数组
数组为什么特殊


package arrays; //: arrays/ContainerComparison.java import java.util.*; class BerylliumSphere { private static long counter; private final long id = counter++; public String toString() { return "Sphere " + id; } } public class ContainerComparison { public static void main(String[] args) { BerylliumSphere[] spheres = new BerylliumSphere[10]; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) spheres[i] = new BerylliumSphere(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(spheres)); System.out.println(spheres[4]); List<BerylliumSphere> sphereList = new ArrayList<BerylliumSphere>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) sphereList.add(new BerylliumSphere()); System.out.println(sphereList); System.out.println(sphereList.get(4)); int[] integers = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(integers)); System.out.println(integers[4]); List<Integer> intList = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5)); intList.add(97); System.out.println(intList); System.out.println(intList.get(4)); } }
输出结果:


数组是第一级对象

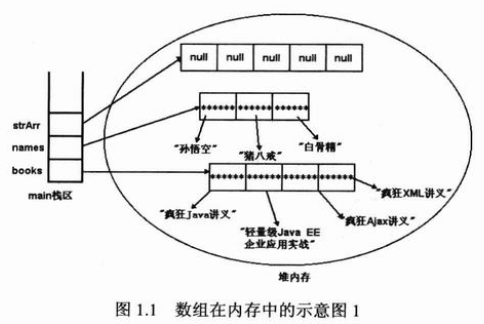

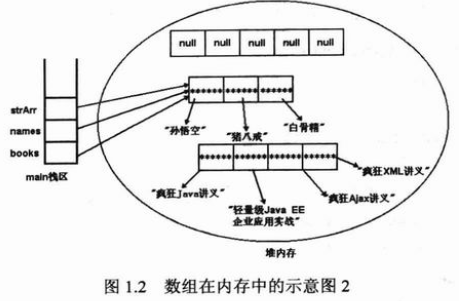


package arrays; //: arrays/ArrayOptions.java //Initialization & re-assignment of arrays. import java.util.*; public class ArrayOptions { public static void main(String[] args) { // Arrays of objects: BerylliumSphere[] a; // 未初始化的局部变量,在对它正确地初始化之前,编译器不能用此引用做任何事情 BerylliumSphere[] b = new BerylliumSphere[5];//此时并没有对象注入数组,但可以询问数组大小 。缺点:无法知道数组中有多少个确切的元素,length只表示数组能够容纳多少个元素,而不是实际保持元素个数 // The references inside the array are // automatically initialized to null: System.out.println("b: " + Arrays.toString(b)); BerylliumSphere[] c = new BerylliumSphere[4];//动态初始化 for (int i = 0; i < c.length; i++) if (c[i] == null) // Can test for null reference c[i] = new BerylliumSphere(); // 静态初始化的简化形式(聚集初始化) BerylliumSphere[] d = { new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere() }; // 动态的聚集初始化,可以在任何位置创建和初始化数组对象 a = new BerylliumSphere[] { new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), }; // (Trailing comma is optional in both cases) System.out.println("a.length = " + a.length); System.out.println("b.length = " + b.length); System.out.println("c.length = " + c.length); System.out.println("d.length = " + d.length); a = d; System.out.println("a.length = " + a.length); // Arrays of primitives: int[] e; // Null reference int[] f = new int[5]; // The primitives inside the array are // automatically initialized to zero: System.out.println("f: " + Arrays.toString(f)); int[] g = new int[4]; for (int i = 0; i < g.length; i++) g[i] = i * i; int[] h = { 11, 47, 93 }; // Compile error: variable e not initialized: // !System.out.println("e.length = " + e.length); System.out.println("f.length = " + f.length); System.out.println("g.length = " + g.length); System.out.println("h.length = " + h.length); e = h; System.out.println("e.length = " + e.length); e = new int[] { 1, 2 }; System.out.println("e.length = " + e.length); } }

注:

基本类型数据的初始化

public class Test { public static void main(String args[]){ //定義一個int[]类型的数组变量 int[] iArr; //静态初始化数组,数组长度为3 iArr=new int[]{2,5,-12}; } }





注:当通过引用变量来访问实例属性,或者调用非静态方法时,如果该引用变量还未引用一个有效的对象,程序就会引发NullPointerException运行时异常
引用型数组的初始化



返回一个数组

package arrays; //: arrays/IceCream.java // Returning arrays from methods. import java.util.*; public class IceCream { private static Random rand = new Random(47); static final String[] FLAVORS = { "Chocolate", "Strawberry", "Vanilla Fudge Swirl", "Mint Chip", "Mocha Almond Fudge", "Rum Raisin", "Praline Cream", "Mud Pie" }; public static String[] flavorSet(int n) { if (n > FLAVORS.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set too big"); String[] results = new String[n]; boolean[] picked = new boolean[FLAVORS.length]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int t; do t = rand.nextInt(FLAVORS.length); while (picked[t]); results[i] = FLAVORS[t]; picked[t] = true; } return results; } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) System.out.println(Arrays.toString(flavorSet(3))); } }
输出:



多维数组

package arrays; import java.util.*; public class MultidimensionalPrimitiveArray { public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] a = { { 1, 2, 3, }, { 4, 5, 6, }, }; System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(a)); } }
输出:


package arrays; import java.util.*; public class ThreeDWithNew { public static void main(String[] args) { // 3-D array with fixed length: int[][][] a = new int[2][2][4]; System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(a)); } }
输出:


package arrays; import java.util.*; public class RaggedArray { public static void main(String[] args) { Random rand = new Random(47); // 3-D array with varied-length vectors: int[][][] a = new int[rand.nextInt(7)][][]; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { a[i] = new int[rand.nextInt(5)][]; for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) a[i][j] = new int[rand.nextInt(5)]; } System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(a)); } }


import java.util.*; public class MultidimensionalObjectArrays { public static void main(String[] args) { BerylliumSphere[][] spheres = { { new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere() }, { new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere() }, { new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere(), new BerylliumSphere() }, }; System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(spheres)); } } /* Output: [[Sphere 0, Sphere 1], [Sphere 2, Sphere 3, Sphere 4, Sphere 5], [Sphere 6, Sphere 7, Sphere 8, Sphere 9, Sphere 10, Sphere 11, Sphere 12, Sphere 13]] *///:~

import java.util.*; public class AutoboxingArrays { public static void main(String[] args) { Integer[][] a = { // Autoboxing: { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 }, { 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30 }, { 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60 }, { 71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80 }, }; System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(a)); } } /* Output: [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], [21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30], [51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60], [71, 72, 73, 74, 75, 76, 77, 78, 79, 80]] *///:~






