.NETCore 之 中间件 02
上一篇我们知道可以使用 app.use 注册中间件,但是 这样都写在 Startup 文件可能不是我们想要的。.NET Core 提供了 使用 UseMiddlewareExtensions 扩展中间件。我们看一下需要什么。
// Copyright (c) .NET Foundation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0. See License.txt in the project root for license information.
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Linq.Expressions;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http.Abstractions;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Internal;
namespace Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder
{
/// <summary>
/// Extension methods for adding typed middleware.
/// </summary>
public static class UseMiddlewareExtensions
{
internal const string InvokeMethodName = "Invoke";
internal const string InvokeAsyncMethodName = "InvokeAsync";
private static readonly MethodInfo GetServiceInfo = typeof(UseMiddlewareExtensions).GetMethod(nameof(GetService), BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Static)!;
/// <summary>
/// Adds a middleware type to the application's request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="TMiddleware">The middleware type.</typeparam>
/// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param>
/// <param name="args">The arguments to pass to the middleware type instance's constructor.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns>
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware<TMiddleware>(this IApplicationBuilder app, params object[] args)
{
return app.UseMiddleware(typeof(TMiddleware), args);
}
/// <summary>
/// Adds a middleware type to the application's request pipeline.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="app">The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</param>
/// <param name="middleware">The middleware type.</param>
/// <param name="args">The arguments to pass to the middleware type instance's constructor.</param>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IApplicationBuilder"/> instance.</returns>
public static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddleware(this IApplicationBuilder app, Type middleware, params object[] args)
{
if (typeof(IMiddleware).GetTypeInfo().IsAssignableFrom(middleware.GetTypeInfo()))
{
// IMiddleware doesn't support passing args directly since it's
// activated from the container
if (args.Length > 0)
{
throw new NotSupportedException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareExplicitArgumentsNotSupported(typeof(IMiddleware)));
}
return UseMiddlewareInterface(app, middleware);
}
var applicationServices = app.ApplicationServices;
return app.Use(next =>
{
var methods = middleware.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public);
var invokeMethods = methods.Where(m =>
string.Equals(m.Name, InvokeMethodName, StringComparison.Ordinal)
|| string.Equals(m.Name, InvokeAsyncMethodName, StringComparison.Ordinal)
).ToArray();
if (invokeMethods.Length > 1)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddleMutlipleInvokes(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName));
}
if (invokeMethods.Length == 0)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoInvokeMethod(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, middleware));
}
var methodInfo = invokeMethods[0];
if (!typeof(Task).IsAssignableFrom(methodInfo.ReturnType))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNonTaskReturnType(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, nameof(Task)));
}
var parameters = methodInfo.GetParameters();
if (parameters.Length == 0 || parameters[0].ParameterType != typeof(HttpContext))
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoParameters(InvokeMethodName, InvokeAsyncMethodName, nameof(HttpContext)));
}
var ctorArgs = new object[args.Length + 1];
ctorArgs[0] = next;
Array.Copy(args, 0, ctorArgs, 1, args.Length);
var instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(app.ApplicationServices, middleware, ctorArgs);
if (parameters.Length == 1)
{
return (RequestDelegate)methodInfo.CreateDelegate(typeof(RequestDelegate), instance);
}
var factory = Compile<object>(methodInfo, parameters);
return context =>
{
var serviceProvider = context.RequestServices ?? applicationServices;
if (serviceProvider == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareIServiceProviderNotAvailable(nameof(IServiceProvider)));
}
return factory(instance, context, serviceProvider);
};
});
}
private static IApplicationBuilder UseMiddlewareInterface(IApplicationBuilder app, Type middlewareType)
{
return app.Use(next =>
{
return async context =>
{
var middlewareFactory = (IMiddlewareFactory?)context.RequestServices.GetService(typeof(IMiddlewareFactory));
if (middlewareFactory == null)
{
// No middleware factory
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareNoMiddlewareFactory(typeof(IMiddlewareFactory)));
}
var middleware = middlewareFactory.Create(middlewareType);
if (middleware == null)
{
// The factory returned null, it's a broken implementation
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_UseMiddlewareUnableToCreateMiddleware(middlewareFactory.GetType(), middlewareType));
}
try
{
await middleware.InvokeAsync(context, next);
}
finally
{
middlewareFactory.Release(middleware);
}
};
});
}
private static Func<T, HttpContext, IServiceProvider, Task> Compile<T>(MethodInfo methodInfo, ParameterInfo[] parameters)
{
// If we call something like
//
// public class Middleware
// {
// public Task Invoke(HttpContext context, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
// {
//
// }
// }
//
// We'll end up with something like this:
// Generic version:
//
// Task Invoke(Middleware instance, HttpContext httpContext, IServiceProvider provider)
// {
// return instance.Invoke(httpContext, (ILoggerFactory)UseMiddlewareExtensions.GetService(provider, typeof(ILoggerFactory));
// }
// Non generic version:
//
// Task Invoke(object instance, HttpContext httpContext, IServiceProvider provider)
// {
// return ((Middleware)instance).Invoke(httpContext, (ILoggerFactory)UseMiddlewareExtensions.GetService(provider, typeof(ILoggerFactory));
// }
var middleware = typeof(T);
var httpContextArg = Expression.Parameter(typeof(HttpContext), "httpContext");
var providerArg = Expression.Parameter(typeof(IServiceProvider), "serviceProvider");
var instanceArg = Expression.Parameter(middleware, "middleware");
var methodArguments = new Expression[parameters.Length];
methodArguments[0] = httpContextArg;
for (int i = 1; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
var parameterType = parameters[i].ParameterType;
if (parameterType.IsByRef)
{
throw new NotSupportedException(Resources.FormatException_InvokeDoesNotSupportRefOrOutParams(InvokeMethodName));
}
var parameterTypeExpression = new Expression[]
{
providerArg,
Expression.Constant(parameterType, typeof(Type)),
Expression.Constant(methodInfo.DeclaringType, typeof(Type))
};
var getServiceCall = Expression.Call(GetServiceInfo, parameterTypeExpression);
methodArguments[i] = Expression.Convert(getServiceCall, parameterType);
}
Expression middlewareInstanceArg = instanceArg;
if (methodInfo.DeclaringType != null && methodInfo.DeclaringType != typeof(T))
{
middlewareInstanceArg = Expression.Convert(middlewareInstanceArg, methodInfo.DeclaringType);
}
var body = Expression.Call(middlewareInstanceArg, methodInfo, methodArguments);
var lambda = Expression.Lambda<Func<T, HttpContext, IServiceProvider, Task>>(body, instanceArg, httpContextArg, providerArg);
return lambda.Compile();
}
private static object GetService(IServiceProvider sp, Type type, Type middleware)
{
var service = sp.GetService(type);
if (service == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(Resources.FormatException_InvokeMiddlewareNoService(type, middleware));
}
return service;
}
}
}
关键点我们看到 要在 自定义中间件中要实现 Invoke 或 InvokeAsync 方法

并且在构造函数中 注册了 next ->RequestDelegate
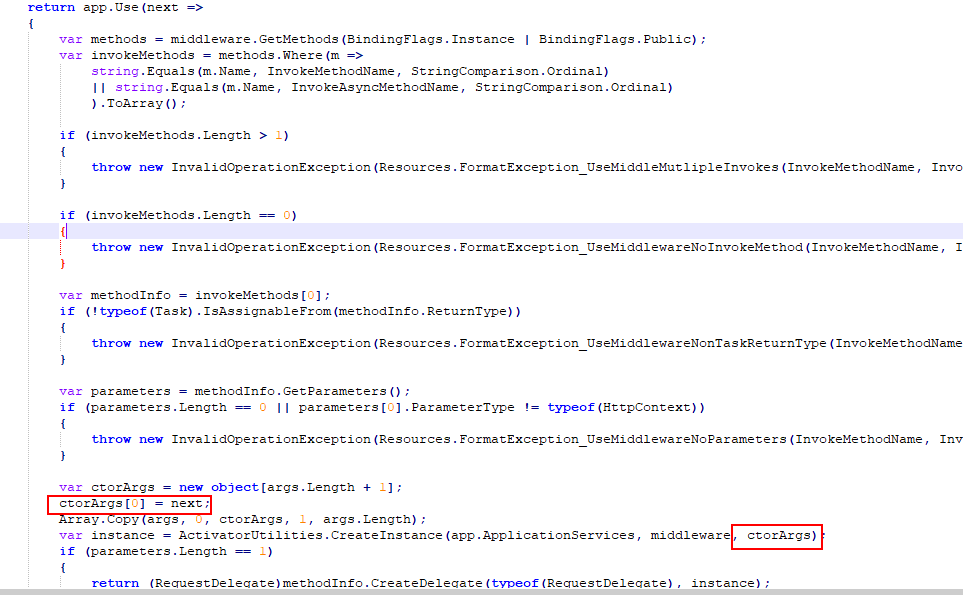
所以有了上面的基础,我们可以方面实现自定义中间件。
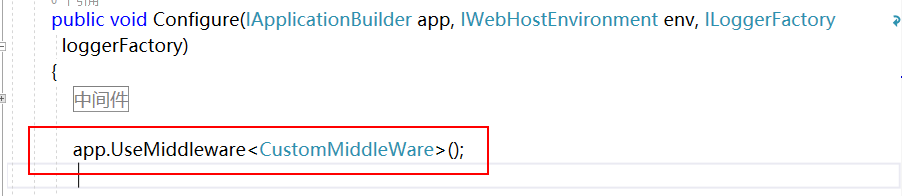
public class CustomMiddleWare
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _next;
public CustomMiddleWare(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public async Task Invoke(HttpContext context)
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync($"{nameof(CustomMiddleWare)},Hello World1!<br/>");
await _next(context);
await context.Response.WriteAsync($"{nameof(CustomMiddleWare)},Hello World2");
}
}
在 Startup 文件中注册即可。
PYTHON



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号