线程
线程
1.概念

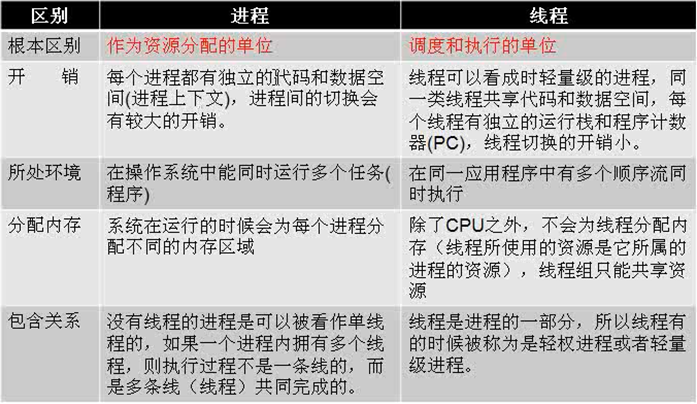
一.线程与进程的区别
2.创建
一.继承 Thread

|
/** * 模拟龟兔赛跑 1、创建多线程 继承 Thread +重写run(线程体) 2、使用线程: 创建子类对象 + 对象.start() 线程启动*/ public class Rabbit extends Thread { public void run() {//线程体 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("兔子跑了"+i+"步"); } } } class Tortoise extends Thread { public void run() {//线程体 for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ System.out.println("乌龟跑了"+i+"步"); } } } public class RabbitApp { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建子类对象 Rabbit rab = new Rabbit(); Tortoise tor =new Tortoise(); //调用start 方法 rab.start(); //不要调用run方法 tor.start(); for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("main==>"+i); } } } |
二.实现 Runnable接口

1.静态代理 设计模式
12. } 13. //接口 14. interface Marry{ public abstract void marry();} 15. //真实角色 16. class You implements Marry{
20. } 21. //代理角色 22. class WeddingCompany implements Marry{
29. } |
2.Runnable创建线程
|
/** 推荐 Runnable 创建线程: 1)、避免单继承的局限性 2)、便于共享资源 使用 Runnable 创建线程 1、类 实现 Runnable接口 +重写 run() -->真实角色类 2、启动多线程 使用静态代理 1)、创建真实角色 2)、创建代理角色 +真实角色引用 3)、调用 .start() 启动线程*/ public class Programmer implements Runnable { public void run() { for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("一边敲helloworld...."); } } } public class ProgrammerApp { public static void main(String[] args) { Programmer pro =new Programmer(); //1)、创建真实角色 Thread proxy =new Thread(pro); //2)、创建代理角色 +真实角色引用 proxy.start(); //3)、调用 .start() 启动线程 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("一边聊qq...."); } } } /** 方便共享资源*/ public class Web12306 implements Runnable { private int num =50; public void run() { while(true){ if(num<=0){ break; //跳出循环 } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢到了"+num--); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Web12306 web = new Web12306();//真实角色 //代理 Thread t1 =new Thread(web,"路人甲"); Thread t2 =new Thread(web,"黄牛已"); Thread t3 =new Thread(web,"攻城师"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start();//启动线程 } } |
三.通过Callable接口实现多线程

|
/**使用Callable创建线程*/ public class Call { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { //创建线程 ExecutorService ser=Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); Race tortoise = new Race("老不死",1000); Race rabbit = new Race("小兔子",500); //获取值 Future<Integer> result1 =ser.submit(tortoise) ; Future<Integer> result2 =ser.submit(rabbit) ;
Thread.sleep(2000); //2秒 tortoise.setFlag(false); //停止线程体循环 rabbit.setFlag(false);
int num1 =result1.get(); int num2 =result2.get(); System.out.println("乌龟跑了-->"+num1+"步"); System.out.println("小兔子跑了-->"+num2+"步"); //停止服务 ser.shutdownNow(); } }
class Race implements Callable<Integer>{ private String name ; //名称 private long time; //延时时间 private boolean flag =true; private int step =0; //步 public Race() { } public Race(String name) { super(); this.name = name; } public Race(String name,long time) { super(); this.name = name; this.time =time; } public Integer call() throws Exception { while(flag){ Thread.sleep(time); //延时 step++; } return step; } public String getName() { return name;} public void setName(String name) { this.name = name;} public long getTime() { return time;} public void setTime(long time) { this.time = time;} public boolean isFlag() { return flag;} public void setFlag(boolean flag) { this.flag = flag;} public int getStep() { return step;} public void setStep(int step) { this.step = step; } } |
3.状态
一. 线程状态

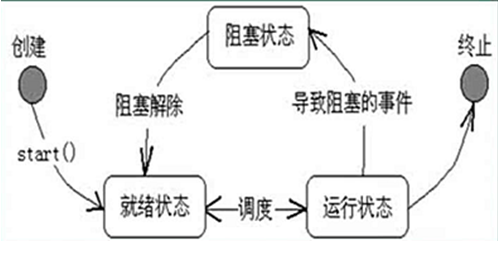
二.停止线程

|
public class StopDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Study s =new Study(); new Thread(s).start(); for(int i=0;i<100;i++){ if(50==i){ //外部干涉 s.stop(); } System.out.println("main.....-->"+i); } } } class Study implements Runnable{ //1)、线程类中 定义 线程体使用的标识 private boolean flag =true; @Override public void run() { //2)、线程体使用该标识 while(flag){ System.out.println("study thread...."); } } //3)、对外提供方法改变标识 public void stop(){ this.flag =false; } }
|
三.阻塞

|
/** join:合并线程*/ public class JoinDemo01 extends Thread { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { JoinDemo01 demo = new JoinDemo01(); Thread t = new Thread(demo); //新生 t.start();//就绪 //cpu调度 运行 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ if(50==i){ t.join(); //main阻塞... } System.out.println("main...."+i); } } public void run() { for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("join...."+i); } } } /** yield:暂停线程*/ public class YieldDemo01 extends Thread { public static void main(String[] args) { YieldDemo01 demo = new YieldDemo01(); Thread t = new Thread(demo); //新生 t.start();//就绪 //cpu调度 运行 for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ if(i%20==0){ //暂停本线程 main Thread.yield(); } System.out.println("main...."+i); } } public void run() { for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){ System.out.println("yield...."+i); } } }
/**倒计时:1、倒数10个数,一秒内打印一个2、倒计时*/ public class SleepDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Date endTime =new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()+10*1000); long end =endTime.getTime(); while(true){ //输出 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("mm:ss").format(endTime)); //等待一秒 Thread.sleep(1000); //构建下一秒时间 endTime =new Date(endTime.getTime()-1000); //10秒以内 继续 否则 退出 if(end-10000>endTime.getTime()){ break; } } } public static void test1() throws InterruptedException{ int num =10; while(true){ System.out.println(num--); Thread.sleep(1000); //暂停 if(num<=0){ break; } } } } /**Sleep模拟 网络延时 线程不安全的类*/ public class SleepDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //真实角色 Web12306 web= new Web12306(); Web12306 web2 = new Web12306(); //代理 Thread t1 =new Thread(web,"路人甲"); Thread t2 =new Thread(web,"黄牛已"); Thread t3 =new Thread(web,"攻城师"); //启动线程 t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); } }
class Web12306 implements Runnable { private int num =50; public void run() { while(true){ if(num<=0){ break; //跳出循环 } try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"抢到了"+num--); } } }
|
4.基本信息
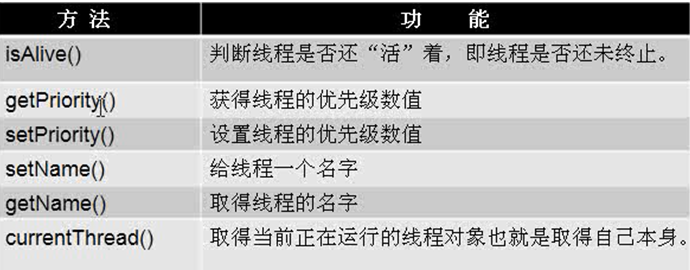
|
public class MyThread implements Runnable { private boolean flag =true; private int num =0; public void run() { while(flag){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->"+num++);} } public void stop(){ this.flag=!this.flag; } }
/** Thread.currentThread():当前线程 setName():设置名称 getName():获取名称 isAlive():判断状态 */ public class InfoDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThread it =new MyThread(); Thread proxy =new Thread(it,"挨踢"); proxy.setName("test"); System.out.println(proxy.getName()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()); //main
proxy.start(); System.out.println("启动后的状态:"+proxy.isAlive()); Thread.sleep(200); it.stop(); Thread.sleep(100); System.out.println("停止后的状态:"+proxy.isAlive()); } } /**优先级:概率,不是绝对的先后顺序 MAX_PRIORITY 10 NORM_PRIORITY 5 (默认) MIN_PRIORITY 1 setPriority() getPriority() */ public class InfoDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { MyThread it =new MyThread(); Thread p1 =new Thread(it,"挨踢1"); MyThread it2 =new MyThread(); Thread p2 =new Thread(it2,"挨踢2"); p1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); //设置优先级 p2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);//设置优先级 p1.start(); p2.start(); Thread.sleep(100); it.stop(); it2.stop(); } } |
5.同步
一.单例设计模式
|
/**单例创建的方式 * 1、懒汉式 * 1)、构造器私有化 2)、声明私有的静态属性 * 3)、对外提供访问属性的静态方法,确保该对象存在*/ public class MyJvm { private static MyJvm instance; private MyJvm(){} public static MyJvm getInstance (){ if(null==instance){ //提供效率 synchronized(MyJvm.class){ if(null==instance){ //安全 instance =new MyJvm(); } } } return instance; } } /**饿汉式 1)、构造器私有化 2)、声明私有的静态属性,同时创建该对象 * 3)、对外提供访问属性的静态方法*/ class MyJvm2 { private static MyJvm2 instance =new MyJvm2(); private MyJvm2(){} public static MyJvm2 getInstance (){ return instance; } } /**类在使用的时候加载 ,延缓加载时间*/ class MyJvm3 { private static class JVMholder{ private static MyJvm3 instance =new MyJvm3(); } private MyJvm3(){} public static MyJvm3 getInstance (){ return JVMholder.instance; } } |

二.同步块与同步方法
|
/**单例设计模式:确保一个类只有一个对象 */ public class SynDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { JvmThread thread1 = new JvmThread(100); JvmThread thread2 = new JvmThread(500); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } } class JvmThread extends Thread{ private long time; public JvmThread() {} public JvmThread(long time) { this.time =time; } public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->创建:"+Jvm.getInstance(time)); } } /** * 单例设计模式 * 确保一个类只有一个对象 * 懒汉式 double checking * 1、构造器私有化,避免外部直接创建对象 * 2、声明一个私有的静态变量 * 3、创建一个对外的公共的静态方法 访问该变量,如果变量没有对象,创建该对象 */ class Jvm { //声明一个私有的静态变量 private static Jvm instance =null; //构造器私有化,避免外部直接创建对象 private Jvm(){ } //创建一个对外的公共的静态方法 访问该变量,如果变量没有对象,创建该对象 public static Jvm getInstance(long time){ // c d e -->效率 提供 已经存在对象的访问效率 if(null==instance){ // a b synchronized(Jvm.class){ if(null==instance ){ try { Thread.sleep(time); //延时 ,放大错误 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } instance =new Jvm(); } } }//a return instance; }
public static Jvm getInstance3(long time){ //a b c d e -->效率不高 c 存在对象也需要等待 synchronized(Jvm.class){ if(null==instance ){ try { Thread.sleep(time); //延时 ,放大错误 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } instance =new Jvm(); } return instance; } } public static synchronized Jvm getInstance2(long time){ //线程安全synchronized if(null==instance ){ try { Thread.sleep(time); //延时 ,放大错误 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } instance =new Jvm(); } return instance; } public static Jvm getInstance1(long time){//线程不安全 if(null==instance ){ try { Thread.sleep(time); //延时 ,放大错误 } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } instance =new Jvm(); } return instance; } } |
三.死锁
|
/**过多的同步方法可能造成死锁*/ public class SynDemo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { Object g =new Object(); Object m = new Object(); Test t1 =new Test(g,m); Test2 t2 = new Test2(g,m); Thread proxy = new Thread(t1); Thread proxy2 = new Thread(t2); proxy.start(); proxy2.start(); } } class Test implements Runnable{ Object goods ; Object money ; public Test(Object goods, Object money) { super(); this.goods = goods; this.money = money; } public void run() { while(true){ test(); } } public void test(){ synchronized(goods){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized(money){} } System.out.println("一手给钱"); } }
class Test2 implements Runnable{ Object goods ; Object money ; public Test2(Object goods, Object money) { super(); this.goods = goods; this.money = money;} public void run() { while(true){ test(); } } public void test(){ synchronized(money){ try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized(goods){} } System.out.println("一手给货"); } } |
6.生产者消费者
|
/**一个场景,共同的资源 生产者消费者模式 信号灯法 wait() :等待,释放锁 sleep 不释放锁 notify()/notifyAll():唤醒 与 synchronized 一起使用*/ public class Movie { private String pic ; //信号灯: //flag -->T 生产生产,消费者等待 ,生产完成后通知消费 //flag -->F 消费者消费 生产者等待, 消费完成后通知生产 private boolean flag =true; public synchronized void play(String pic){//播放 if(!flag){ //生产者等待 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //开始生产 try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("生产了:"+pic); this.pic =pic; //生产完毕 this.notify();//通知消费 this.flag =false; //生产者停下 }
public synchronized void watch(){ if(flag){ //消费者等待 try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //开始消费 try { Thread.sleep(200); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("消费了"+pic); //消费完毕 this.notifyAll();//通知生产 this.flag=true; //消费停止 } } /**生产者*/ public class Player implements Runnable { private Movie m ; public Player(Movie m) { super(); this.m = m; } public void run() { for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ if(0==i%2){ m.play("左青龙"); }else{ m.play("右白虎"); } } } } /**消费者*/ public class Watcher implements Runnable { private Movie m ; public Watcher(Movie m) { super(); this.m = m; } public void run() { for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ m.watch(); } } } public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { //共同的资源 Movie m = new Movie(); //多线程 Player p = new Player(m); Watcher w = new Watcher(m);
new Thread(p).start(); new Thread(w).start(); } } |
7.任务调度
|
/**了解 Timer() schedule(TimerTask task, Date time) schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) 自学 quartz */ public class TimeDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Timer timer =new Timer(); timer.schedule(new TimerTask(){
@Override public void run() { System.out.println("so easy...."); }}, new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()+1000), 200); }
}
|
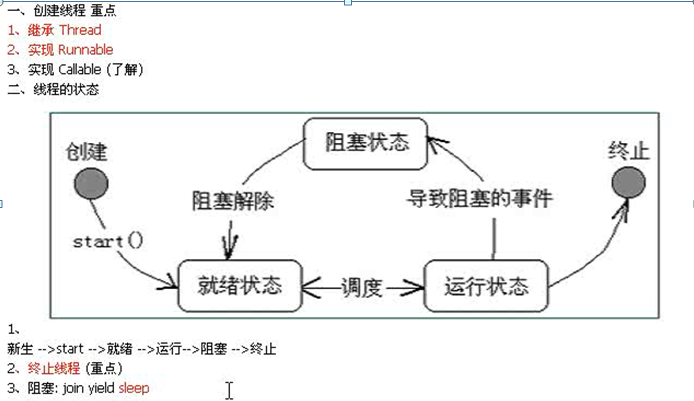
8.总结





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号