Android控件进阶-自定义流式布局和热门标签控件
概述
详细
一、概述:
在日常的app使用中,我们会在android 的app中看见 热门标签等自动换行的流式布局,今天,我们就来看看如何
自定义一个类似热门标签那样的流式布局吧
类似的自定义换行流式布局控件。下面我们就来详细介绍流式布局的应用特点以及用的的技术点:
1.流式布局的特点以及应用场景
特点:当上面一行的空间不够容纳新的TextView时候,
才开辟下一行的空间
原理图:
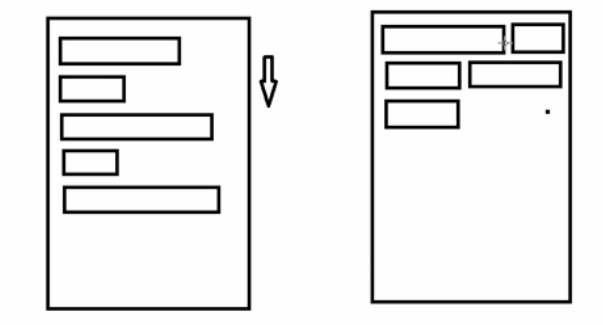
场景:主要用于关键词搜索或者热门标签等场景
2.自定义ViewGroup,重点重写下面两个方法
1、onMeasure:测量子view的宽高,设置自己的宽和高
2、onLayout:设置子view的位置
onMeasure:根据子view的布局文件中属性,来为子view设置测量模式和测量值
测量=测量模式+测量值;
测量模式有3种:
EXACTLY:表示设置了精确的值,一般当childView设置其宽、高为精确值、match_parent时,ViewGroup会将其设置为EXACTLY;
AT_MOST:表示子布局被限制在一个最大值内,一般当childView设置其宽、高为wrap_content时,ViewGroup会将其设置为AT_MOST;
UNSPECIFIED:表示子布局想要多大就多大,一般出现在AadapterView的item的heightMode中、ScrollView的childView的heightMode中;此种模式比较少见。
3.LayoutParams
ViewGroup LayoutParams :每个 ViewGroup 对应一个 LayoutParams; 即 ViewGroup -> LayoutParams
getLayoutParams 不知道转为哪个对应的LayoutParams ,其实很简单,就是如下:
子View.getLayoutParams 得到的LayoutParams对应的就是 子View所在的父控件的LayoutParams;
例如,LinearLayout 里面的子view.getLayoutParams ->LinearLayout.LayoutParams
所以 咱们的FlowLayout 也需要一个LayoutParams,由于上面的效果图是子View的 margin,
所以应该使用MarginLayoutParams。即FlowLayout->MarginLayoutParams
4.最后来看看实现的最终效果图:
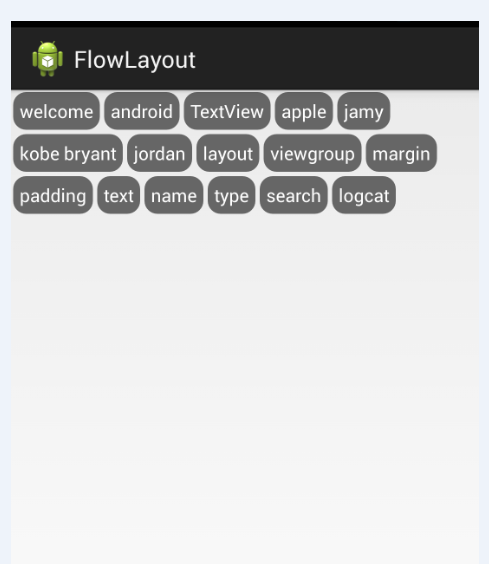
二、热门标签的流式布局的实现:
1. 自定义热门标签的ViewGroup实现
根据上面的技术分析,自定义类继承于ViewGroup,并重写 onMeasure和onLayout等方法。具体核心实现代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 | package com.czm.flowlayout;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import android.content.Context;import android.util.AttributeSet;import android.view.View;import android.view.ViewGroup;/** * * @author caizhiming * */public class XCFlowLayout extends ViewGroup{ @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //父控件传进来的宽度和高度以及对应的测量模式 int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); //如果当前ViewGroup的宽高为wrap_content的情况 int width = 0;//自己测量的 宽度 int height = 0;//自己测量的高度 //记录每一行的宽度和高度 int lineWidth = 0; int lineHeight = 0; //获取子view的个数 int childCount = getChildCount(); for(int i = 0;i < childCount; i ++){ View child = getChildAt(i); //测量子View的宽和高 measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); //得到LayoutParams MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); //子View占据的宽度 int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin; //子View占据的高度 int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin; //换行时候 if(lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth){ //对比得到最大的宽度 width = Math.max(width, lineWidth); //重置lineWidth lineWidth = childWidth; //记录行高 height += lineHeight; lineHeight = childHeight; }else{//不换行情况 //叠加行宽 lineWidth += childWidth; //得到最大行高 lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight); } //处理最后一个子View的情况 if(i == childCount -1){ width = Math.max(width, lineWidth); height += lineHeight; } } //wrap_content setMeasuredDimension(modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width, modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight : height); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub mAllChildViews.clear(); mLineHeight.clear(); //获取当前ViewGroup的宽度 int width = getWidth(); int lineWidth = 0; int lineHeight = 0; //记录当前行的view List<View> lineViews = new ArrayList<View>(); int childCount = getChildCount(); for(int i = 0;i < childCount; i ++){ View child = getChildAt(i); MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); //如果需要换行 if(childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width){ //记录LineHeight mLineHeight.add(lineHeight); //记录当前行的Views mAllChildViews.add(lineViews); //重置行的宽高 lineWidth = 0; lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin; //重置view的集合 lineViews = new ArrayList(); } lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin; lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin); lineViews.add(child); } //处理最后一行 mLineHeight.add(lineHeight); mAllChildViews.add(lineViews); //设置子View的位置 int left = 0; int top = 0; //获取行数 int lineCount = mAllChildViews.size(); for(int i = 0; i < lineCount; i ++){ //当前行的views和高度 lineViews = mAllChildViews.get(i); lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i); for(int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j ++){ View child = lineViews.get(j); //判断是否显示 if(child.getVisibility() == View.GONE){ continue; } MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); int cLeft = left + lp.leftMargin; int cTop = top + lp.topMargin; int cRight = cLeft + child.getMeasuredWidth(); int cBottom = cTop + child.getMeasuredHeight(); //进行子View进行布局 child.layout(cLeft, cTop, cRight, cBottom); left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin; } left = 0; top += lineHeight; } } } |
2.相关的布局文件:
引用自定义控件:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <com.czm.flowlayout.XCFlowLayout android:id="@+id/flowlayout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > </com.czm.flowlayout.XCFlowLayout></RelativeLayout> |
三、使用该自定义布局控件类
最后,如何使用该自定义的热门标签控件类呢?很简单,请看下面实例代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 | package com.czm.flowlayout;import android.app.Activity;import android.graphics.Color;import android.os.Bundle;import android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;import android.view.ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams;import android.widget.TextView;/** * * @author caizhiming * */public class MainActivity extends Activity { private String mNames[] = { "welcome","android","TextView", "apple","jamy","kobe bryant", "jordan","layout","viewgroup", "margin","padding","text", "name","type","search","logcat" }; private XCFlowLayout mFlowLayout; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); initChildViews(); } private void initChildViews() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub mFlowLayout = (XCFlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.flowlayout); MarginLayoutParams lp = new MarginLayoutParams( LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT); lp.leftMargin = 5; lp.rightMargin = 5; lp.topMargin = 5; lp.bottomMargin = 5; for(int i = 0; i < mNames.length; i ++){ TextView view = new TextView(this); view.setText(mNames[i]); view.setTextColor(Color.WHITE); view.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.textview_bg)); mFlowLayout.addView(view,lp); } }} |
四、项目代码目录结构图




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· Windows编程----内核对象竟然如此简单?