async详解
转载:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/49742331
一、什么是async
async其实是ES7的才有的关键字,放在这里说,其实是和我们前面所说的Promise,Generator有很大关联的。async的意思是"异步",顾名思义是有关异步操作有关的关键字。下面我们就来构造一个async方法。
1 2 3 4 | async function helloAsync(){ return "helloAsync"; } console.log(helloAsync())//Promise {<resolved>: "helloAsync"} |
申明async方法比较简单,只需要在普通的函数前加上"async"关键字即可。我们执行下这个函数,发现并没有返回字符串"helloAsync",而是通过Promise.resolved()将字符串封装成了一个Promise对象返回。
既然是返回的Promise对象,我们就是用then方法来处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 | async function helloAsync(){ return "helloAsync"; } helloAsync().then(v=>{ console.log(v);//"helloAsync" }) |
到这,道友们可能纳闷了,就是封装一个Promise的对象返回,这有个毛用啊。别急,await关键字闪亮登场。
二、await关键字
await关键字也不能单独使用,是需要使用在async方法中。 await字面意思是"等待",那它是在等什么呢?它是在等待后面表达式的执行结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | function testAwait(){ return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(function(){ console.log("testAwait"); resolve(); }, 1000); }); } async function helloAsync(){ await testAwait(); console.log("helloAsync"); } helloAsync(); |
我们来分析下这段代码
1、testAwait()方法中new一个Promise对象返回,promise对象中用setTimeout模拟一个异步过程,即1s后打印"testAwait"。
2、helloAsync()方法中,await testAwait(),表示将阻塞这里,等待testAwait这个异步方法执行并返回结果后,才继续下面的代码。
执行下,1s后打印了下面的日志。
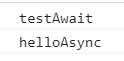
到此,道友们是不是理解了await的作用,就是阻塞主函数的执行,直到后面的Promise函数返回结果。
聪明的道友可能要问,await后面只能 是Promise对象么?答案是否定的,可以是字符串,布尔值,数值以及普通函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | function testAwait(){ setTimeout(function(){ console.log("testAwait"); }, 1000); } async function helloAsync(){ await testAwait(); console.log("helloAsync"); } helloAsync(); |
执行结果:
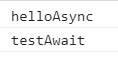
方法没有报错,说明await后面是支持非Promise函数的,但是执行的结果是不一样的,所以await针对所跟的表达式不同,有两种处理方式:
1、对于Promise对象,await会阻塞主函数的执行,等待 Promise 对象 resolve,然后得到 resolve 的值,作为 await 表达式的运算结果,然后继续执行主函数接下来的代码。
2、对于非Promise对象,await等待函数或者直接量的返回,而不是等待其执行结果。
我们知道Promise对象有两种状态,除了resolved,还有rejected,我们来看下如果promise对象变为rejected,会如何处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | function testAwait(){ return Promise.reject("error"); } async function helloAsync(){ await testAwait(); console.log("helloAsync");//没有打印 } helloAsync().then(v=>{ console.log(v); }).catch(e=>{ console.log(e);//"error" }); |
从执行结果看,返回reject状态被外层的catch捕获到,然后终止了后面的执行。
但是在有些情况下,出错后是希望继续执行,而不是中断。对于这种情况可以采用tcy...catch在函数内部捕获异常。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | function testAwait(){ return Promise.reject("error"); } async function helloAsync(){ try{ await testAwait(); }catch(e){ console.log("this error:"+e)//this error:error } console.log("helloAsync");//helloAsync } helloAsync().then(v=>{ }).catch(e=>{ console.log(e);//没有打印 }); |
异常被try...catch捕获后,继续执行下面的代码,没有导致中断。
三、应用场景
上面说到,await可以阻塞主函数,直到后面的Promise对象执行完成。这个特性就能很轻松的解决按顺序控制异步操作,即我们前一章节讲的异步流程的问题。
道友们还记得在Generator章节的肚包鸡的制作过程的实例,我们用async/await来重写这个例子,并比较下两者实现的区别。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 | //准备 function prepare(){ return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(function(){ console.log("prepare chicken"); resolve(); },500) }); } //炒鸡 function fired(){ return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(function(){ console.log("fired chicken"); resolve(); },500) }); } //炖鸡 function stewed(){ return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(function(){ console.log("stewed chicken"); resolve(); },500) }); } //上料 function sdd(){ return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(function(){ console.log("sdd chicken"); resolve(); },500) }); } //上菜 function serve(){ return new Promise((resolve) => { setTimeout(function(){ console.log("serve chicken"); resolve(); },500) }); } async function task(){ console.log("start task"); await prepare(); await fired(); await stewed(); await sdd(); await serve(); console.log("end task"); } task(); |
这段代码看上去神清气爽,我们来分析下代码:
1、首先每个制作异步过程封装成Promise对象。
2、利用await阻塞原理,实现每个制作的顺序执行。
相比较Generator实现,无需run流程函数,完美的实现了异步流程。
四、总结
从Promise到Generator,再到async,对于异步编程的解决方案越来越完美,这就是ES6不断发展的魅力所在。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通