JavaIO流三
IO流三
一、案例
1.1、集合到文件
//需求:把Arraylist集合中的字符串数据写入到文本文件,要求:每一个字符串元素作为文件中的一行数据
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
//添加元素到集合
al.add("王华");
al.add("李康");
al.add("周星");
al.add("刘明");
//创建缓冲输出流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Java基础语法\\osw.txt"));
//遍历集合得到每一个字符串对象
for(String s:al){
//写入数据
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
}
1.2、文件到集合
//需求:把文本文件中的数据读取到集合中,并遍历集合。要求:文件中每一行数据是一个集合
public class demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符缓冲流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Java基础语法\\osw.txt"));
//创建ArrayList集合对象
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
//调用字符缓冲流对象的方法读数据
String len;
while((len=br.readLine())!=null){
al.add(len);
}
//释放资源
br.close();
//遍历集合
for (String s:al){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
1.3、点名器
//需求:现有一个写有许多网名的文件,每一个网名占一行。要求:要求通过程序随机点名器
public class demo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符缓冲输入流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\test\\DM.txt"));
//创建ArrayList集合对象
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>();
//调用缓冲流方法读数据
String len;
while((len=br.readLine())!=null){
//把读取的数据添加到集合中
al.add(len);
}
//释放资源
br.close();
//使用Random创建随机数
Random random = new Random();
int index = random.nextInt(al.size());
//把产生的随机数作为索引到ArrayList中获取值
String s = al.get(index);
//输出上一步所获取的值
System.out.println("点到者:"+s);
}
}
1.4、集合到文件(升级版)
//需求:把ArrayList集合中的学生数据写入到文本文件。需求:每一个学生对象的数据作为文件中的一行数据
//格式:学号,姓名,年龄,居住地 举例:202201,李明,18,北京
public class demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<Student> al = new ArrayList<Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student(202201,"李明",18,"北京");
Student s2 = new Student(202202,"王芳",16,"上海");
Student s3 = new Student(202203,"郑科",23,"西安");
Student s4 = new Student(202204,"钱军",34,"天津");
//把学生对象添加到集合中
al.add(s1);
al.add(s2);
al.add(s3);
al.add(s4);
//创建字符缓冲输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Java基础语法\\bw.txt"));
//方法一
//遍历集合
// Iterator<Student> it = al.iterator();
// while(it.hasNext()){
// Student s = it.next();
// //写数据
// bw.write(String.valueOf(s.getNum()+","+s.getName()+","+s.getAge()+","+s.getAddress()));
// bw.newLine();
// bw.flush();
// }
//方法二
for (Student s:al){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(s.getNum()).append(",").append(s.getName()).append(",").append(s.getAge()).append(",").append(s.getAddress());
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
}
1.5、文件到集合(升级版)
//需求:把文本文件中的数据读取到集合中,并遍历集合。要求:文件中每一行数据是一个学生对象的成员变量
public class demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符缓冲输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Java基础语法\\bw.txt"));
//创建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<Student> al = new ArrayList<Student>();
//读数据
String len;
while ((len=br.readLine())!=null) {
//把读取到的字符串数据用split()方法分割,得到一个字符串数组
String[] split = len.split(",");
//创建学生对象
Student s = new Student();
//把字符串数组中每一个元素取出来作为对应的值赋给学生对象做成员变量
s.setNum(Integer.parseInt(split[0]));
s.setName(split[1]);
s.setAge(Integer.parseInt(split[2]));
s.setAddress(split[3]);
//添加到集合
al.add(s);
}
//释放资源
br.close();
//遍历集合
for (Student s:al){
System.out.println(s.getNum()+","+s.getName()+","+s.getAge()+","+s.getAddress());
}
}
}
1.6、集合到文件(进行数据排序)
//需求:键盘录入5个学生信息。要求按总成绩从高到低排序写入文件
public class demo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建学生类
//创建TreeSet集合
TreeSet<Greade> ts = new TreeSet<Greade>(new Comparator<Greade>() {
@Override
public int compare(Greade g1, Greade g2) {
//主要条件,按从高到低排序
int num = g2.getsum()-g1.getsum();
//次要条件
int num2=num==0?g2.getChinese()-g1.getChinese():num;
int num3=num2==0?g2.getMath()-g1.getMath():num2;
int num4=num3==0?g2.getEnglish()-g1.getEnglish():num3;
return num4;
}
});
//键盘录入学生成绩
for(int i=0; i<5; i++){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请录入第"+(i+1)+"个学生信息");
System.out.println("姓名:");
String name1 = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("语文成绩:");
int chinese1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("数学成绩:");
int math1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("英语成绩");
int english1 = sc.nextInt();
//创建学生成绩对象,把键盘录入数据赋值给学生对象的成员变量
Greade s = new Greade();
s.setName(name1);
s.setChinese(chinese1);
s.setMath(math1);
s.setEnglish(english1);
//把学生对象添加到集合
ts.add(s);
}
//创建字符缓冲输出流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("Java基础语法\\ts.txt"));
//遍历集合,得到每一个学生对象
for (Greade s : ts){
//把学生对象的数据拼接成指定的字符串
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(s.getName()).append(",").append(s.getChinese()).append(",").append(s.getMath()).append(",").append(s.getEnglish()).append(",").append(s.getsum());
//调用缓冲输出流方法写数据
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//释放资源
bw.close();
}
}
1.7、复制单级文件夹(单级文件夹指的是文件夹下只有文件、图片、音频等内容)
public class CopyFiledemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建数据源目录File对象,路径是D:\\test
File srcFolder = new File("D:\\test");
//获取数据源目录File对象的名称test
String srcFolderName = srcFolder.getName();
//创建目的地目录File对象,路径名为Java基础语法:\\test
File destFolder = new File("Java基础语法",srcFolderName);
//判断目的地目录对应的File是否存在,如果不存在就创建
if (!destFolder.exists()){
destFolder.mkdir();
}
//获取所有数据源目录下的File数组
File[] listFiles = srcFolder.listFiles();
//遍历File数组,得到File对象,该对象,其实就是数据源
for (File srcfile:listFiles){
//数据源文件:D:\\test\\AL.png
//获取数据源文件对象名称
String srcfilename = srcfile.getName();
//创建目的地文件对象
File destfile = new File(destFolder,srcfilename);
//复制文件
copyFile(srcfile,destfile);
}
}
private static void copyFile(File srcFile,File destFile) throws IOException{
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){
bos.write(bys,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
1.8、复制多级文件夹(多级文件夹指的是文件夹下不只是文件这些,里面还包含文件夹)
public class CopyFilesDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//创建数据源File对象
File srcFile = new File("D:\\test");
//创建目的地File对象
File destFile = new File("C:\\");
//写方法复制文件夹的方法,参数为数据源对象和目的地对象
copyFolder(srcFile,destFile);
}
//复制文件夹
private static void copyFolder(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException{
//判断数据源是否是目录
if(srcFile.isDirectory()){
//在目的地目录下创建和数据源一样的名称
String srcFileName = srcFile.getName();
File newFolder = new File(destFile,srcFileName);//C:\\test
if (!newFolder.exists()){
newFolder.mkdir();
}
//获取数据源下所有文件或者目录的File数组
File[] fileArray = srcFile.listFiles();
//遍历该File数组,得到其每一个对象
for (File file:fileArray){
//把file作为数据源File对象,递归调用复制文件夹的方法
copyFolder(file,newFolder);
}
}else {
//如果是文件,直接复制,用字节流
File newFile = new File(destFile,srcFile.getName());
copyFile(srcFile,newFile);
}
}
//字节缓冲流复制文件
private static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcFile));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destFile));
byte[] bys = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bys))!=-1){
bos.write(bys,0,len);
}
bos.close();
bis.close();
}
}
二、复制文件的异常处理

public class ExceptionHandledemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//JDK9改进方案
private static void method3() throws IOException{
FileReader fr = new FileReader("fr.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");
try(fr;fw) {
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1){
fw.write(chs,0,len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//JDK7改进方案
private static void method2(){
try(FileReader fr = new FileReader("fr.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");) {
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1){
fw.write(chs,0,len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//try...catch..finally
private static void method1() {
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("fr.txt");
fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chs)) != -1) {
fw.write(chs, 0, len);
}
}catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (fw!=null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fr!=null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//抛出异常
private static void method() throws IOException{
FileReader fr = new FileReader("fr.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("fw.txt");
char[] chs = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1){
fw.write(chs,0,len);
}
fw.close();
fr.close();
}
}
三、特殊操作流
3.1、标准输入输出流
System类中有两个静态的成员变量:
-
public static final InputStream in:标准输入流。该流已经打开,准备提供输入数据。通常该流对应于键盘输入或由主机环境或用户指定的另一个输入源。
-
public static final PrintStream out:标准输出流。此流已经打开并准备好接受输出数据。通常此流对应于显示输出或由主机环境或用户指定的另一个输出目标。
3.2、标准输入流
/*
* public static final InputStream in:标准输入流。该流已经打开,准备提供输入数据。通常该流对应于键盘输入或由主机环境或用户指定的另一个输入源。
*/
public class SystemIndemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1、public static final InputStream in:标准输入流
// InputStream is = System.in;
//
// //一次读一个字节
//// int by;
//// while((by=is.read())!=-1){
//// System.out.println((char)by);
//// }
//
// //2、如何把字节流转换为字符流?//用转换流
// InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
// //3、使用字符流能不能够一次读取一行数据呢?可以
// //但是,一次读取一行是字符缓冲流特有的方法
// BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
//以上方式合并为一
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( System.in));//自己实现键盘录入数据
System.out.println("请输入一个字符串:");
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println("你输入的字符串是:"+line);
System.out.println("请输入一个整数:");
int i = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
System.out.println("你输入的整数是:"+i);
//由于自己实现键盘录入数据过于麻烦,所以Java就提供了一个类供我们使用
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
}
}
3.3、标准输出流
/*public static final PrintStream out:标准输出流。此流已经打开并准备好接受输出数据。通常此流对应于显示输出或由主机环境或用户指定的另一个输出目标。 */
public class SystemOut {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public static final PrintStream out:标准输出流
PrintStream ps = System.out;
//PrintStream类有的方法,System.out都可以用
//能够方便打印各种输出值
//print:不换行;println:换行
// ps.print("hello");
// ps.print(99);
// ps.println("hello");
// ps.println(99);
//System.out的本质就是一个字节输出流
System.out.println("hello");
System.out.print("hello");
System.out.print(99);
}
}
3.4、打印流
打印流分类:
- 字节打印流:PrintStream
- 字符打印流:Printwriter
打印流特点:
- 只负责输出数据,不负责读取数据
- 有自己特有方法
3.5、字节打印流
- PrintStream(String fileName):使用指定的文件名创建新的打印流
- 使用继承父类的方法写数据,查看的时候会转码;使用自己的特有方法写数据,查看数据原样输出
public class PrintStreamdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("Java基础语法\\ps.txt");
//写数据
//字节输出流有的方法
ps.write(99);
//使用其特有方法写数据
ps.println(96);
ps.print(97);
//释放资源
ps.close();
}
}
3.6、字符打印流
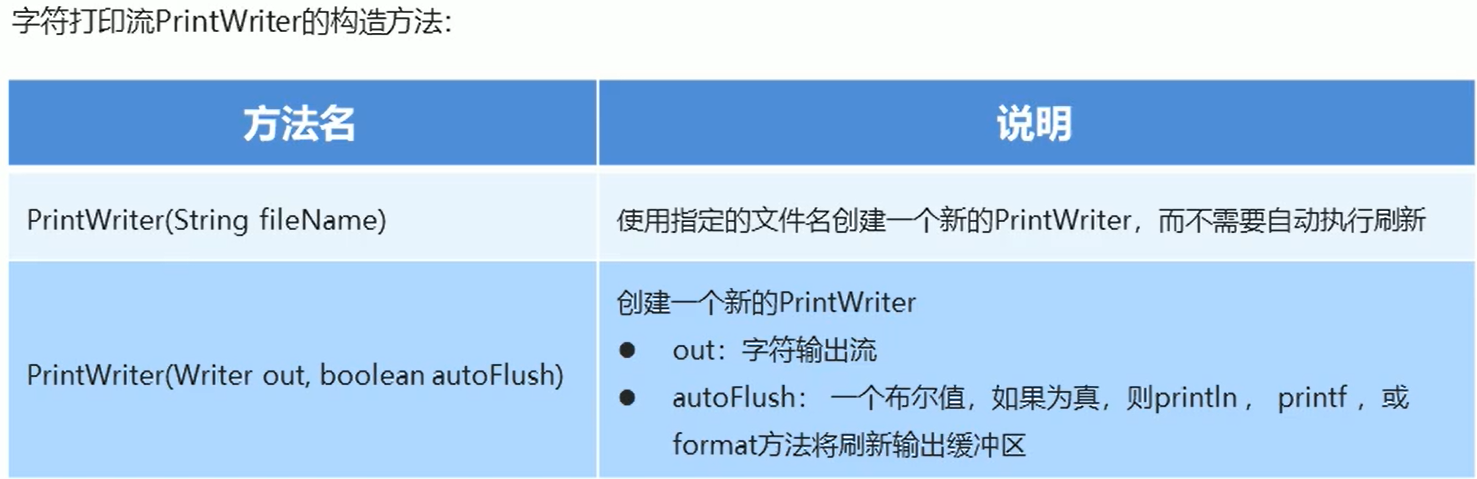
public class PrintWriterdemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//PrintWriter(String fileName):使用指定的文件名创建一个新的PrintWriter,而不需要自动执行行刷新。
// PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("Java基础语法\\pw.txt");
// pw.write("hello");//这是一个字符打印流,是不能直接打印出来,需要刷新的
// pw.write("\n");
// pw.flush();
// pw.write("world");
// pw.write("\n");
// pw.flush();
// pw.println("hello");
// /*pw.write("hello");
// * pw.write("\n");*/
// pw.flush();
// pw.println("world");
// pw.flush();
//PrintWriter(Writer out, boolean autoFlush):创建一个新的PrintWriter。out:字符输出流;autoFlush:自动刷新
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("Java基础语法\\pw.txt"),true);
// PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("Java基础语法\\pw.txt"),false);
pw.println("hello");
pw.println("world");
pw.close();
}
}
3.7、复制Java文件
public class CopyJavademo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//使用打印流
//创建字符输入流对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("Java基础语法\\PrintStreamdemo.java"));
//创建字符输出流对象
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("Java基础语法\\Copy.java"),true);
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
pw.println(line);
}
pw.close();
br.close();
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号