对象的深度复制和浅复制 (深度拷贝和浅拷贝)
对象的深度复制和浅复制
(深度拷贝和浅拷贝)
作者:Jesai
时间:2018年2月11日 21:46:22
我们在实际的开发项目里面为了使得开发更加的便捷和方便,总会不经意的使用一些第三方的持久化框架(Object Relational Mapping,简称ORM,或O/RM,或O/R mapping),比如C#里面的ADO.NET Entity Framework、Nhibernate以及java里面的MyBaits和Hibernate等等,有时候,我们需要复制一个持久化对象,然后再持久化到数据库里面去,往往有同学是这么操作的,下面我以java的Hibernate为例子。
1 public Car getCarById(Long id) { 2 Criteria criteria = getSession().createCriteria(Car.class); 3 criteria.add(Restrictions.eq("id", id)); 4 return (Car)criteria.uniqueResult(); 5 }
通过上面代码我们等到一个Car的持久化对象。然后我现在要新增一辆一模一样的车,除了车牌号不一样和ID主键不一样。我们是怎么做的呢,首先,刚写编程不久的同学就想到了下面的方法
1 public void Save(Car car) { 2 Car carNew=new Car(); 3 carNew.Id=”1”; 4 carNew.Color= car. Color; 5 carNew.Price= car. Price; 6 carNew.No=”33333”; 7 …… 8 getSession().Save(car); 9 }
这是新手最喜欢用的方式,但是对于一个老程序员来说,他们可不想写那么长长的一段代码,老程序员的思想总是写最少的代码,干更多的事情。于是,有“聪明”的同学是这么做的
1 public void Save(Car car) { 2 Car carNew=new Car(); 3 carNew =car; 4 carNew.Id=”3”; 5 carNew.No=”33333”; 6 getSession().Save(car); 7 }
的确是简洁了很多呢,当这个同学很兴奋的去执行测试的时候就会发现Hibernate报错,
我们总会在平常的工作里遇到对象克隆的问题。也许有很多同学会被这个问题所困扰。这到底是怎么回事呢?
这就需要用值引用和地址引用的知识来解释这个现象了,我们先来看看什么是值引用和地址引用,
引用传递的是对象的地址,值传递的是变量的值
使用引用传递,被调用函数使用的是调用函数传入的对象本身,也就是说在被调用函数中对对象进行修改将直接导致外部对象的值被修改。
而值传递,传递进去的是变量的副本(即拷贝),此时在被调用函数中对形参的任何修改都不会改变外部变量的值。
值传递是传递数据:如基本数据类型都是值传递
引用传递是把形参和实参的指针指向了堆中的同一对象,对象的引用和数组的引用。
如
1 Int a=10; 2 3 Int b=a; 4 5 a=20;
变量和对象的实例化的时候都会在计算机的内存里面申请一个内存,值引用是a和b各自申请一个区域存放数据。当a再次改变值的时候,b并不会随着a的改变而改变。
1 Student s=new Student(); 2 3 s.Name=”Tom”; 4 5 Student s1=new Student(); 6 7 s1=s; 8 9 s.Name=“Jon”;
对象就是地址引用,在这里,当后面s的Name发生改变的时候,s1也是跟随着改变的。
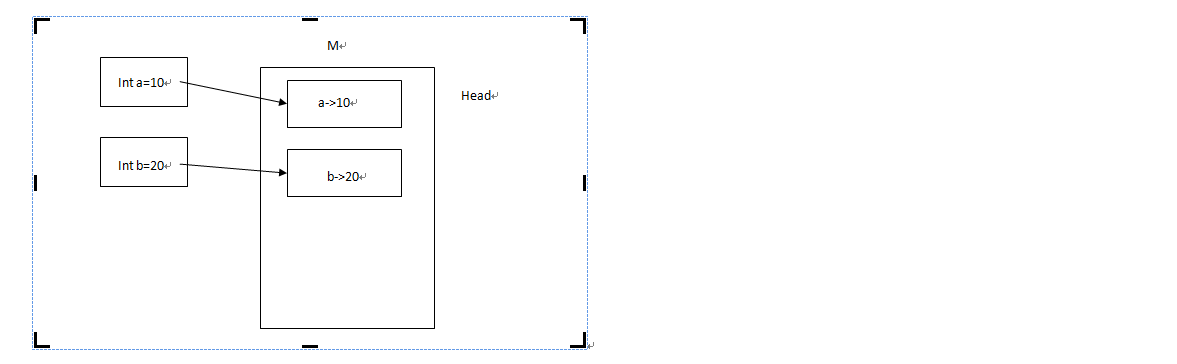
值引用
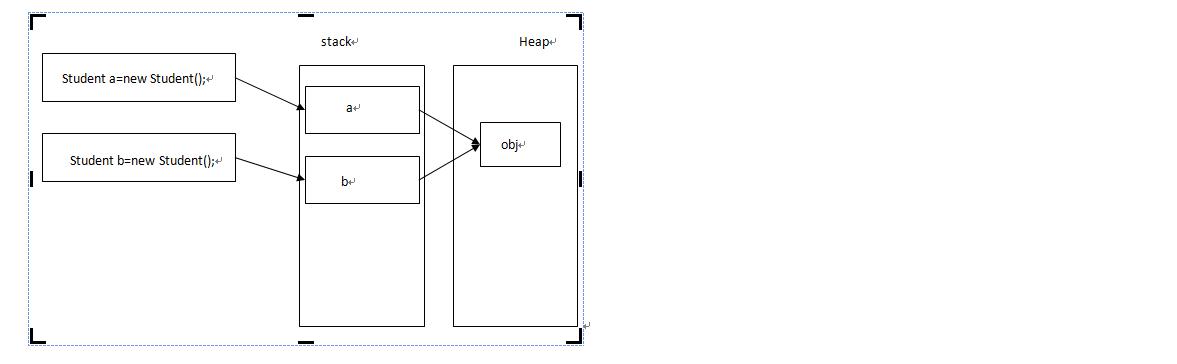
地址引用
在上面图示我们可以看出,值引用是各自分配内存的,本质上不是同一个东西。就好比一对双胞胎,长得很像,但是根本是两个人。而地址引用就好比李明有一个小名叫小明。但是小明和李明都是同一个人。
什么是值传递,地址传递和引用传递?首先,看以下三段代码。
1 void Test(int x, int y) 2 { 3 int tmp=x; 4 x=y; 5 y=tmp; 6 print(“x=%d, y=%d\n”, x, y); 7 } 8 9 void main() 10 { 11 12 int a=4,b=5; 13 Test(a,b) ; 14 printf(“a=%d, b=%d\n”, a, b); 15 }
输出结果
x=4, y=5
a=5, b=4
1 void Test(int *px, int *py) 2 { 3 int tmp=*px; 4 *px=*py; 5 *py=tmp; 6 print(“*px=%d, *py=%d\n”, *px, *py); 7 } 8 9 void main() 10 { 11 12 int a=4; 13 int b=5; 14 swap2(&a,&b); 15 Print(“a=%d, b=%d\n”, a, b); 16 }
这次输出结果
*px=5, *py=5
a=5, b=4
1 void Test(int &x, int &y) 2 { 3 int tmp=x; 4 x=y; 5 y=tmp; 6 print(“x=%d, y=%d\n”, x, y); 7 } 8 9 void main() 10 { 11 12 int a=4; 13 int b=5; 14 swap3(a,b); 15 Print(“a=%d, b=%d\n”, a, b); 16 }
这次输出结果是
---
x=5, y=4
a=5, b=4
上面的分别是值传递,地址传递,和引用传递。
先看值传递。是将x,y进行对调。需要注意的是,对形参的操作不会影响到a,b。当a,b把值赋给x,y之后,对x,y发生改变,不会影响到a,b本身。
再看地址传递。a的地址代入到了px,b的地址代入到了py。这样一来,对*px, *py的操作就是a,b本身的操作。所以a,b的值被对调了。
引用传递。定义的x,y前面有&取地址符,a,b分别代替了x,y,即x,y分别引用了a,b变量。因此,函数里的操作,实际上是对实参a,b本身的操作,其值发生了对调。
我们怎么判断两个对象是相等(深复制)的呢?可以使用object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)。
好了,那么下面我们回来探讨一下对象的深度克隆和浅克隆的几种方法:
写一个Sudent类:
1 using System; 2 3 using System.Collections.Generic; 4 5 using System.Linq; 6 7 using System.Text; 8 9 using System.Threading.Tasks; 10 11 12 13 namespace Model.test 14 15 { 16 17 [Serializable] 18 19 public class Student 20 21 { 22 23 public Student() { } 24 25 private string _name; 26 27 private string _age; 28 29 private string _sex; 30 31 private string _address; 32 33 private string _tel; 34 35 public Student(string name, string age, string sex, string address, string tel) 36 37 { 38 39 this.address = address; 40 41 this.age = age; 42 43 this.name = name; 44 45 this.sex = sex; 46 47 this.tel = tel; 48 49 } 50 51 public string name { get; set; } 52 53 public string age { get; set; } 54 55 public string sex { get; set; } 56 57 public string address { get; set; } 58 59 public string email { get; set; } 60 61 public string tel { get; set; } 62 63 } 64 65 }
我们先来看看对象直接赋值:
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 3 { 5 Student s1 = new Student(); 6 7 s1.address = "北京"; 8 9 s1.sex = "男"; 10 11 s1.tel = "18825196284"; 12 13 s1.name = "张峰"; 14 15 s1.email = "777663548@QQ.COM"; 16 17 s1.age = "25"; 18 19 Student s2 = new Student(); 20 21 s2 = s1; 25 //更改s2的年龄 26 27 s2.age = "44"; 28 33 Console.WriteLine("s1的年龄:" + s1.age + " S2 HashCode:" + s2.GetHashCode() + " S1 HashCode:" + s1.GetHashCode() + " 直接复制 s2 = s1 的ReferenceEquals结果:" + object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)); 34 35 Console.ReadLine(); 36 37 }
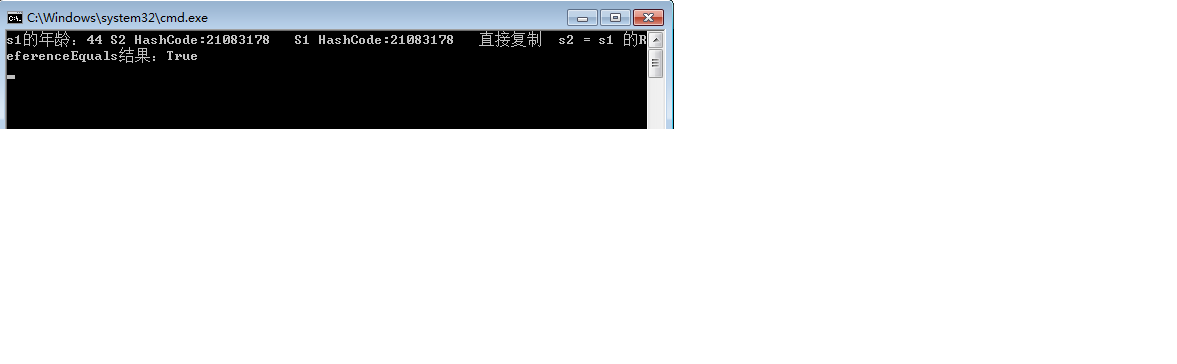
结果说明这两个对象是地址引用,即浅复制。
再来看下面的情况:
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 3 { 4 5 Student s1 = new Student(); 6 7 s1.address = "北京"; 8 9 s1.sex = "男"; 10 11 s1.tel = "18825196284"; 12 13 s1.name = "张峰"; 14 15 s1.email = "777663548@QQ.COM"; 16 17 s1.age = "25"; 27 Student s2 = new Student(); 28 29 s2.address = s1.address; 30 31 s2.sex = s1.sex; 32 33 s2.tel = s1.tel; 34 35 s2.name = s1.name; 36 37 s2.email = s1.email; 38 39 s2.age = s1.age; 40 41 //更改s2的年龄 42 43 s2.age = "55"; 47 Console.WriteLine("s1的年龄:" + s1.age + " S2 HashCode:" + s2.GetHashCode() + " S1 HashCode:" + s1.GetHashCode() + " 直接复制 s2 = s1 的ReferenceEquals结果:" + object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)); 48 49 Console.ReadLine(); 50 51 }
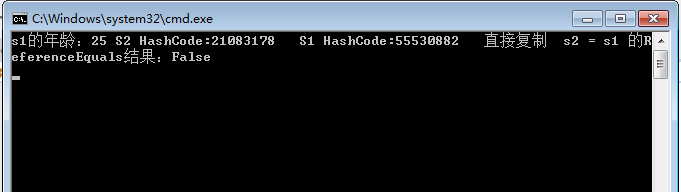
可以看出来属性一个一个赋值是深度克隆,但是这样代码量就大了。那么有什么办法写很少的代码吗?
第一种方法-对象映射:
1 public static object CloneObject(object o) 2 3 { 4 5 Type t = o.GetType(); 6 7 PropertyInfo[] properties = t.GetProperties(); 8 9 Object p = t.InvokeMember("", System.Reflection.BindingFlags.CreateInstance, null, o, null); 10 11 foreach (PropertyInfo pi in properties) 12 13 { 14 15 if (pi.CanWrite) 16 17 { 18 object value = pi.GetValue(o, null); 19 20 pi.SetValue(p, value, null); 21 22 } 23 24 } 25 26 return p; 27 28 } 29 30 static void Main(string[] args) 31 32 { 33 34 Student s1 = new Student(); 35 36 s1.address = "北京"; 37 38 s1.sex = "男"; 39 40 s1.tel = "18825196284"; 41 42 s1.name = "张峰"; 43 44 s1.email = "777663548@QQ.COM"; 45 46 s1.age = "25"; 47 48 Student s2 = new Student(); 49 50 s2 = (Student)CloneObject(s1); 51 52 //更改S2的年龄 53 54 s2.age = "88"; 55 Console.WriteLine("s1的年龄:" + s1.age + " S2 HashCode:" + s2.GetHashCode() + " S1 HashCode:" + s1.GetHashCode() + " 直接复制 s2 = s1 的ReferenceEquals结果:" + object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)); 56 57 Console.ReadLine(); 58 59 }

第二种方法(二进制流序列化反序列化):
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 3 { 4 5 Student s1 = new Student(); 6 7 s1.address = "北京"; 8 9 s1.sex = "男"; 10 11 s1.tel = "18825196284"; 12 13 s1.name = "张峰"; 14 15 s1.email = "777663548@QQ.COM"; 16 17 s1.age = "25"; 18 19 Student s2 = new Student(); 20 21 BinaryFormatter inputFormatter = new BinaryFormatter(); 22 23 MemoryStream inputStream; 24 25 using (inputStream = new MemoryStream()) 26 27 { 28 29 inputFormatter.Serialize(inputStream, s1); 30 } 31 32 //将二进制流反序列化为对象 33 34 using (MemoryStream outputStream = new MemoryStream(inputStream.ToArray())) 35 36 { 37 BinaryFormatter outputFormatter = new BinaryFormatter(); 38 39 s2 = (Student)outputFormatter.Deserialize(outputStream); 40 41 } 42 43 //更改S2的年龄 44 45 s2.age = "88"; 46 47 Console.WriteLine("s1的年龄:" + s1.age + " S2 HashCode:" + s2.GetHashCode() + " S1 HashCode:" + s1.GetHashCode() + " 直接复制 s2 = s1 的ReferenceEquals结果:" + object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)); 48 49 Console.ReadLine(); 50 51 }
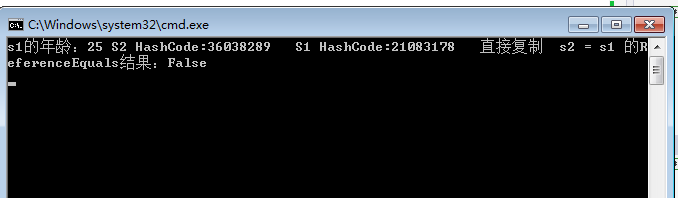
第三种(AutoMapper):
1 using System; 2 3 using System.Collections; 4 5 using System.Collections.Generic; 6 7 using System.Data; 8 9 using System.Linq; 10 11 using System.Text; 12 13 using System.Threading.Tasks; 14 15 16 17 namespace AutoMapper.AutoMapperHelpers 18 19 { 20 21 /// <summary> 22 23 /// AutoMapper扩展帮助类 24 25 /// </summary> 26 27 public static class AutoMapperHelper 28 29 { 30 31 /// <summary> 32 33 /// 类型映射 34 35 /// </summary> 36 37 public static T MapTo<T>(this object obj) 38 39 { 40 41 if (obj == null) return default(T); 42 43 Mapper.CreateMap(obj.GetType(), typeof(T)); 44 45 return Mapper.Map<T>(obj); 46 47 } 48 49 /// <summary> 50 51 /// 集合列表类型映射 52 53 /// </summary> 54 55 public static List<TDestination> MapToList<TDestination>(this IEnumerable source) 56 57 { 58 59 foreach (var first in source) 60 61 { 62 63 var type = first.GetType(); 64 65 Mapper.CreateMap(type, typeof(TDestination)); 66 67 break; 68 69 } 70 71 return Mapper.Map<List<TDestination>>(source); 72 73 } 74 75 /// <summary> 76 77 /// 集合列表类型映射 78 79 /// </summary> 80 81 public static List<TDestination> MapToList<TSource, TDestination>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source) 82 83 { 84 85 //IEnumerable<T> 类型需要创建元素的映射 86 87 Mapper.CreateMap<TSource, TDestination>(); 88 89 return Mapper.Map<List<TDestination>>(source); 90 91 } 92 93 /// <summary> 94 95 /// 类型映射 96 97 /// </summary> 98 99 public static TDestination MapTo<TSource, TDestination>(this TSource source, TDestination destination) 100 101 where TSource : class 102 103 where TDestination : class 104 105 { 106 107 if (source == null) return destination; 108 109 Mapper.CreateMap<TSource, TDestination>(); 110 111 return Mapper.Map(source, destination); 112 113 } 114 115 /// <summary> 116 117 /// DataReader映射 118 119 /// </summary> 120 121 public static IEnumerable<T> DataReaderMapTo<T>(this IDataReader reader) 122 123 { 124 125 Mapper.Reset(); 126 127 Mapper.CreateMap<IDataReader, IEnumerable<T>>(); 128 129 return Mapper.Map<IDataReader, IEnumerable<T>>(reader); 130 131 } 132 133 } 134 135 }
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 3 { 4 5 Student s1 = new Student(); 6 7 s1.address = "北京"; 8 9 s1.sex = "男"; 10 11 s1.tel = "18825196284"; 12 13 s1.name = "张峰"; 14 15 s1.email = "777663548@QQ.COM"; 16 17 s1.age = "25"; 18 19 Student s2 = new Student(); 20 21 s2 = AutoMapperHelper.MapTo<Student>(s1); 22 23 //更改S2的年龄 24 s2.age = "88"; 25 26 Console.WriteLine("s1的年龄:" + s1.age + " S2 HashCode:" + s2.GetHashCode() + " S1 HashCode:" + s1.GetHashCode() + " 直接复制 s2 = s1 的ReferenceEquals结果:" + object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)); 27 28 Console.ReadLine(); 29 30 }
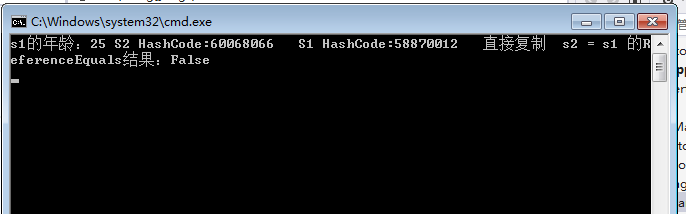
第四种JSON序列化和反序列化:
1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 3 { 4 5 Student s1 = new Student(); 6 7 s1.address = "北京"; 8 9 s1.sex = "男"; 10 11 s1.tel = "18825196284"; 12 13 s1.name = "张峰"; 14 15 s1.email = "777663548@QQ.COM"; 16 17 s1.age = "25"; 18 19 Student s2 = Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Student>(Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.SerializeObject(s1)); 20 21 //更改S2的年龄 22 23 s2.age = "88"; 24 25 Console.WriteLine("s1的年龄:" + s1.age + " S2 HashCode:" + s2.GetHashCode() + " S1 HashCode:" + s1.GetHashCode() + " 直接复制 s2 = s1 的ReferenceEquals结果:" + object.ReferenceEquals(s1, s2)); 26 27 Console.ReadLine(); 28 29 }



