从文本到图像——文本识别数据集生成器
一、开发背景
图像中的文本识别近几年来备受瞩目。通常来说,图片中的文本能够比图片中其他内容提供更加丰富的信息。因此,图像文本识别能够将图像中的文本区域转化成计算机可以读取和编辑的符号,打通了从图像到文本再到信息的通路。
随着计算机算力的提升,基于深度学习方法的本文识别技术逐渐成为主流,而深度学习中数据集的获取是重中之重。本脚本实现读取语料集中的文本内容,以保存为图像形式的数据集,用于模型训练。
二、脚本效果
1、IDE中的运行界面
(1)选择字体文件
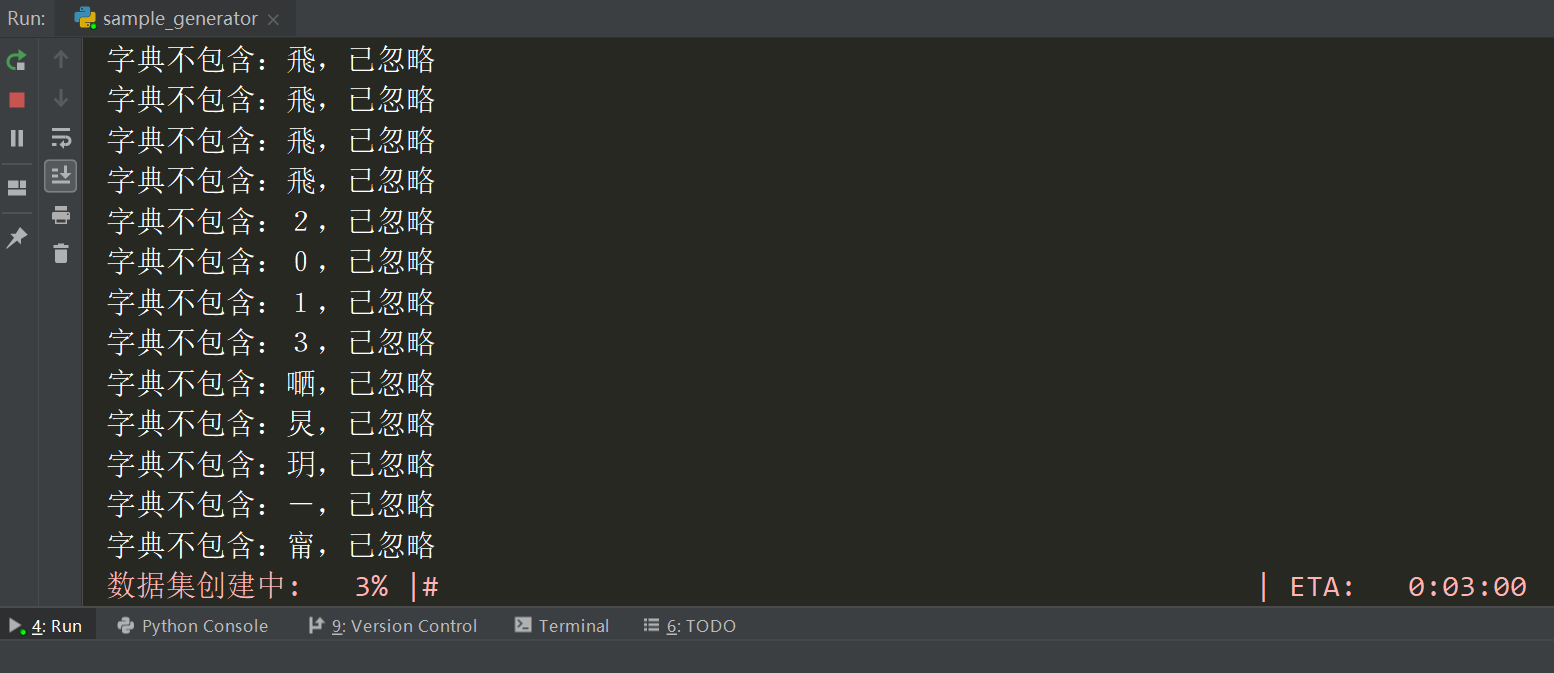
(2)生成数据集
2、生成的图像
不使用数据增强


使用数据增强


3、映射表
存储图像文件名和类别序列标注的对应关系
三、具体开发
1、功能需求
- 根据用户指定的语料数据生成图像文件及映射表
- 用户可自行更改文本长度,图像数量及图像尺寸
- 用户可自行选择是否进行增强处理
2、实际项目
1. 项目结构
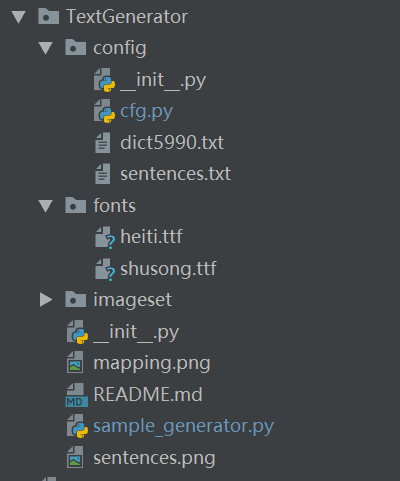
(1)根目录下的fonts文件夹用于存放ttf字体文件, imageset文件夹用于存放输出图像和映射表
(2)config中设置相关参数并存放语料文件, dict5990.txt是字典, sentences.txt是语料集
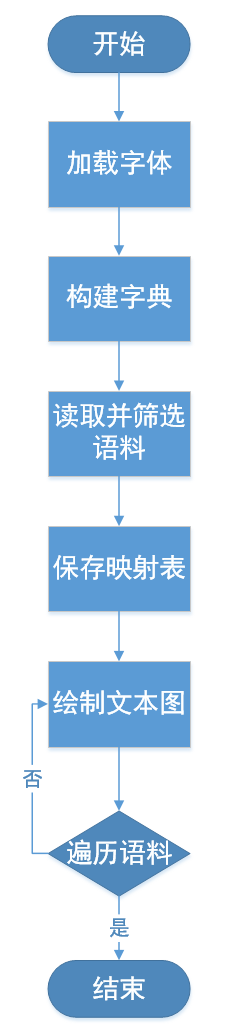
2. 实现思路
3. 代码实现
1. 设置参数
# 语料集
corpus = 'config/sentences.txt'
dict = 'config/dict5990.txt'
# 字体文件路径
FONT_PATH = 'fonts/'
# 输出路径
OUTPUT_DIR = 'imageset/'
# 样本总数
n_samples = 50
# 每行最大长度
sentence_lim = 10
# 画布能容纳的最大序列长度,对应img_w
canvas_lim = 50
2. 构建生成器
1. 加载字体文件
# 选择字体
root = tk.Tk()
root.withdraw()
self.font_path = filedialog.askopenfilename()
def load_fonts(self, factor, font_path):
""" 加载字体文件并设定字体大小
"""
self.fonts = []
# 加载字体文件
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, int(self.img_h*factor), 0)
self.fonts.append(font)
2. 构建字典
def build_dict(self):
""" 打开字典,加载全部字符到list
每行是一个字
"""
with codecs.open(self.dictfile, mode='r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
# 按行读取语料
for line in f:
# 当前行单词去除结尾,为了正常读取空格,第一行两个空格
word = line.strip('\r\n')
# 只要没超出上限就继续添加单词
self.dict.append(word)
# 最后一位作为空白符
self.blank_label = len(self.dict)
3. 加载语料
def build_train_list(self, num_rows, max_row_len=None):
# 过滤语料,留下适合的内容组成训练list
assert max_row_len <= self.img_lim
self.num_rows = num_rows
self.max_row_len = max_row_len
sentence_list = []
self.train_list = []
with codecs.open(self.corpus_file, mode='r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
# 按行读取语料
for line in f:
sentence = line.rstrip().replace(' ', '') # 当前行单词
if len(sentence) <= max_row_len and len(sentence_list) < num_rows:
# 只要句子长度不超过画布上限且句子数量没超出上限就继续添加
sentence_list.append(sentence)
elif len(sentence) > max_row_len and len(sentence_list) < num_rows:
# 截断句子
sentence_list.append(sentence[0:max_row_len])
if len(sentence_list) < self.num_rows:
raise IOError('语料不够')
for i, sentence in enumerate(sentence_list):
# 遍历语料中的每一句(行)
# 将单词分成字符,然后找到每个字符对应的整数ID list
label_sequence = []
for j, word in enumerate(sentence): # 检查句子中是否包含生僻字
try:
index = self.dict.index(word)
label_sequence.append(index)
except ValueError:
print("字典不包含:{},已忽略".format(word))
sentence_list[i] = sentence_list[i][0:j] + sentence_list[i][j+1:] # 从该句中删除生僻字
self.train_list = sentence_list # 过滤后的训练集
np.random.shuffle(self.train_list) # 打乱顺序
4. 保存映射表
def mapping_list(self):
# 写图像文件名和类别序列的对照表
file_path = os.path.join(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, 'map_list.txt')
with codecs.open(file_path, mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for i in range(len(self.train_list)):
f.write("{}.png {} \n".format(i, self.train_list[i]))
5. 绘制图像
def paint_text(self, text, i):
""" 使用PIL绘制文本图像,传入画布尺寸,返回文本图像
:param h: 画布高度
:param w: 画布宽度
"""
# 创建画布
canvas = np.zeros(shape=(self.img_h, self.img_w), dtype=np.uint8)
canvas[0:] = 255
# 转换图像模式,保证合成的两张图尺寸模式一致
ndimg = Image.fromarray(canvas).convert('RGBA')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(ndimg)
font = self.fonts[-1]
text_size = font.getsize(text) # 获取当前字体下的文本区域大小
# 自动调整字体大小避免超出边界, 至少留白水平20%
margin = [self.img_w - int(0.2*self.img_w), self.img_h - int(0.2*self.img_h)]
while (text_size[0] > margin[0]) or (text_size[1] > margin[1]):
self.font_factor -= 0.1
self.load_fonts(self.font_factor, self.font_path)
font = self.fonts[-1]
text_size = font.getsize(text)
# 随机平移
horizontal_space = self.img_w - text_size[0]
vertical_space = self.img_h - text_size[1]
start_x = np.random.randint(2, horizontal_space-2)
start_y = np.random.randint(2, vertical_space-2)
# 绘制当前文本行
draw.text((start_x, start_y), text, font=font, fill=(0, 0, 0, 255))
img_array = np.array(ndimg)
# 转灰度图
grey_img = img_array[:, :, 0] # [32, 256, 4]
if self.aug == True:
auged = augmentation(grey_img)
ndimg = Image.fromarray(auged).convert('RGBA')
save_path = os.path.join(cfg.OUTPUT_DIR, '{}.png'.format(i)) # 类别序列即文件名
ndimg.save(save_path)
6. 数据增强
def speckle(img):
severity = np.random.uniform(0, 0.6*255)
blur = ndimage.gaussian_filter(np.random.randn(*img.shape) * severity, 1)
img_speck = (img + blur)
img_speck[img_speck > 255] = 255
img_speck[img_speck <= 0] = 0
return img_speck
def augmentation(img, ):
# 不能直接在原始image上改动
image = img.copy()
img_h, img_w = img.shape
mode = np.random.randint(0, 9)
'''添加随机模糊和噪声'''
# 高斯模糊
if mode == 0:
image = cv2.GaussianBlur(image,(5, 5), np.random.randint(1, 10))
# 模糊后二值化,虚化边缘
if mode == 1:
image = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (9, 9), np.random.randint(1, 8))
ret, th = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
thresh = image.copy()
thresh[thresh >= th] = 0
thresh[thresh < th] = 255
image = thresh
# 横线干扰
if mode == 2:
for i in range(0, img_w, 2):
cv2.line(image, (0, i), (img_w, i), 0, 1)
# 竖线
if mode == 3:
for i in range(0, img_w, 2):
cv2.line(image, (i, 0), (i, img_h), 0, 1)
# 十字线
if mode == 4:
for i in range(0, img_h, 2):
cv2.line(image, (0, i), (img_w, i), 0, 1)
for i in range(0, img_w, 2):
cv2.line(image, (i, 0), (i, img_h), 0, 1)
# 左右运动模糊
if mode == 5:
kernel_size = 5
kernel_motion_blur = np.zeros((kernel_size, kernel_size))
kernel_motion_blur[int((kernel_size - 1) / 2), :] = np.ones(kernel_size)
kernel_motion_blur = kernel_motion_blur / kernel_size
image = cv2.filter2D(image, -1, kernel_motion_blur)
# 上下运动模糊
if mode == 6:
kernel_size = 9
kernel_motion_blur = np.zeros((kernel_size, kernel_size))
kernel_motion_blur[:, int((kernel_size - 1) / 2)] = np.ones(kernel_size)
kernel_motion_blur = kernel_motion_blur / kernel_size
image = cv2.filter2D(image, -1, kernel_motion_blur)
# 高斯噪声
if mode == 7:
row, col = [img_h, img_w]
mean = 0
sigma = 1
gauss = np.random.normal(mean, sigma, (row, col))
gauss = gauss.reshape(row, col)
noisy = image + gauss
image = noisy.astype(np.uint8)
# 污迹
if mode == 8:
image = speckle(image)
return image
4. 使用说明
运行sample_generator.py后会跳出对话框, 选择字体文件即可生成数据集
从文本到图像——文本识别数据集生成器
注:本文著作权归作者,由demo大师代发,拒绝转载,转载需要作者授权




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· Windows编程----内核对象竟然如此简单?
2018-03-05 Android基于UDP的局域网聊天通信
2018-03-05 基于React实现的【绿色版电子书阅读器】,支持离线下载
2018-03-05 破解 zip 压缩包程序
2018-03-05 小小数据统计(柱状图、折线图、扇形图)
2018-03-05 iOS活体人脸识别的Demo和一些思路
2018-03-05 iOS蓝牙原生封装,助力智能硬件开发
2018-03-05 基于python实现的DDoS