有关git&&ssh
之前按照这里https://confluence.atlassian.com/bitbucket/set-up-ssh-for-git-728138079.html的步骤进行git的设置,本来以为以后push的时候就不需要密码了,结果一开始好好的,时间长了就还是要输入密码,于是乎到处找资料,也是醉了。
=============================================================
0x01
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-26284395-id-2949145.html
第一步:在本地机器上使用ssh-keygen产生公钥私钥对
- jsmith@local-host$ [Note: You are on local-host here]
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-keygen
- Generating public/private rsa key pair.
- Enter file in which to save the key (/home/jsmith/.ssh/id_rsa):[Enter key]
- Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): [Press enter key]
- Enter same passphrase again: [Pess enter key]
- Your identification has been saved in /home/jsmith/.ssh/id_rsa.
- Your public key has been saved in /home/jsmith/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
- The key fingerprint is:
- 33:b3:fe:af:95:95:18:11:31:d5:de:96:2f:f2:35:f9 jsmith@local-host
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub remote-host
- jsmith@remote-host's password:
- Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh 'remote-host'", and check in:
- .ssh/authorized_keys
- to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
注意: ssh-copy-id 将key写到远程机器的 ~/ .ssh/authorized_key.文件中
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh remote-host
- Last login: Sun Nov 16 17:22:33 2008 from 192.168.1.2
- [Note: SSH did not ask for password.]
- jsmith@remote-host$ [Note: You are on remote-host here]
常见问题:
- ssh-copy-id -u eucalyptus -i ~eucalyptus/.ssh/id_rsa.pub eucalyptus@remote_host
上述是给eucalyptus用户赋予无密码登陆的权利
[1]
- /usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: ERROR: No identities found
使用选项 -i ,当没有值传递的时候或者 如果 ~/.ssh/identity.pub 文件不可访问(不存在), ssh-copy-id 将显示上述的错误信息 ( -i选项会优先使用将ssh-add -L的内容)
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-agent $SHELL
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-add -L
- The agent has no identities.
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-add
- Identity added: /home/jsmith/.ssh/id_rsa (/home/jsmith/.ssh/id_rsa)
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-add -L
- ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEAsJIEILxftj8aSxMa3d8t6JvM79DyBV
- aHrtPhTYpq7kIEMUNzApnyxsHpH1tQ/Ow== /home/jsmith/.ssh/id_rsa
- jsmith@local-host$ ssh-copy-id -i remote-host
- jsmith@remote-host's password:
- Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh 'remote-host'", and check in:
- .ssh/authorized_keys
- to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
- [Note: This has added the key displayed by ssh-add -L]
[2] ssh-copy-id应注意的三个小地方
- Default public key: ssh-copy-id uses ~/.ssh/identity.pub as the default public key file (i.e when no value is passed to option -i). Instead, I wish it uses id_dsa.pub, or id_rsa.pub, or identity.pub as default keys. i.e If any one of them exist, it should copy that to the remote-host. If two or three of them exist, it should copy identity.pub as default.
- The agent has no identities: When the ssh-agent is running and the ssh-add -L returns “The agent has no identities” (i.e no keys are added to the ssh-agent), the ssh-copy-id will still copy the message “The agent has no identities” to the remote-host’s authorized_keys entry.
- Duplicate entry in authorized_keys: I wish ssh-copy-id validates duplicate entry on the remote-host’s authorized_keys. If you execute ssh-copy-id multiple times on the local-host, it will keep appending the same key on the remote-host’s authorized_keys file without checking for duplicates. Even with duplicate entries everything works as expected. But, I would like to have my authorized_keys file clutter free.
0x02
执行ssh-add时出现Could not open a connection to your authentication agent
执行ssh-add ~/.ssh/rsa
先执行 eval `ssh-agent` (是~键上的那个`) 再执行 ssh-add ~/.ssh/rsa成功
ssh-add -l 就有新加的rsa了
0x03
是否必须每次添加ssh-add
首先我得说和 ssh 相关的一切机制的确比较复杂,很容易让人晕头转向,如果你想彻底掌握这个知识体系就必须系统的学习一下相关的知识。所以 first thing first,我推荐一本书给你,不妨抽时间把它一劳永逸了:
SSH, The Secure Shell,这本书的第一版有中文的。
接着说你的这个特定的问题。
你首先得了解一件事:ssh-add 这个命令不是用来永久性的记住你所使用的私钥的。实际上,它的作用只是把你指定的私钥添加到 ssh-agent 所管理的一个 session 当中。而 ssh-agent 是一个用于存储私钥的临时性的 session 服务,也就是说当你重启之后,ssh-agent 服务也就重置了。
如果是为了永久记住对应的私钥是哪个,我们不能依赖 ssh-agent 服务。能依赖什么则取决于以下哪些方案适合你的使用场景。
使用某种安全的秘钥管理机制
你没有在问题里描述你所使用的操作系统,所以我以我日常使用的 Mac OS X 为例。Mac 系统内置了一个Keychain 的服务及其管理程序,可以方便的帮你管理各种秘钥,其中包括 ssh 秘钥。ssh-add 默认将制定的秘钥添加在当前运行的 ssh-agent 服务中,但是你可以改变这个默认行为让它添加到 keychain 服务中,让 Mac 来帮你记住、管理并保障这些秘钥的安全性。
你所要做的就是执行下面的命令:
$ ssh-add -K [path/to/your/ssh-key]
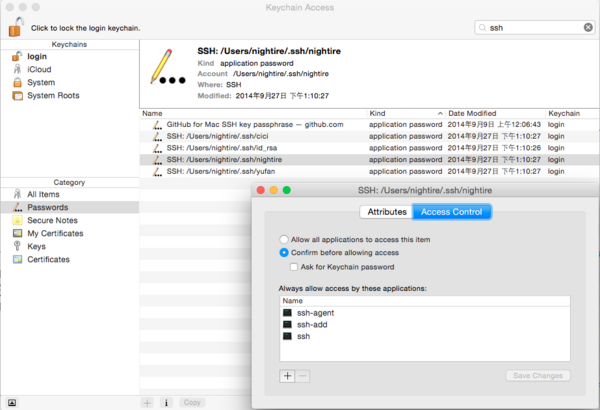
之后,其他的程序请求 ssh 秘钥的时候,会通过 Keychain 服务来请求。下面的截图里你可以看到我当前的机器上 Keychain 为我管理的有关 ssh 的秘钥,这其中包括我自己生成的四个,以及 Github Client App 自己使用的一个——前者几个都是供 ssh 相关的命令所使用,而后者则指明了仅供 Github.app 这个应用程序使用。 另外,它们都是 login keychains 也就是只有当前用户登录之后才会生效的,换了用户或是未登录状态是不能使用的,这就是 Keychain 服务所帮你做的事情。
如何使用多个 ssh 秘钥并对应不同的应用程序?
这个问题也是我没有完全吃透的,按照某些资料描述,做了以上的工作之后,应用程序应该能够自动匹配适用的 ssh 秘钥了。但是在我学习的过程中也遇到过非得手动指定的情况(那个时候我还不了解 Keychain 的作用,都是手动去 ssh-add 的),于是另外一种机制可以帮你解决这个问题,即 ssh config。
一言蔽之,ssh config 就是一个配置文件,描述不同的秘钥对应的设置——包括主机名、用户名、访问策略等等。
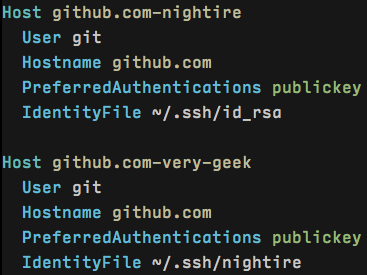
以下我截取了本地配置的两个片段:
这两段配置分别对应 Github 和 Coding 这两个服务所使用的秘钥。第一行的 Host 只是一个名字,第三行的Hostname 才是对应的真实地址,但是两者最好保持一致,这样不用在脑袋里转换。
用这样的配置,当我 git clone https://github.com/user/repo 的时候,id_rsa 秘钥会被使用,当我git clone https://coding.net/user/repo 的时候,很显然 nightire 秘钥会被使用。
当然,此配置不局限于 Git,所有底层使用 SSH 的应用和命令都会遵照配置文件的指示来找到对应的私钥。
回到本节开始的话题,我相信有了 Keychain 做管理应该是不需要这个配置文件的,但是我还没有机会去做测试。目前的环境一切正常,等到我换新机器重新配置环境的时候我会试一试看。
关于 Host 和 Hostname 的对应关系,如果 Hostname 是域名则最好保持一致。但是这里有两个诀窍:
1. 如果同一域名下有两个不同的配置怎么办?
以 Github 为例,如果我有两个账户,一个个人的,一个组织的,并且要使用不同的秘钥,那么我可以这么写:
这里 Host 后面对应的是 Github 的两个用户名,也就是 github.com/nightire 和 github.com/very-geek
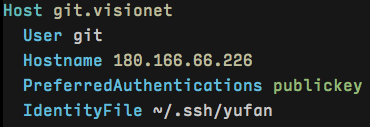
2. 如果域名是数字 IP,是否可以简化呢?
Host 可以帮助你把对应的 IP 变成好记的名字。比如说我在公司内部配置了 Git Server(基于 gitolite 或 Gitlab 或任何工具),正常的访问地址是:git://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:repo.git,如下的配置则可以帮你把它简化成:git.visionet:repo.git
非常有用。
有没有简单点的办法?
有。如果 ssh-add 已经可以满足你的要求(除了启动以后还要再来一遍以外),那么你完全可以用脚本自动化这件事。简单地把你输入的 ssh-add 命令的内容写进 .bashrc 或 .bash_profile(或其他任何你使用的 shell 环境配置文件)中去,这样只要你打开终端,就等于自动做了这件事情。
不过如我之前所说,这个机制是依赖 ssh-agent 服务的,并且只能在终端下有效。而用 Keychain 机制的话,是整个系统内都有效的(包括不依赖终端的应用程序)并且无需开启 ssh-agent 服务。
最后 Keychain 服务不是只有 Mac 才有的,我刚才搜索了一下,Windows 和 各种 Linux 都有对应的机制,不过我没用过,只能以 Mac 为例了。了解了这些概念,相信你可以自己查得到具体的方法。
原文地址:http://segmentfault.com/q/1010000000835302/a-1020000000883441
===========================================================================
最终的处理是:ssh-agent $SHELL
ssh-add





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号