Java集合三
Java集合三
一、Map
1.1、Map集合概述和使用
Map集合概述:
- public interface Map<K,V> K:键的类型;V:值的类型
- 将键映射到值的对象;不能包含重复的键;每个键可以映射到最多一个值
创建Map集合的对象
- 多态的方式
- 具体的实现类HashMap
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class mapdemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//创建Map集合对象
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//添加元素:put(K key, V value):将指定的值与此映射中的指定键相关联。
map.put("d001","李明");
map.put("d002","张东");
map.put("d003","王强");
//当键重复时,第二次出现的值会替换掉第一次的值;原理:HashMap中Hash就是Hash表,Hash表它在这里保证了键的唯一性
// map.put("d003","钱军");//{d002=张东, d003=钱军, d001=李明}
// map.put("d003","王强");//{d002=张东, d003=王强, d001=李明}
// map.put("d004","王强");//{d002=张东, d003=王强, d001=李明, d004=王强}
System.out.println(map);//{d002=张东, d003=王强, d001=李明}
}
}
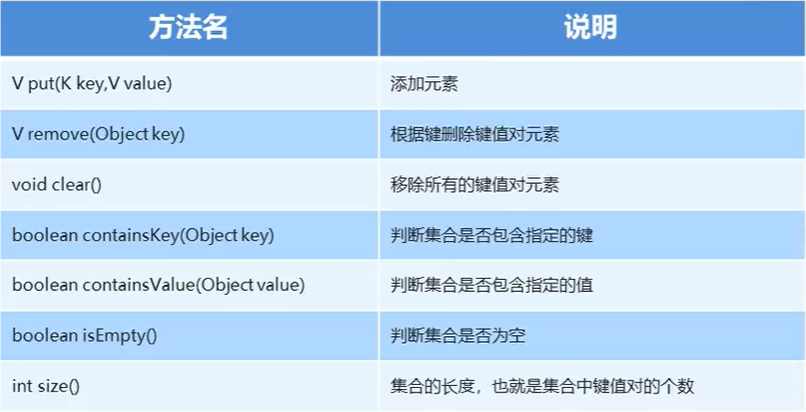
1.2、Map集合的基本功能
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class mapdemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
//put(K key, V value):添加元素
map.put(01,"李阳");
map.put(02,"张东");
map.put(03,"夏星");
// System.out.println(map);//{1=李阳, 2=张东, 3=夏星}
//remove(Object key):根据键删除键值对元素
// System.out.println(map.remove("李阳"));//null
//clear():移除所有的键值对元素
// map.clear();
// System.out.println(map);//{}
//containsKey(Object key):判断是否包含指定的键
// System.out.println(map.containsKey(02));//true
//containsValue(Object value):判断是否包含指定的值
// System.out.println(map.containsValue("李阳"));//true
// System.out.println(map.containsValue("李华"));//false
//isEmpty():判断是否为空
// System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//false
//size():返回集合长度,也就是集合中键值对的个数
System.out.println(map.size());//3
}
}
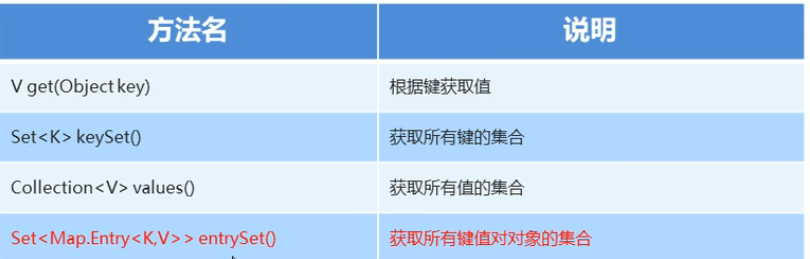
1.3、Map集合的获取功能
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class mapdemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//添加元素
map.put("李华","李东");
map.put("夏雪","夏冬");
map.put("秋草","秋菊");
//V get(Object key):根据键获取值
// System.out.println(map.get("李华"));//李东
// System.out.println(map.get("张三"));//null
//Set<K> keySet():获取所有键的集合
// Set<String> set = map.keySet();
// for (String s:set){
// System.out.println(s);
// }
//Collection<V> values():获取所有值的集合
Collection<String> c = map.values();
for (String s:c){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
1.4、Map集合的遍历
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class mapdemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
//添加元素
map.put("李华","李东");
map.put("夏雪","夏冬");
map.put("秋草","秋菊");
//集合遍历
//方式一:
// //1、获取所有键的集合
// Set<String> keyset = map.keySet();
// //2、遍历键集合,获取每一个键
// for (String key:keyset){
// //3、根据键去找值
// String s = map.get(key);
// System.out.println(key+","+s);
// }
//方式二
//1、Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet():获取所有键值对对象的集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> en = map.entrySet();
//2、遍历键值对对象的集合,得到每一个键值对对象
for (Map.Entry<String, String> me:en){
//3、根据键值对对象获取键和值
//System.out.println(me.getKey()+","+me.getValue());
String key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
}
}
1.5、HashMap集合练习
//HashMap集合存储学生对象并遍历
//案例要求1:创建一个HashMap集合,键的学号是(String),值是学生对象(Student),存储三个键值对元素,并遍历
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class mapdemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
HashMap<String,Student> map = new HashMap<String, Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("李华",12);
Student s2 = new Student("张东",17);
Student s3 = new Student("刘恋",18);
//添加元素
map.put("100",s1);
map.put("101",s2);
map.put("102",s3);
//遍历集合
//方式一
// Set<String> keySet = map.keySet();
// for (String value:keySet){
// Student st = map.get(value);
// System.out.println(value+","+st.getName()+","+st.getAge());
// }
//方式二
Set<Map.Entry<String, Student>> en = map.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Student> me:en){
String key = me.getKey();
Student value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key+","+value.getName()+","+value.getAge());
}
}
}
//案例要求改变:创建一个HashMap集合,键是学生对象(Student),值是学生居住地(String),存储多个键值对元素,并遍历,且保证键得唯一性,如果学生成员变量相同,认为是同一个对象
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class mapdemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Student,String> hm = new HashMap<Student, String>();
Student s1 = new Student("李晓",30);
Student s2 = new Student("季风",23);
Student s3 = new Student("丰华",18);
Student s4 = new Student("丰华",18);
hm.put(s1,"北京");
hm.put(s2,"广东");
hm.put(s3,"重庆");
hm.put(s4,"武汉");
Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> en = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student, String> me:en){
Student key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key.getName()+","+key.getAge()+","+value);
}
}
}
这里为了保证键的唯一性,只需在学生对象中重写hashcode和equals即可
1.6、集合嵌套
//ArrayList嵌套HashMap
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、创建ArrayList集合
ArrayList<HashMap<String,String>> array = new ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>>();
//2、创建HashMap集合,并添加键值对元素
HashMap<String,String> hm1 = new HashMap<String, String>();
hm1.put("赵","钱");
hm1.put("孙","李");
HashMap<String,String> hm2 = new HashMap<String, String>();
hm2.put("周","吴");
hm2.put("郑","王");
HashMap<String,String> hm3 = new HashMap<String, String>();
hm3.put("冯","陈");
hm3.put("褚","卫");
//3、把HashMap集合作为元素添加到HashMap集合中
array.add(hm1);
array.add(hm2);
array.add(hm3);
//4、遍历ArrayList
for (HashMap<String,String> hm:array){
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> en = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> me:en){
String key = me.getKey();
String value = me.getValue();
System.out.println(key+","+value);
}
}
}
}
//HashMap嵌套ArrayList
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、创建HashMap集合
HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>> hm = new HashMap<String, ArrayList<String>>();
//2、创建ArrayList集合,并添加元素
ArrayList<String> a1 = new ArrayList<String>();
a1.add("蒋");
a1.add("沈");
ArrayList<String> a2 = new ArrayList<String>();
a2.add("韩");
a2.add("阳");
ArrayList<String> a3 = new ArrayList<String>();
a3.add("朱");
a3.add("秦");
//3、把ArrayList作为元素添加到HashMap中
hm.put("01",a1);
hm.put("02",a2);
hm.put("03",a3);
//4、遍历HashMap集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<String>>> en = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, ArrayList<String>> me:en){
String key = me.getKey();
ArrayList<String> value = me.getValue();
for (String s:value){
System.out.println(key+","+s);
}
}
}
}
1.7、具体案例:统计字符串中每个字符出现的次数

import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class FinallyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1、键盘录入一个字符串
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入字符串:");
String line = sc.nextLine();
//2、创建HashMap集合,键是Character,值是Integer
// HashMap<Character,Integer> hm = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();//结果为无序
TreeMap<Character,Integer> hm = new TreeMap<Character, Integer>();//结果为有序
//3、遍历字符串,得到每一个字符
for (int i = 0;i<line.length();i++){
char key = line.charAt(i);
//4、拿到每个一字符作为键到HashMap中找对应的值,并判断
Integer value = hm.get(key);//自动装箱
if (value==null){
//如果返回得是null,则说明该字符在HashMap集合中不存在,就把该字符作为键,1作为值存储
hm.put(key,1);//自动装箱
}else{
//如果返回得不是null,则说明该字符在HashMap中存在,就把值加1,然后重新存储该字符和值
value++;//自动拆箱
hm.put(key,value);
}
}
//5、遍历HashMap集合,得到对应得键和值,按要求进行拼接
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Set<Character> keySet = hm.keySet();
for (Character key:keySet){
Integer value = hm.get(key);
sb.append(key).append(":").append("(").append(value).append(")");
}
//6、输出结果
String result = sb.toString();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
二、Collections
2.1、Collections的概述和使用
-
Collections是针对集合操作的工具类
-
Collections类的常用方法
- public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List
list):将指定的列表按升序排序 - public static void reverse(List<?> list):反转指定列表中元素的顺序
- public static void shuffle(List<?> list):使用默认的随机源随机排列指定的列表
- public static <T extends Comparable<? super T>> void sort(List
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//添加元素
list.add(30);
list.add(20);
list.add(50);
list.add(10);
list.add(40);
//sort方法
// Collections.sort(list);//[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
//reverse方法
// Collections.reverse(list);//[40, 10, 50, 20, 30]
//shuffle方法
Collections.shuffle(list);//[20, 30, 40, 10, 50];[30, 50, 40, 20, 10]...
System.out.println(list);//[30, 20, 50, 10, 40]
}
}
2.2、案例
//ArrayList集合存储学生对象
//要求:按照年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同时,按照姓名字母排序
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
public class demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1 = new Student("李明",30);
Student s2 = new Student("王华",10);
Student s3 = new Student("秦天",46);
Student s4 = new Student("韩信",28);
Student s5 = new Student("张莉",28);
array.add(s1);
array.add(s2);
array.add(s3);
array.add(s4);
array.add(s5);
//sort(List<T> list, Comparator<? super T> c):根据指定的比较器引起的顺序对指定的列表进行排序。
Collections.sort(array, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s, Student t1) {
int num = s.getAge()-t1.getAge();
int num2= num==0?s.getName().compareTo(t1.getName()):num;
return num2;
}
});
for (Student s : array){
System.out.println(s.getName()+","+s.getAge());
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号