Java -- MyBatis学习笔记12、联合查询
1、一对一关联
以客户表和客户详情表为例,客户表里存放基本信息,客户详情表存放详细信息。
1.1、提出需求
根据客户id,查询客户信息并查到详情表对应的信息。
- 表字段以及对应关系
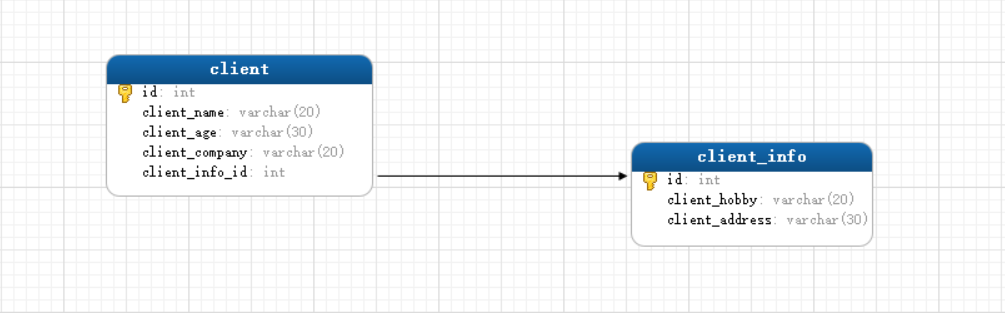
1.2、创建实体类
- 首先定义客户实体类
client表中有一个client_info_id字段,所以在Client类中定义一个clientInfo属性,用于维护Client和ClientInfo之间的一对一关系,将联合查询的结果中的客户详情信息,映射的该属性当中。
public class Client {
private int id;
private String client_name;
private String client_age;
private String client_company;
//客户详情
private ClientInfo clientInfo;
//getter and setter...
}
- 定义客户详情实体类
public class ClientInfo {
private int id;
private String client_hobby;
private String client_address;
//getter and setter...
}
- 定义Dao层接口
public interface ClientDao {
Client queryClientAndInfo(int id);
}
- mapper映射文件
<mapper namespace="com.rg.dao.ClientDao">
<!--
方式一:直接联合查询、通过association标签、将查询到的客户详情信息
映射到clientInfo属性当中来。
-->
<select id="queryClientAndInfo" resultMap="client_info_map">
SELECT c.client_name, c.client_age, c.client_company, c.client_info_id,ci.id, ci.client_hobby, client_address
FROM client as c
INNER JOIN client_info as ci on c.client_info_id = ci.id
where c.id = #{id}
</select>
<resultMap id="client_info_map" type="com.rg.bean.Client">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="client_name" column="client_name"/>
<result property="client_age" column="client_age"/>
<result property="client_company" column="client_company"/>
<!--
类型为:ClientInfo、也就是客户详情
-->
<association property="clientInfo" javaType="com.rg.bean.ClientInfo">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="client_address" column="client_address"/>
<result property="client_hobby" column="client_hobby"/>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--
方式二:嵌套查询:通过执行另外一个SQL映射语句来返回预期的复杂类型
-->
<select id="queryClientAndInfo" resultMap="client_Info_map">
select * from client where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--
resultMap 可以自定义 sql 的结果和 java 对象属性的映射关系。
更灵活的把列值赋值给指定属性。
常用在列名和 java 对象属性名不一样的情况。
property:对象属性名称
JavaType:对象属性类型
column:数据库表字段名称
select:使用另一个查询的封装结果
-->
<resultMap id="client_Info_map" type="com.rg.bean.Client">
<!-- 主键字段使用id -->
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<!-- 非主键字段使用result -->
<result property="client_name" column="client_name"/>
<result property="client_age" column="client_age"/>
<result property="client_company" column="client_company"/>
<!--通过select、执行另一个sql语句-->
<association property="clientInfo" column="client_info_id" javaType="com.rg.bean.ClientInfo" select="selectClientInfo"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectClientInfo" resultType="com.rg.bean.ClientInfo">
select * from client_info where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
- 测试
@Test
public void test01() {
Client client = clientDao.queryClientAndInfo(1);
System.out.println(client);
}
- 结果
Client{id=1, client_name='王经理', client_age='18', client_company='阿里巴巴', clientInfo=ClientInfo{id=1, client_hobby='打篮球', client_address='上海'}}
个人感觉第二种方式更简洁,首先它不需要写很长的联合语句,其次结构更加简洁明了。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号