0, 3)); if(code!=null) return code; return 5; } }
2.3.2 mapper和reducer类基本不要改变,只需要在main中添加自定义的分区组件
package cn.itcast.mapreduce; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; public class FlowSumProvince { // 在kv中传输我们的自定义的对象是可以的 ,不过必须要实现hadoop的序列化机制 也就是implement Writable public static class FlowSumMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, FlowBean> { Text k = new Text(); FlowBean v = new FlowBean(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 将读取到的每一行数据进行字段的切分 String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, "\t"); // 抽取我们业务所需要的字段 String phoneNum = fields[1]; long upFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 3]); long downFlow = Long.parseLong(fields[fields.length - 2]); k.set(phoneNum); v.set(upFlow, downFlow); context.write(k, v); } } public static class FlowSumReducer extends Reducer<Text, FlowBean, Text, FlowBean> { FlowBean value = new FlowBean(); // 这里reduce方法接收到的key就是某一组《a手机号,bean》《a手机号,bean》 // 《b手机号,bean》《b手机号,bean》当中的第一个手机号 // 这里reduce方法接收到的values就是这一组kv对中的所以bean的一个迭代器 @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<FlowBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { long upFlowCount = 0; long downFlowCount = 0; for (FlowBean bean : values) { upFlowCount += bean.getUpFlow(); downFlowCount += bean.getDownFlow(); } value.set(upFlowCount, downFlowCount); context.write(key, value); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf=new Configuration(); Job job=Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(FlowSumProvince.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(FlowSumMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(FlowSumReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型,如果mapper的输出类型与最后的输出类型一致,可省略 // job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); // job.setMapOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(FlowBean.class); //设置我们的shuffer的分区组件使用我们自定义的组件 job.setPartitionerClass(ProvivcePartitioner.class); //这里设置我们的reduce task个数 默认是一个partition分区对应一个reduce task 输出文件也是一对一 //如果我们的Reduce task个数 < partition分区数 就会报错Illegal partition //如果我们的Reduce task个数 > partition分区数 不会报错,会有空文件产生 //如果我们的Reduce task个数 = 1 partitoner组件就无效了 不存在分区的结果 job.setNumReduceTasks(6); //告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么 //TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("/flowsum/input")); Path out = new Path("/flowsum/output"); FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(conf); if (fileSystem.exists(out)) { fileSystem.delete(out, true);//仅建议在测试中使用 } //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, out); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
在pom.xml中把mainClass修改为当前要执行的主函数类<mainClass>cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumProvince</mainClass>,然后打包上传到Linux服务器
注:修改pom.xml文件后通常会有异常,处理:maven--》update project ;并把jdk版本改为1.7
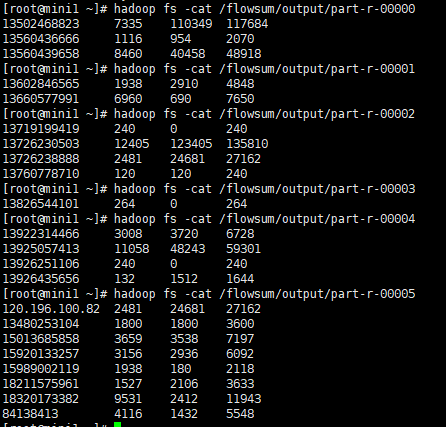
然后运行程序:[root@mini1 ~]# hadoop jar FlowSumProvince-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar cn.itcast.mapreduce.FlowSumProvince
查看输出结果:
3. MAPREDUCE原理篇(1)
Mapreduce是一个分布式运算程序的编程框架,是用户开发“基于hadoop的数据分析应用”的核心框架;
Mapreduce核心功能是将用户编写的业务逻辑代码和自带默认组件整合成一个完整的分布式运算程序,并发运行在一个hadoop集群上;
3.1 为什么要MAPREDUCE
(1)海量数据在单机上处理因为硬件资源限制,无法胜任
(2)而一旦将单机版程序扩展到集群来分布式运行,将极大增加程序的复杂度和开发难度
(3)引入mapreduce框架后,开发人员可以将绝大部分工作集中在业务逻辑的开发上,而将分布式计算中的复杂性交由框架来处理
设想一个海量数据场景下的wordcount需求:
单机版:内存受限,磁盘受限,运算能力受限 分布式: 1、文件分布式存储(HDFS) 2、运算逻辑需要至少分成2个阶段(一个阶段独立并发,一个阶段汇聚) 3、运算程序如何分发 4、程序如何分配运算任务(切片) 5、两阶段的程序如何启动?如何协调? 6、整个程序运行过程中的监控?容错?重试?
可见在程序由单机版扩成分布式时,会引入大量的复杂工作。为了提高开发效率,可以将分布式程序中的公共功能封装成框架,让开发人员可以将精力集中于业务逻辑。
而mapreduce就是这样一个分布式程序的通用框架,其应对以上问题的整体结构如下:
1、MRAppMaster(mapreduce application master) 2、MapTask 3、ReduceTask
3.2 MAPREDUCE框架结构及核心运行机制
3.2.1 结构
一个完整的mapreduce程序在分布式运行时有三类实例进程:
1、MRAppMaster:负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调
2、mapTask:负责map阶段的整个数据处理流程
3、ReduceTask:负责reduce阶段的整个数据处理流程
3.2.2 MR程序运行流程
3.2.2.1 流程示意图
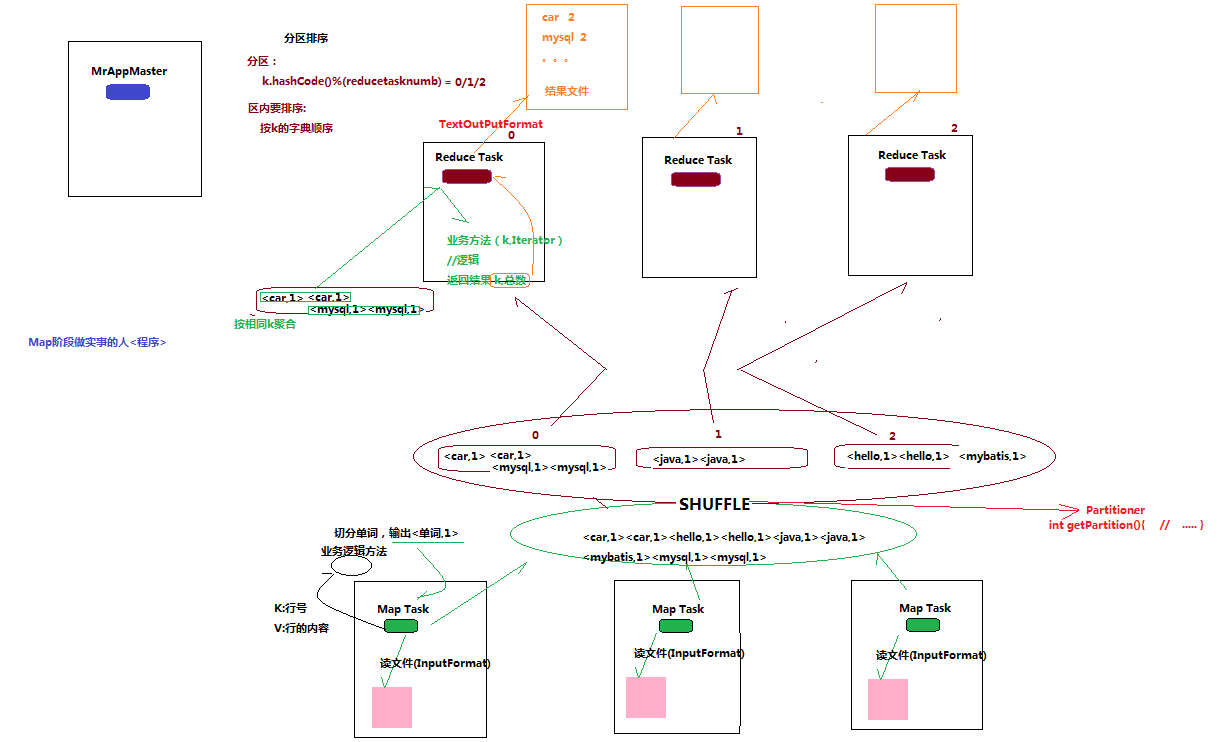
------------------------

3.2.2.2 流程解析
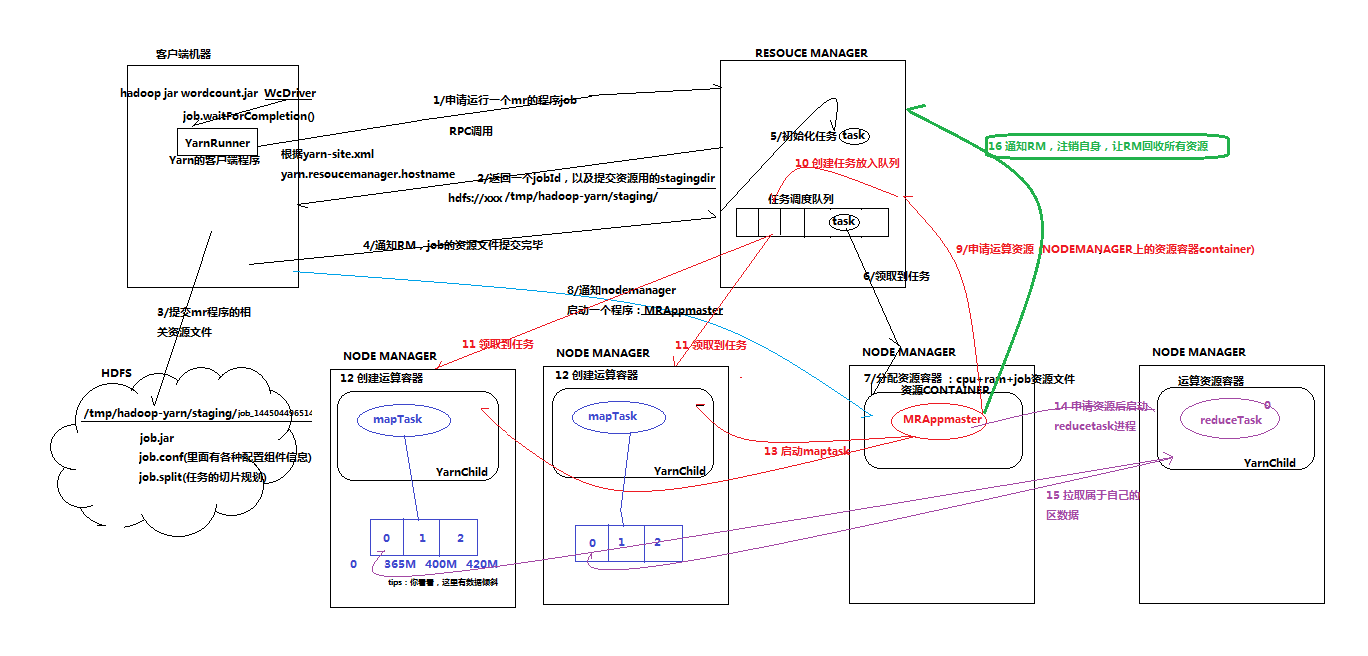
1、 一个mr程序启动的时候,最先启动的是MRAppMaster,MRAppMaster启动后根据本次job的描述信息,计算出需要的maptask实例数量,然后向集群申请机器启动相应数量的maptask进程
2、 maptask进程启动之后,根据给定的数据切片范围进行数据处理,主体流程为:
a) 利用客户指定的inputformat来获取RecordReader读取数据,形成输入KV对
b) 将输入KV对传递给客户定义的map()方法,做逻辑运算,并将map()方法输出的KV对收集到缓存
c) 将缓存中的KV对按照K分区排序后不断溢写到磁盘文件
3、 MRAppMaster监控到所有maptask进程任务完成之后,会根据客户指定的参数启动相应数量的reducetask进程,并告知reducetask进程要处理的数据范围(数据分区)
4、 Reducetask进程启动之后,根据MRAppMaster告知的待处理数据所在位置,从若干台maptask运行所在机器上获取到若干个maptask输出结果文件,并在本地进行重新归并排序,然后按照相同key的KV为一个组,调用客户定义的reduce()方法进行逻辑运算,并收集运算输出的结果KV,然后调用客户指定的outputformat将结果数据输出到外部存储
3.3 MapTask并行度决定机制
maptask的并行度决定map阶段的任务处理并发度,进而影响到整个job的处理速度
那么,mapTask并行实例是否越多越好呢?其并行度又是如何决定呢?
3.3.1 mapTask并行度的决定机制
一个job的map阶段并行度由客户端在提交job时决定
而客户端对map阶段并行度的规划的基本逻辑为:
将待处理数据执行逻辑切片(即按照一个特定切片大小,将待处理数据划分成逻辑上的多个split),然后每一个split分配一个mapTask并行实例处理
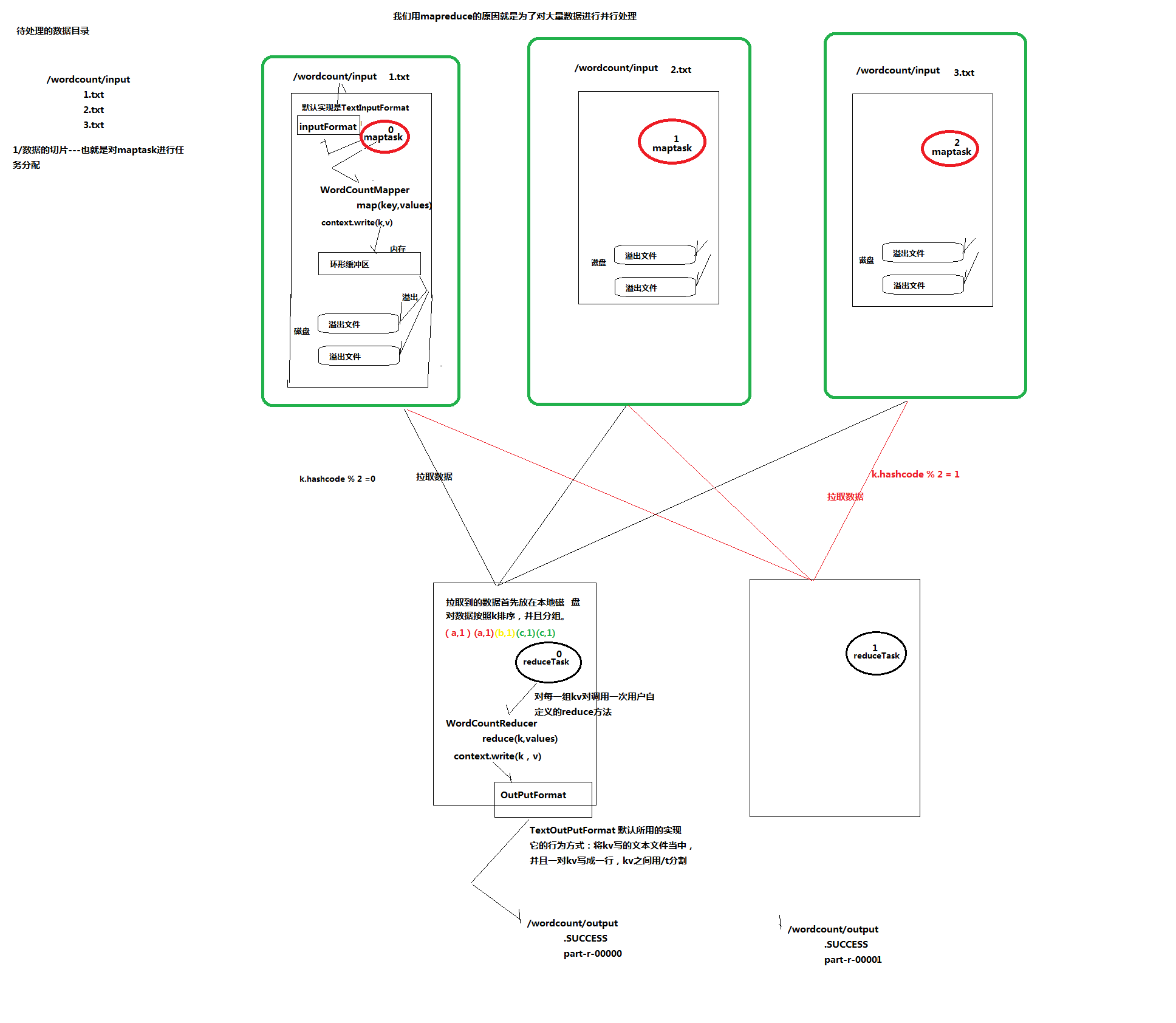
这段逻辑及形成的切片规划描述文件,由FileInputFormat实现类的getSplits()方法完成,其过程如下图:
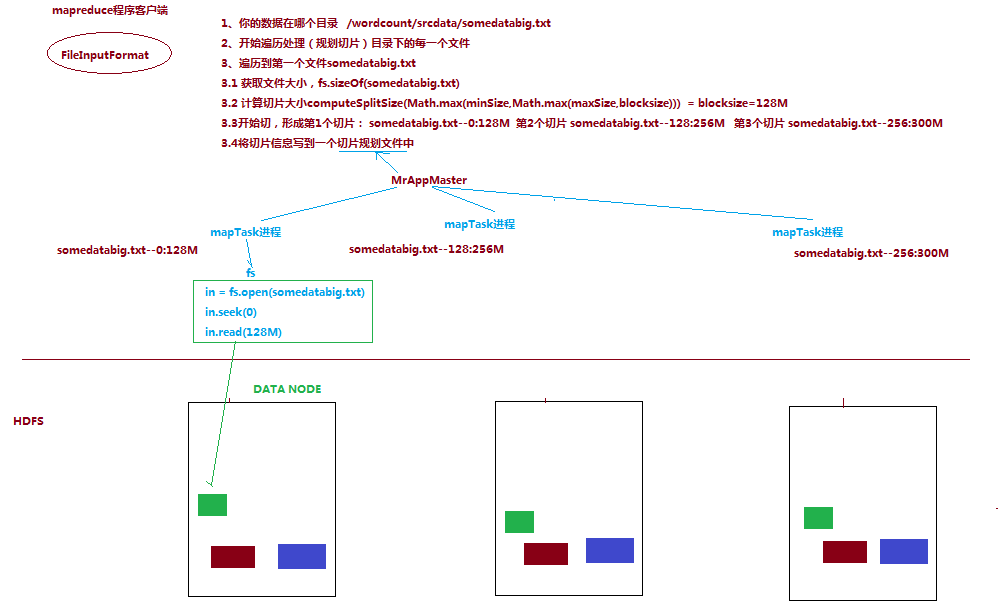
------------------------------
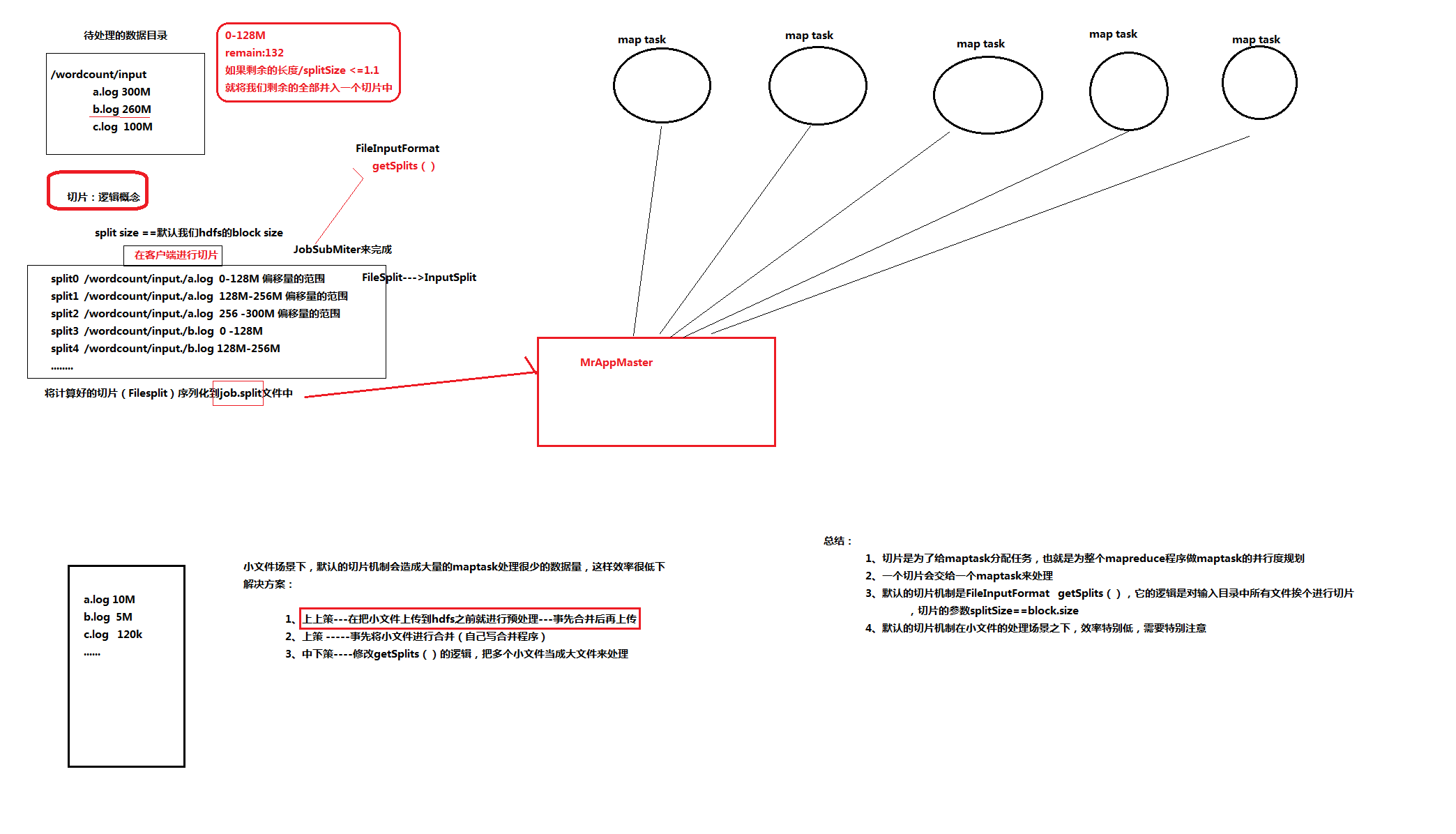
3.3.2 FileInputFormat切片机制
1、切片定义在InputFormat类中的getSplit()方法
2、FileInputFormat中默认的切片机制:
a) 简单地按照文件的内容长度进行切片
b) 切片大小,默认等于block大小
c) 切片时不考虑数据集整体,而是逐个针对每一个文件单独切片
比如待处理数据有两个文件:
file1.txt 320M
file2.txt 10M
经过FileInputFormat的切片机制运算后,形成的切片信息如下:
file1.txt.split1-- 0~128 file1.txt.split2-- 128~256 file1.txt.split3-- 256~320 file2.txt.split1-- 0~10M
3、FileInputFormat中切片的大小的参数配置
通过分析源码,在FileInputFormat中,计算切片大小的逻辑:
Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize)); 切片主要由这几个值来运算决定
minsize:默认值:1
配置参数: mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize
maxsize:默认值:Long.MAXValue
配置参数:mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize
blocksize
maxsize(切片最大值):因此,默认情况下,切片大小=blocksize
参数如果调得比blocksize小,则会让切片变小,而且就等于配置的这个参数的值
minsize (切片最小值):
参数调的比blockSize大,则可以让切片变得比blocksize还大
但是,不论怎么调参数,都不能让多个小文件“划入”一个split
选择并发数的影响因素:
1、运算节点的硬件配置
2、运算任务的类型:CPU密集型还是IO密集型
3、运算任务的数据量
3.4 map并行度的经验之谈
如果硬件配置为2*12core + 64G,恰当的map并行度是大约每个节点20-100个map,最好每个map的执行时间至少一分钟。
l 如果job的每个map或者 reduce task的运行时间都只有30-40秒钟,那么就减少该job的map或者reduce数,每一个task(map|reduce)的setup和加入到调度器中进行调度,这个中间的过程可能都要花费几秒钟,所以如果每个task都非常快就跑完了,就会在task的开始和结束的时候浪费太多的时间。
配置task的JVM重用(JVM重用技术不是指同一Job的两个或两个以上的task可以同时运行于同一JVM上,而是排队按顺序执行)可以改善该问题:
(mapred.job.reuse.jvm.num.tasks,默认是1,表示一个JVM上最多可以顺序执行的task
数目(属于同一个Job)是1。也就是说一个task启一个JVM)
l 如果input的文件非常的大,比如1TB,可以考虑将hdfs上的每个block size设大,比如设成256MB或者512MB
3.5 ReduceTask并行度的决定
reducetask的并行度同样影响整个job的执行并发度和执行效率,但与maptask的并发数由切片数决定不同,Reducetask数量的决定是可以直接手动设置:
//默认值是1,手动设置为4
job.setNumReduceTasks(4);
如果数据分布不均匀,就有可能在reduce阶段产生数据倾斜
注意: reducetask数量并不是任意设置,还要考虑业务逻辑需求,有些情况下,需要计算全局汇总结果,就只能有1个reducetask
尽量不要运行太多的reduce task。对大多数job来说,最好rduce的个数最多和集群中的reduce持平,或者比集群的 reduce slots小。这个对于小集群而言,尤其重要。
3.6 MAPREDUCE程序运行演示
Hadoop的发布包中内置了一个hadoop-mapreduce-example-2.4.1.jar,这个jar包中有各种MR示例程序,可以通过以下步骤运行:
启动hdfs,yarn
然后在集群中的任意一台服务器上启动执行程序(比如运行wordcount):
hadoop jar hadoop-mapreduce-example-2.4.1.jar wordcount /wordcount/data /wordcount/out
4. MAPREDUCE原理篇(2)
4.1 mapreduce的shuffle机制
4.1.1 概述:
- mapreduce中,map阶段处理的数据如何传递给reduce阶段,是mapreduce框架中最关键的一个流程,这个流程就叫shuffle;
- shuffle: 洗牌、发牌——(核心机制:数据分区,排序,缓存);
- 具体来说:就是将maptask输出的处理结果数据,分发给reducetask,并在分发的过程中,对数据按key进行了分区和排序;
4.1.2 主要流程:
Shuffle缓存流程:

shuffle是MR处理流程中的一个过程,它的每一个处理步骤是分散在各个map task和reduce task节点上完成的,整体来看,分为3个操作:
1、分区partition
2、Sort根据key排序
3、Combiner进行局部value的合并
4.1.3 详细流程
1、 maptask收集我们的map()方法输出的kv对,放到内存缓冲区中
2、 从内存缓冲区不断溢出本地磁盘文件,可能会溢出多个文件
3、 多个溢出文件会被合并成大的溢出文件
4、 在溢出过程中,及合并的过程中,都要调用partitoner进行分组和针对key进行排序
5、 reducetask根据自己的分区号,去各个maptask机器上取相应的结果分区数据
6、 reducetask会取到同一个分区的来自不同maptask的结果文件,reducetask会将这些文件再进行合并(归并排序)
7、 合并成大文件后,shuffle的过程也就结束了,后面进入reducetask的逻辑运算过程(从文件中取出一个一个的键值对group,调用用户自定义的reduce()方法)
Shuffle中的缓冲区大小会影响到mapreduce程序的执行效率,原则上说,缓冲区越大,磁盘io的次数越少,执行速度就越快
缓冲区的大小可以通过参数调整, 参数:io.sort.mb 默认100M
4.1.4 详细流程示意图
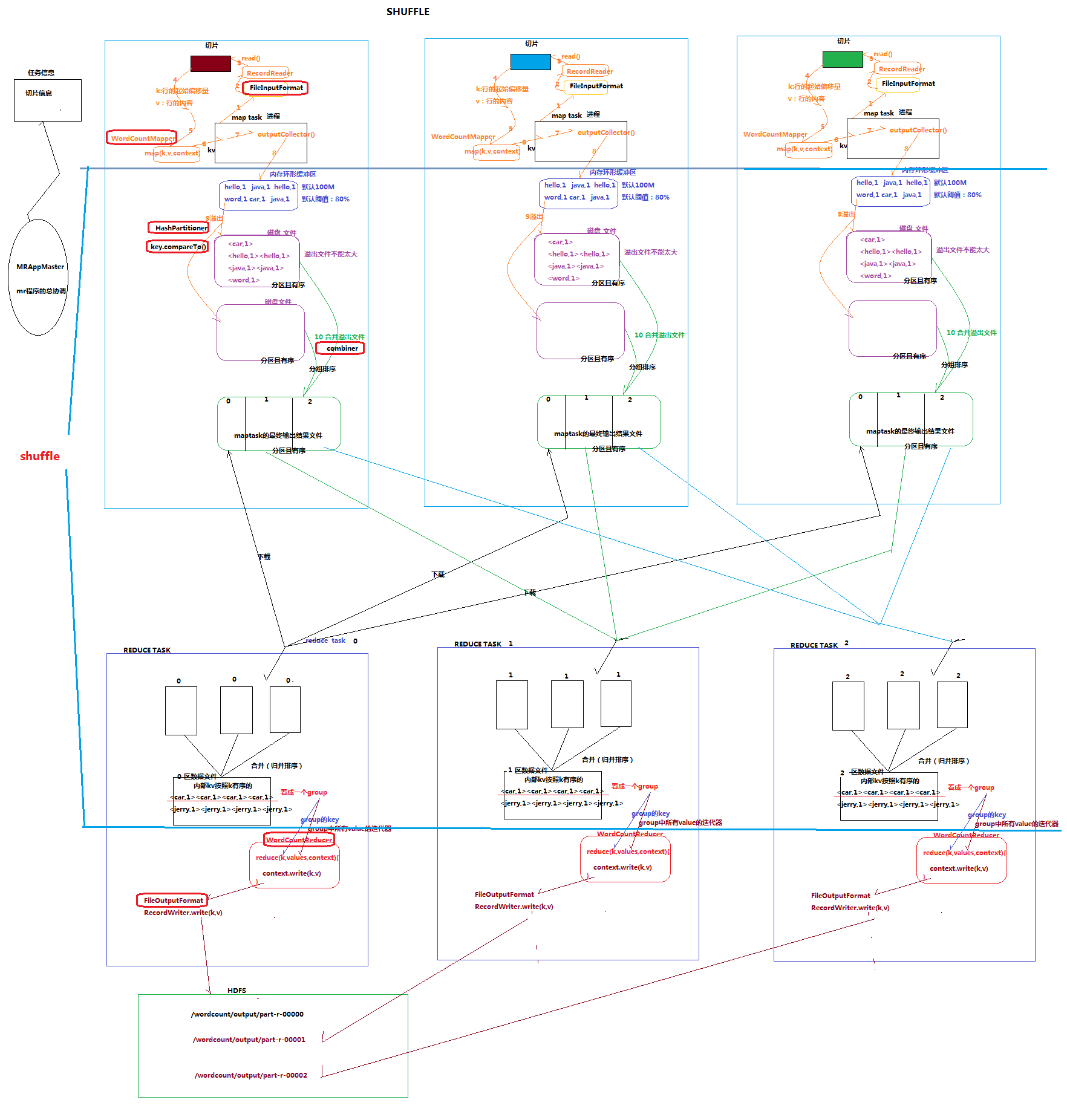
4.2. MAPREDUCE中的序列化
4.2.1 概述
Java的序列化是一个重量级序列化框架(Serializable),一个对象被序列化后,会附带很多额外的信息(各种校验信息,header,继承体系。。。。),不便于在网络中高效传输;
所以,hadoop自己开发了一套序列化机制(Writable),精简,高效
4.2.2 Jdk序列化和MR序列化之间的比较
简单代码验证两种序列化机制的差别:
public class TestSeri { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //定义两个ByteArrayOutputStream,用来接收不同序列化机制的序列化结果 ByteArrayOutputStream ba = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); ByteArrayOutputStream ba2 = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //定义两个DataOutputStream,用于将普通对象进行jdk标准序列化 DataOutputStream dout = new DataOutputStream(ba); DataOutputStream dout2 = new DataOutputStream(ba2); ObjectOutputStream obout = new ObjectOutputStream(dout2); //定义两个bean,作为序列化的源对象 ItemBeanSer itemBeanSer = new ItemBeanSer(1000L, 89.9f); ItemBean itemBean = new ItemBean(1000L, 89.9f); //用于比较String类型和Text类型的序列化差别 Text atext = new Text("a"); // atext.write(dout); itemBean.write(dout); byte[] byteArray = ba.toByteArray(); //比较序列化结果 System.out.println(byteArray.length); for (byte b : byteArray) { System.out.print(b); System.out.print(":"); } System.out.println("-----------------------"); String astr = "a"; // dout2.writeUTF(astr); obout.writeObject(itemBeanSer); byte[] byteArray2 = ba2.toByteArray(); System.out.println(byteArray2.length); for (byte b : byteArray2) { System.out.print(b); System.out.print(":"); } } }
4.2.3 自定义对象实现MR中的序列化接口
如果需要将自定义的bean放在key中传输,则还需要实现comparable接口,因为mapreduce框中的shuffle过程一定会对key进行排序,此时,自定义的bean实现的接口应该是:
public class FlowBean implements WritableComparable<FlowBean>
需要自己实现的方法是:
/** * 反序列化的方法,反序列化时,从流中读取到的各个字段的顺序应该与序列化时写出去的顺序保持一致 */ @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { upflow = in.readLong(); dflow = in.readLong(); sumflow = in.readLong(); } /** * 序列化的方法 */ @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeLong(upflow); out.writeLong(dflow); //可以考虑不序列化总流量,因为总流量是可以通过上行流量和下行流量计算出来的 out.writeLong(sumflow); } @Override public int compareTo(FlowBean o) { //实现按照sumflow的大小倒序排序 return sumflow>o.getSumflow()?-1:1; }
4.3. MapReduce与YARN
4.3.1 YARN概述
Yarn是一个资源调度平台,负责为运算程序提供服务器运算资源,相当于一个分布式的操作系统平台,而mapreduce等运算程序则相当于运行于操作系统之上的应用程序
4.3.2 YARN的重要概念
1、 yarn并不清楚用户提交的程序的运行机制
2、 yarn只提供运算资源的调度(用户程序向yarn申请资源,yarn就负责分配资源)
3、 yarn中的主管角色叫ResourceManager
4、 yarn中具体提供运算资源的角色叫NodeManager
5、 这样一来,yarn其实就与运行的用户程序完全解耦,就意味着yarn上可以运行各种类型的分布式运算程序(mapreduce只是其中的一种),比如mapreduce、storm程序,spark程序,tez ……
6、 所以,spark、storm等运算框架都可以整合在yarn上运行,只要他们各自的框架中有符合yarn规范的资源请求机制即可
7、 Yarn就成为一个通用的资源调度平台,从此,企业中以前存在的各种运算集群都可以整合在一个物理集群上,提高资源利用率,方便数据共享
4.3.3 Yarn中运行运算程序的示例
mapreduce程序的调度过程,如下图
案例加强
(1)倒排索引
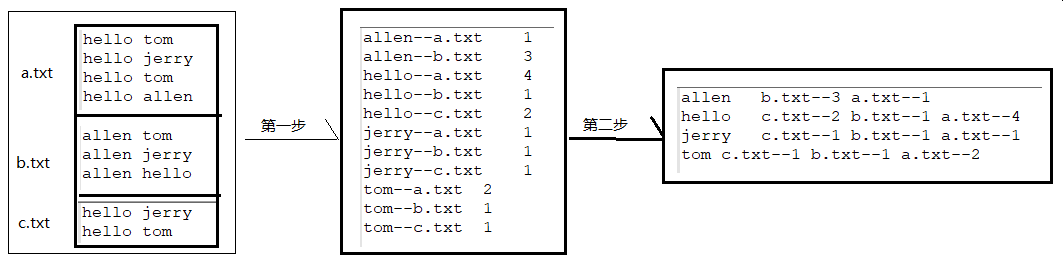
1.第一步
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.index; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat; public class IndexStepOne { public static class IndexStepOneMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>{ Text k = new Text(); IntWritable v = new IntWritable(1); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] words = line.split(" "); FileSplit Split = (FileSplit)context.getInputSplit(); String filename = Split.getPath().getName(); //输出key :单词--文件名 value:1 for(String word : words){ k.set(word +"--"+ filename); context.write(k, v); } } } public static class IndexStepOneReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable>{ IntWritable v = new IntWritable(); @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { int count = 0; for(IntWritable value : values){ count += value.get(); } v.set(count); context.write(key, v); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(IndexStepOne.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(IndexStepOneMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(IndexStepOneReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //这里可以进行combiner组件的设置 job.setCombinerClass(IndexStepOneReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序使用的数据读取组件 结果输出所用的组件是什么 //TextInputFormat是mapreduce程序中内置的一种读取数据组件 准确的说 叫做 读取文本文件的输入组件 job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class); job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/index/input")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/index/output-1")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
2.第二步
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.index; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class IndexStepTwo { public static class IndexStepTwoMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ Text k = new Text(); Text v = new Text(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = line.split("\t"); String word_file = fields[0]; String count = fields[1]; String[] split = word_file.split("--"); String word = split[0]; String file = split[1]; k.set(word); v.set(file+"--"+count); context.write(k, v); } } public static class IndexStepTwoReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ Text v = new Text(); @Override protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer(); for (Text value : values) { sBuffer.append(value.toString()).append(" "); } v.set(sBuffer.toString()); context.write(key, v); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(IndexStepTwo.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(IndexStepTwoMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(IndexStepTwoReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); //这里可以进行combiner组件的设置 job.setCombinerClass(IndexStepTwoReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/index/output-1")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/index/output-2")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
(2)共同好友
A:B,C,D,F,E,O
B:A,C,E,K
C:F,A,D,I
D:A,E,F,L
E:B,C,D,M,L
F:A,B,C,D,E,O,M
G:A,C,D,E,F
H:A,C,D,E,O
I:A,O
J:B,O
K:A,C,D
L:D,E,F
M:E,F,G
O:A,H,I,J
求出哪些人两两之间有共同好友,及他俩的共同好友都是谁
思路图:

1 第一步,输出有某个共同好友的所有用户,例如A I-K-C-B-G-F-H-O-D-,即意味着A 是I,K,C,B,G,F,H,O,D的共同好友
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.commonfriends; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import cn.itcast.mapreduce.index.IndexStepTwo; import cn.itcast.mapreduce.index.IndexStepTwo.IndexStepTwoMapper; import cn.itcast.mapreduce.index.IndexStepTwo.IndexStepTwoReducer; public class CommonFriendsStepOne { public static class CommonFriendsStepOneMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] splits = line.split(":"); String person = splits[0]; String[] friends = splits[1].split(","); for(String fString :friends){ context.write(new Text(fString), new Text(person)); } } } public static class CommonFriendsStepOneReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override protected void reduce(Text friend, Iterable<Text> persons, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer(); for(Text pText :persons){ sBuffer.append(pText).append("-"); } context.write(friend, new Text(sBuffer.toString())); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(CommonFriendsStepOne.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(CommonFriendsStepOneMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(CommonFriendsStepOneReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/commonfriends/input")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/commonfriends/output-1")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
2.第二步,输出结果
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.commonfriends; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class CommonFriendsStepTwo { /** * A I-K-C-B-G-F-H-O-D- B A-F-J-E- C A-E-B-H-F-G-K- * */ public static class CommonFriendsStepTwoMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] splits = line.split("\t"); String friend = splits[0]; String[] persons = splits[1].split("-"); Arrays.sort(persons); for (int i = 0; i < persons.length-1; i++) { for (int j = i+1; j < persons.length; j++) { context.write(new Text(persons[i]+"-"+persons[j]), new Text(friend)); } } } } public static class CommonFriendsStepTwoReducer extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text>{ @Override protected void reduce(Text person_pair, Iterable<Text> friends, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer(); for(Text fText : friends){ sBuffer.append(fText).append(" "); } context.write(person_pair, new Text(sBuffer.toString())); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(CommonFriendsStepTwo.class); //告诉程序,我们的程序所用的mapper类和reducer类是什么 job.setMapperClass(CommonFriendsStepTwoMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(CommonFriendsStepTwoReducer.class); //告诉框架,我们程序输出的数据类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class); //告诉框架,我们要处理的数据文件在那个路劲下 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/commonfriends/output-1")); //告诉框架,我们的处理结果要输出到什么地方 FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/commonfriends/output-2")); boolean res = job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(res?0:1); } }
(3)map端的join算法
1、原理阐述
适用于关联表中有小表的情形;
可以将小表分发到所有的map节点,这样,map节点就可以在本地对自己所读到的大表数据进行join并输出最终结果,可以大大提高join操作的并发度,加快处理速度
2、实现示例
--先在mapper类中预先定义好小表,进行join
--引入实际场景中的解决方案:一次加载数据库或者用distributedcache
pdts.txt
pd001,apple
pd002,banana
pd003,orange
order.txt
Order_0000001,pd001,222.8 Order_0000001,pd002,25.8 Order_0000002,pd005,325.8 Order_0000002,pd003,522.8 Order_0000002,pd004,122.4 Order_0000003,pd001,222.8 Order_0000003,pd001,322.8
TestDistributedCache.java
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.cachefile; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; import java.util.HashMap; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class TestDistributedCache { static class TestDistributedCacheMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text>{ FileReader in = null; BufferedReader reader = null; HashMap<String,String> b_tab = new HashMap<String, String>(); String localpath =null; String uirpath = null; //是在map任务初始化的时候调用一次 @Override protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // //通过这几句代码可以获取到cache file的本地绝对路径,测试验证用 // Path[] files = context.getLocalCacheFiles(); // localpath = files[0].toString(); // URI[] cacheFiles = context.getCacheFiles(); //缓存文件的用法——直接用本地IO来读取 //这里读的数据是map task所在机器本地工作目录中的一个小文件 in = new FileReader("e:/testHadoop/cachefile/pdts.txt"); reader =new BufferedReader(in); String line =null; while(null!=(line=reader.readLine())){ String[] fields = line.split(","); b_tab.put(fields[0],fields[1]); } IOUtils.closeStream(reader); IOUtils.closeStream(in); } @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { //这里读的是这个map task所负责的那一个切片数据(在hdfs上) String[] fields = value.toString().split(","); String a_itemid = fields[0]; String pid = fields[1]; String a_amount = fields[2]; String b_name = b_tab.get(pid); // 输出结果 1001 98.9 banan context.write(new Text(a_itemid), new Text(a_amount + "\t" +b_name )); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(TestDistributedCache.class); job.setMapperClass(TestDistributedCacheMapper.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class); //这里是我们正常的需要处理的数据所在路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/cachefile/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/cachefile/ouput")); //不需要reducer job.setNumReduceTasks(0); //分发一个文件到task进程的工作目录 // job.addCacheFile(new URI("hdfs://hadoop-server01:9000/cachefile/pdts.txt")); job.addCacheFile(new URI("file:/e:/testHadoop/cachefile/pdts.txt")); //分发一个归档文件到task进程的工作目录 // job.addArchiveToClassPath(archive); //分发jar包到task节点的classpath下 // job.addFileToClassPath(jarfile); job.waitForCompletion(true); } }
(4)TopN问题
Order_0000001,pd001,222.8 Order_0000001,pd002,25.8 Order_0000002,pd005,325.8 Order_0000002,pd003,522.8 Order_0000002,pd004,122.4 Order_0000003,pd001,222.8 Order_0000003,pd001,322.8
ItemidGroupingComparator.java
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.topOne; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator; /** * 用于控制shuffle过程中reduce端对kv对的聚合逻辑 * @author duanhaitao@itcast.cn * */ public class ItemidGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator { protected ItemidGroupingComparator() { super(OrderBean.class, true); } @Override public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) { OrderBean abean = (OrderBean) a; OrderBean bbean = (OrderBean) b; //将item_id相同的bean都视为相同,从而聚合为一组 return abean.getItemid().compareTo(bbean.getItemid()); } }
ItemIdPartitioner.java
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.topOne; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; public class ItemIdPartitioner extends Partitioner<OrderBean, NullWritable>{ @Override public int getPartition(OrderBean key, NullWritable value, int numPartitions) { return (key.getItemid().hashCode()& Integer.MAX_VALUE)%numPartitions; } }
OrderBean.java
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.topOne; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.DoubleWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; /** * 订单信息bean,实现hadoop的序列化机制 * @author duanhaitao@itcast.cn * */ public class OrderBean implements WritableComparable<OrderBean>{ private Text itemid; private DoubleWritable amount; public OrderBean() { } public OrderBean(Text itemid, DoubleWritable amount) { set(itemid, amount); } public void set(Text itemid, DoubleWritable amount) { this.itemid = itemid; this.amount = amount; } public Text getItemid() { return itemid; } public DoubleWritable getAmount() { return amount; } @Override public int compareTo(OrderBean o) { int cmp = this.itemid.compareTo(o.getItemid()); if (cmp == 0) { cmp = -this.amount.compareTo(o.getAmount()); } return cmp; } @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeUTF(itemid.toString()); out.writeDouble(amount.get()); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { String readUTF = in.readUTF(); double readDouble = in.readDouble(); this.itemid = new Text(readUTF); this.amount= new DoubleWritable(readDouble); } @Override public String toString() { return itemid.toString() + "\t" + amount.get(); } }
1.TopOne.java
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.topOne; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.DoubleWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /** * 利用secondarysort机制输出每种item订单金额最大的记录 * @author duanhaitao@itcast.cn */ public class TopOne { static class SecondarySortMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, NullWritable>{ OrderBean bean = new OrderBean(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, ","); bean.set(new Text(fields[0]), new DoubleWritable(Double.parseDouble(fields[2]))); context.write(bean, NullWritable.get()); } } static class SecondarySortReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, NullWritable, OrderBean, NullWritable>{ //在设置了groupingcomparator以后,这里收到的kv数据 就是: <1001 87.6>,null <1001 76.5>,null .... //此时,reduce方法中的参数key就是上述kv组中的第一个kv的key:<1001 87.6> //要输出同一个item的所有订单中最大金额的那一个,就只要输出这个key @Override protected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<NullWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { context.write(key, NullWritable.get()); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(TopOne.class); job.setMapperClass(SecondarySortMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(SecondarySortReducer.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/top/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/top/output1")); //指定shuffle所使用的GroupingComparator类 job.setGroupingComparatorClass(ItemidGroupingComparator.class); //指定shuffle所使用的partitioner类 job.setPartitionerClass(ItemIdPartitioner.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(1); job.waitForCompletion(true); } }
2.TopN
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.topN; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.DoubleWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /** * 利用secondarysort机制输出每种item订单金额最大的记录 * @author duanhaitao@itcast.cn */ public class TopN { static class TopNMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, OrderBean, OrderBean>{ OrderBean v = new OrderBean(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, ","); v.set(new Text(fields[0]), new DoubleWritable(Double.parseDouble(fields[2]))); context.write(v,v); } } static class TopNReducer extends Reducer<OrderBean, OrderBean,NullWritable, OrderBean> { Integer topn=1; int count=0; @Override protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration(); topn=Integer.parseInt(conf.get("topn")); } //要输出同一个item的所有订单中最大金额的那一个,就只要输出这个key @Override protected void reduce(OrderBean key, Iterable<OrderBean> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { count=0; for(OrderBean bean : values){ if((count++)==topn){ count=0; return; } context.write(NullWritable.get(),bean); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); conf.set("topn", "2"); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(TopN.class); job.setMapperClass(TopNMapper.class); job.setReducerClass(TopNReducer.class); job.setMapOutputKeyClass(OrderBean.class); job.setMapOutputValueClass(OrderBean.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(NullWritable.class); job.setOutputValueClass(OrderBean.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/top/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/top/outputN")); //指定shuffle所使用的GroupingComparator类 job.setGroupingComparatorClass(ItemidGroupingComparator.class); //指定shuffle所使用的partitioner类 job.setPartitionerClass(ItemIdPartitioner.class); job.setNumReduceTasks(1); job.waitForCompletion(true); } }
(5)json解析:1、对原始json数据进行解析,变成普通文本数据
1.在pom.xml中添加依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.1.40</version>
</dependency>
2.编写bean
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.json; import java.io.DataInput; import java.io.DataOutput; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable; public class OriginBean implements WritableComparable<OriginBean>{ private long movie; private long rate; private long timeStamp; private long uid; public OriginBean(long movie, long rate, long timeStamp, long uid) { super(); this.movie = movie; this.rate = rate; this.timeStamp = timeStamp; this.uid = uid; } public OriginBean() { } public long getMovie() { return movie; } public void setMovie(long movie) { this.movie = movie; } public long getRate() { return rate; } public void setRate(long rate) { this.rate = rate; } public long getTimeStamp() { return timeStamp; } public void setTimeStamp(long timeStamp) { this.timeStamp = timeStamp; } public long getUid() { return uid; } public void setUid(long uid) { this.uid = uid; } @Override public String toString() { return movie+"\t"+rate+"\t"+timeStamp+"\t"+uid; } @Override public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException { out.writeLong(movie); out.writeLong(rate); out.writeLong(timeStamp); out.writeLong(uid); } @Override public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException { this.movie=in.readLong(); this.rate=in.readLong(); this.timeStamp=in.readLong(); this.uid=in.readLong(); } @Override public int compareTo(OriginBean o) { return 0; } }
3.JsonToText
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.json; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; public class JsonToText { static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable>{ Text k=new Text(); @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { JSONObject valueJson=JSON.parseObject(value.toString()); Long movie=valueJson.getLong("movie"); OriginBean bean=new OriginBean(movie, valueJson.getLong("rate"), valueJson.getLong("timeStamp"), valueJson.getLong("uid")); k.set(bean.toString()); context.write(k,NullWritable.get()); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); conf.set("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize", "16777216"); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(JsonToText.class); job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/json/input")); FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/json/output")); job.setNumReduceTasks(0); job.waitForCompletion(true); } }
(6)运营商日志增强
需求
现有一些原始日志需要做增强解析处理,流程:
1、 从原始日志文件中读取数据
2、 根据日志中的一个URL字段到外部知识库中获取信息增强到原始日志
3、 如果成功增强,则输出到增强结果目录;如果增强失败,则抽取原始数据中URL字段输出到待爬清单目录

分析
程序的关键点是要在一个mapreduce程序中根据数据的不同输出两类结果到不同目录,这类灵活的输出需求可以通过自定义outputformat来实现
实现
实现要点:
1、 在mapreduce中访问外部资源
2、 自定义outputformat,改写其中的recordwriter,改写具体输出数据的方法write()
代码实现如下:
数据库获取数据的工具
首先要在pom.xml中导包
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.36</version>
</dependency>
并且要执行sql文件
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.flowanalyse; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.Statement; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class DBLoader { public static void dbLoader(Map<String, String> ruleMap) throws Exception { Connection conn = null; Statement st = null; ResultSet res = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hadoop", "root", "root"); st = conn.createStatement(); res = st.executeQuery("select url,content from url_rule"); while (res.next()) { ruleMap.put(res.getString(1), res.getString(2)); } } finally { try{ if(res!=null){ res.close(); } if(st!=null){ st.close(); } if(conn!=null){ conn.close(); } }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
自定义一个outputformat
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.flowanalyse; import java.io.IOException; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; /** * maptask或者reducetask在最终输出时,先调用OutputFormat的getRecordWriter方法拿到一个RecordWriter * 然后再调用RecordWriter的write(k,v)方法将数据写出 * * @author * */ public class LogEnhanceOutputFormat extends FileOutputFormat<Text, NullWritable> { @Override public RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> getRecordWriter(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(context.getConfiguration()); Path enhancePath = new Path("e:/testHadoop/flowanalysz/en/log.dat"); Path tocrawlPath = new Path("e:/testHadoop/flowanalysz/crw/url.dat"); FSDataOutputStream enhancedOs = fs.create(enhancePath); FSDataOutputStream tocrawlOs = fs.create(tocrawlPath); return new EnhanceRecordWriter(enhancedOs, tocrawlOs); } /** * 构造一个自己的recordwriter * * @author * */ static class EnhanceRecordWriter extends RecordWriter<Text, NullWritable> { FSDataOutputStream enhancedOs = null; FSDataOutputStream tocrawlOs = null; public EnhanceRecordWriter(FSDataOutputStream enhancedOs, FSDataOutputStream tocrawlOs) { super(); this.enhancedOs = enhancedOs; this.tocrawlOs = tocrawlOs; } @Override public void write(Text key, NullWritable value) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String result = key.toString(); // 如果要写出的数据是待爬的url,则写入待爬清单文件 /logenhance/tocrawl/url.dat if (result.contains("tocrawl")) { tocrawlOs.write(result.getBytes()); } else { // 如果要写出的数据是增强日志,则写入增强日志文件 /logenhance/enhancedlog/log.dat enhancedOs.write(result.getBytes()); } } @Override public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { if (tocrawlOs != null) { tocrawlOs.close(); } if (enhancedOs != null) { enhancedOs.close(); } } } }
开发mapreduce处理流程
package cn.itcast.mapreduce.flowanalyse; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils; import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Counter; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; public class LogEnhance { static class LogEnhanceMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, NullWritable> { Map<String, String> ruleMap = new HashMap<String, String>(); Text k = new Text(); NullWritable v = NullWritable.get(); // 从数据库中加载规则信息倒ruleMap中 @Override protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { try { DBLoader.dbLoader(ruleMap); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // 获取一个计数器用来记录不合法的日志行数, 组名, 计数器名称 Counter counter = context.getCounter("malformed", "malformedline"); String line = value.toString(); String[] fields = StringUtils.split(line, "\t"); try { String url = fields[26]; String content_tag = ruleMap.get(url); // 判断内容标签是否为空,如果为空,则只输出url到待爬清单;如果有值,则输出到增强日志 if (content_tag == null) { k.set(url + "\t" + "tocrawl" + "\n"); context.write(k, v); } else { k.set(line + "\t" + content_tag + "\n"); context.write(k, v); } } catch (Exception exception) { counter.increment(1); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); job.setJarByClass(LogEnhance.class); job.setMapperClass(LogEnhanceMapper.class); job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); // 要控制不同的内容写往不同的目标路径,可以采用自定义outputformat的方法 job.setOutputFormatClass(LogEnhanceOutputFormat.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/flowanalysz/input")); // 尽管我们用的是自定义outputformat,但是它是继承制fileoutputformat // 在fileoutputformat中,必须输出一个_success文件,所以在此还需要设置输出path FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path("e:/testHadoop/flowanalysz/output")); // 不需要reducer job.setNumReduceTasks(0); job.waitForCompletion(true); System.exit(0); } }
5.mapreduce参数优化
5.1 资源相关参数
1)以下参数是在用户自己的mr应用程序中配置就可以生效
(1) mapreduce.map.memory.mb: 一个Map Task可使用的资源上限(单位:MB),默认为1024。如果Map Task实际使用的资源量超过该值,则会被强制杀死。
(2) mapreduce.reduce.memory.mb: 一个Reduce Task可使用的资源上限(单位:MB),默认为1024。如果Reduce Task实际使用的资源量超过该值,则会被强制杀死。
(3) mapreduce.map.cpu.vcores: 每个Map task可使用的最多cpu core数目, 默认值: 1
(4) mapreduce.reduce.cpu.vcores: 每个Reduce task可使用的最多cpu core数目, 默认值: 1
(5) mapreduce.map.java.opts: Map Task的JVM参数,你可以在此配置默认的java heap size等参数, e.g.
“-Xmx1024m -verbose:gc -Xloggc:/tmp/@taskid@.gc” (@taskid@会被Hadoop框架自动换为相应的taskid), 默认值: “”
(6) mapreduce.reduce.java.opts: Reduce Task的JVM参数,你可以在此配置默认的java heap size等参数, e.g.
“-Xmx1024m -verbose:gc -Xloggc:/tmp/@taskid@.gc”, 默认值: “”
2)应该在yarn启动之前就配置在服务器的配置文件中才能生效
(7) yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-mb 1024 给应用程序container分配的最小内存
(8) yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb 8192 给应用程序container分配的最大内存
(9) yarn.scheduler.minimum-allocation-vcores 1
(10)yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-vcores 32
(11)yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb 8192
3)shuffle性能优化的关键参数,应在yarn启动之前就配置好
(12) mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb 100 //shuffle的环形缓冲区大小,默认100m
(13) mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent 0.8 //环形缓冲区溢出的阈值,默认80%
5.2 容错相关参数
(1) mapreduce.map.maxattempts: 每个Map Task最大重试次数,一旦重试参数超过该值,则认为Map Task运行失败,默认值:4。
(2) mapreduce.reduce.maxattempts: 每个Reduce Task最大重试次数,一旦重试参数超过该值,则认为Map Task运行失败,默认值:4。
(3) mapreduce.map.failures.maxpercent: 当失败的Map Task失败比例超过该值为,整个作业则失败,默认值为0. 如果你的应用程序允许丢弃部分输入数据,则该该值设为一个大于0的值,比如5,表示如果有低于5%的Map Task失败(如果一个Map Task重试次数超过mapreduce.map.maxattempts,则认为这个Map Task失败,其对应的输入数据将不会产生任何结果),整个作业扔认为成功。
(4) mapreduce.reduce.failures.maxpercent: 当失败的Reduce Task失败比例超过该值为,整个作业则失败,默认值为0.
(5) mapreduce.task.timeout: Task超时时间,经常需要设置的一个参数,该参数表达的意思为:如果一个task在一定时间内没有任何进入,即不会读取新的数据,也没有输出数据,则认为该task处于block状态,可能是卡住了,也许永远会卡主,为了防止因为用户程序永远block住不退出,则强制设置了一个该超时时间(单位毫秒),默认是300000。如果你的程序对每条输入数据的处理时间过长(比如会访问数据库,通过网络拉取数据等),建议将该参数调大,该参数过小常出现的错误提示是“AttemptID:attempt_14267829456721_123456_m_000224_0 Timed out after 300 secsContainer killed by the ApplicationMaster.”。
5.3 本地运行mapreduce 作业
设置以下几个参数:
mapreduce.framework.name=local
mapreduce.jobtracker.address=local
fs.defaultFS=local
5.4 效率和稳定性相关参数
(1) mapreduce.map.speculative: 是否为Map Task打开推测执行机制,默认为false
(2) mapreduce.reduce.speculative: 是否为Reduce Task打开推测执行机制,默认为false
(3) mapreduce.job.user.classpath.first & mapreduce.task.classpath.user.precedence:当同一个class同时出现在用户jar包和hadoop jar中时,优先使用哪个jar包中的class,默认为false,表示优先使用hadoop jar中的class。
(4) mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize: FileInputFormat做切片时的最小切片大小,(5)mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize: FileInputFormat做切片时的最大切片大小
(切片的默认大小就等于blocksize,即 134217728)
6.mapreduce数据压缩
6.1 概述
这是mapreduce的一种优化策略:通过压缩编码对mapper或者reducer的输出进行压缩,以减少磁盘IO,提高MR程序运行速度(但相应增加了cpu运算负担)
1、 Mapreduce支持将map输出的结果或者reduce输出的结果进行压缩,以减少网络IO或最终输出数据的体积
2、 压缩特性运用得当能提高性能,但运用不当也可能降低性能
3、 基本原则:
运算密集型的job,少用压缩
IO密集型的job,多用压缩
6.2 MR支持的压缩编码
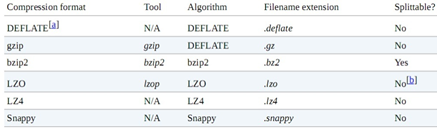
6.3 Reducer输出压缩
在配置参数或在代码中都可以设置reduce的输出压缩
1、在配置参数中设置
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress=false
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec
mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type=RECORD
2、在代码中设置
|
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); FileOutputFormat.setCompressOutput(job, true); FileOutputFormat.setOutputCompressorClass(job, (Class<? extends CompressionCodec>) Class.forName("")); |
6.4 Mapper输出压缩
在配置参数或在代码中都可以设置reduce的输出压缩
1、在配置参数中设置
mapreduce.map.output.compress=false
mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec=org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.DefaultCodec
2、在代码中设置:
|
conf.setBoolean(Job.MAP_OUTPUT_COMPRESS, true); conf.setClass(Job.MAP_OUTPUT_COMPRESS_CODEC, GzipCodec.class, CompressionCodec.class); |
6.5 压缩文件的读取
Hadoop自带的InputFormat类内置支持压缩文件的读取,比如TextInputformat类,在其initialize方法中:
|
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException { FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit; Configuration job = context.getConfiguration(); this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE); start = split.getStart(); end = start + split.getLength(); final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job); fileIn = fs.open(file); //根据文件后缀名创建相应压缩编码的codec CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file); if (null!=codec) { isCompressedInput = true; decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec); //判断是否属于可切片压缩编码类型 if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) { final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn = ((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream( fileIn, decompressor, start, end, SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK); //如果是可切片压缩编码,则创建一个CompressedSplitLineReader读取压缩数据 in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes); start = cIn.getAdjustedStart(); end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd(); filePosition = cIn; } else { //如果是不可切片压缩编码,则创建一个SplitLineReader读取压缩数据,并将文件输入流转换成解压数据流传递给普通SplitLineReader读取 in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn, decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes); filePosition = fileIn; } } else { fileIn.seek(start); //如果不是压缩文件,则创建普通SplitLineReader读取数据 in = new SplitLineReader(fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes); filePosition = fileIn; } |
7. Mapreduce的其他补充
7.1 计数器应用
在实际生产代码中,常常需要将数据处理过程中遇到的不合规数据行进行全局计数,类似这种需求可以借助mapreduce框架中提供的全局计数器来实现
示例代码如下:
public class MultiOutputs { //通过枚举形式定义自定义计数器 enum MyCounter{MALFORORMED,NORMAL} static class CommaMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, LongWritable> { @Override protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { String[] words = value.toString().split(","); for (String word : words) { context.write(new Text(word), new LongWritable(1)); } //对枚举定义的自定义计数器加1 context.getCounter(MyCounter.MALFORORMED).increment(1); //通过动态设置自定义计数器加1 context.getCounter("counterGroupa", "countera").increment(1); } }
7.2 多job串联
一个稍复杂点的处理逻辑往往需要多个mapreduce程序串联处理,多job的串联可以借助mapreduce框架的JobControl实现
示例代码:
ControlledJob cJob1 = new ControlledJob(job1.getConfiguration()); ControlledJob cJob2 = new ControlledJob(job2.getConfiguration()); ControlledJob cJob3 = new ControlledJob(job3.getConfiguration()); cJob1.setJob(job1); cJob2.setJob(job2); cJob3.setJob(job3); // 设置作业依赖关系 cJob2.addDependingJob(cJob1); cJob3.addDependingJob(cJob2);
JobControl jobControl = new JobControl("RecommendationJob"); jobControl.addJob(cJob1); jobControl.addJob(cJob2); jobControl.addJob(cJob3); // 新建一个线程来运行已加入JobControl中的作业,开始进程并等待结束 Thread jobControlThread = new Thread(jobControl); jobControlThread.start(); while (!jobControl.allFinished()) { Thread.sleep(500); } jobControl.stop(); return 0;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号