Region使用全解
前言
Region,即为区域,它表示的是canvas图层上的某一块封闭的区域。很多时候,我们会利用Region来构造一个图形。
今天要讲的内容有:
- Region的直接构造方法
- Region的间接构造方法
- Region的setPath(Path path, Region clip)方法介绍
- Region取区域并集
- Region.Op常量操作Region
- 项目结构图和效果图
一. Region的直接构造方法
Region有以下构造方法:
public Region(Region region);//复制一个Region
public Region(Rect r);//通过Rect构建一个Region
public Region(int left, int top, int right, int bottom);//通过坐标点构建一个region
下面我们试图绘制一个Region,代码如下:
//设置画笔
Paint paint=new Paint();
paint.setColor(getRidColor(R.color.color_0a900a));
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setStrokeWidth(5f);//无描边,设置setStrokeWidth无效
//构建矩形
Rect rect=new Rect();
rect.set(340,50,740,250);
Region region=new Region(rect);
//Android还提供了一个RegionIterator来对Region中的所有矩阵进行迭代,
// 可以使用该类,获得某个Region的所有矩阵
//通过遍历region中的矩阵,并绘制出来,来绘制region
RegionIterator iterator=new RegionIterator(region);
Rect r=new Rect();
while(iterator.next(r)){
canvas.drawRect(r,paint);
}
以上代码值得注意的是,Paint设置的style是FILL,不存在描边的问题,所有设置 stokenWidth无效。
RegionIterator 是Region中所有矩阵的迭代器,我们可以通过遍历region中的矩阵,并绘制出来,来绘制region。
绘制出的Region效果图如下:

由上面的代码可以看出来,Canvas并未提供直接绘制Region的方法,而Region的本意也不是用来绘图的。它的主要作用是来操作图形的,用处理区域间的合并,差集等逻辑关系
二. Region的间接构造方法
Region的间接构造方法主要是通过new一个空的Region,然后结合set相关函数来设置Region。
Region空构造函数:
public Region();
涉及的set函数有:
public void setEmpty();//设置空
public boolean set(Region region);
public boolean set(Rect r);
public boolean set(int left, int top, int right, int bottom);
public boolean setPath(Path path, Region clip);
那么要构建一个Region的话,你可以这样:
Region region=new Region();
region.set(340,50,740,250);
值得注意的是,setXXX系列的方法,都会替换掉之前Region中的区域值。
setEmpty()方法是清空Region中的区域。
其他几个方法都好理解,下面着重讲 setPath 方法。
三. Region的setPath(Path path, Region clip)方法介绍
public boolean setPath(Path path, Region clip);
参数介绍:
Path path:用来构造区域的路径
Region clip:与第一个参数path所构成的路径取交集,并将该交集设为最终区域。
简单的说,就是setPath(Path path, Region clip)方法是将path形成的路径和clip形成的区域取交集,获得一个交集区域。
下面给出setPath方法使用的代码:
//设置paint
Paint paint=new Paint();
paint.setColor(getRidColor(R.color.color_f5cc1d));
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//构造椭圆路径
Path path=new Path();
//构建椭圆path
RectF rectF=new RectF(100,300,980,500);
path.addOval(rectF,Path.Direction.CCW);//Path.Direction.CCW:逆时针;Path.Direction.CW:顺时针
//构建Region
Region region=new Region();
region.set(540,300,980,500);
//取path和region的交集
Region rgn=new Region();
rgn.setPath(path,region);
//绘制区域
drawRegion(canvas,rgn,paint);
效果图如下:

四. Region取区域并集
Region取区域并集的方法如下:
boolean union(Rect r);
返回的是一个boolean,若为true,则表示并集成功,否则表示失败
示例代码如下:
//设置画笔
Paint paint=new Paint();
paint.setColor(getRidColor(R.color.color_12aef7));
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
//设置区域
Region region=new Region(540,550,980,650);
region.union(new Rect(490,600,590,700));
//绘制区域
drawRegion(canvas,region,paint);
效果图如下:

五.Region.Op常量操作Region
当然,region的操作还有多种,简便的操作,由Region.Op常量控制
Region.Op操作常量有:
Region.Op.INTERSECT //交集
Region.Op.DIFFERENCE //补集
Region.Op.REPLACE //替换
Region.Op.REVERSE_DIFFERENCE //反转补集
Region.Op.UNION //并集
Region.Op.XOR //异并集
下面给出Region操作交集的示例代码:
Paint paint=new Paint();
paint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setStrokeWidth(5);
//绘制矩形轨迹
Rect rOne=new Rect(120,750,220,1050);
Rect rTwo=new Rect(20,850,320,950);
canvas.drawRect(rOne,paint);
canvas.drawRect(rTwo,paint);
Region regionOne=new Region(rOne);
Region regionTwo=new Region(rTwo);
regionTwo.op(regionOne,Region.Op.INTERSECT);//交集
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
drawRegion(canvas,regionTwo,paint);
效果图如下:
其他几种Region操作情况与此类似,demo中均有详细代码,现在给出自定义控件RegionView的主要逻辑代码:
//初始化
init(canvas);
//直接构建Region
directbuildRegion(canvas);
//间接构建Region
inDirectBuildRegion(canvas);
//Region的setPath方法求path和region的交集
pathAndRegionIntersection(canvas);
//区域取并集
rectAndRectIntersection(canvas);
//区域操作
controOne(canvas);//交集
controTwo(canvas);//补集
controThree(canvas);//替换
controFour(canvas);//反转补集
controFive(canvas);//并集
controSix(canvas);//异并集
RegionView在MainActivity对应的activity_main.xml中引用如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.android.testdemo.main.MainActivity">
<com.android.testdemo.function.RegionView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
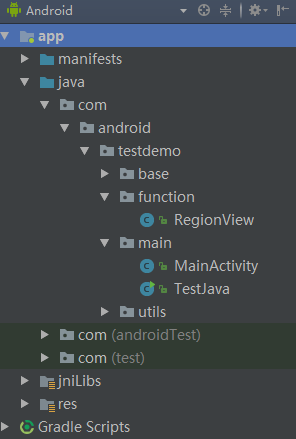
六.项目结构图和效果图
项目结构图
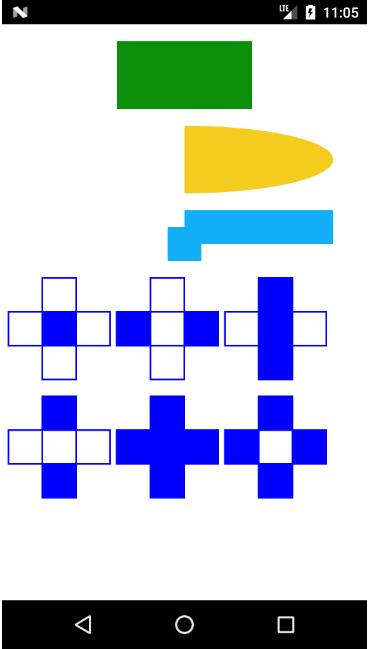
效果图
Region使用全解
注:本文著作权归作者,由demo大师代发,拒绝转载,转载需要作者授权




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· Windows编程----内核对象竟然如此简单?
2018-03-05 Android基于UDP的局域网聊天通信
2018-03-05 基于React实现的【绿色版电子书阅读器】,支持离线下载
2018-03-05 破解 zip 压缩包程序
2018-03-05 小小数据统计(柱状图、折线图、扇形图)
2018-03-05 iOS活体人脸识别的Demo和一些思路
2018-03-05 iOS蓝牙原生封装,助力智能硬件开发
2018-03-05 基于python实现的DDoS