JDK8 - Stream
Stream API (java.util.stream) 简介:
Stream是真正将函数式编程风格引入到java中。
集合讲的是数据,Stream讲的是计算。
stream自己不会储存元素;stream不会改变源对象;stream操作是延时的,会等到需要结果时才执行。
Stream的三个步骤:
1. 创建stream - 一个数据源(如集合,数组),创建一个流。
2. 中间操作 - 一个中间操作链,对数据源进行处理。
3. 终止操作 - 一旦终止操作,就执行中间操作链,并产生结果。之后不会再被使用。
创建stream:
用于测试用的数据:
@Data @AllArgsConstructor public class Employee { private int id; private String name; private int age; private Double salary; @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Employee employee = (Employee) o; return id == employee.id && age == employee.age && Objects.equals(name, employee.name) && Objects.equals(salary, employee.salary); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(id, name, age, salary); } } public class EmployeeData { public static List<Employee> getEmployees() { List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<>(); list.add(new Employee(101, "yi master", 14, 22.3)); list.add(new Employee(102, "shi master", 15, 32.3)); list.add(new Employee(103, "tom master", 16, 42.3)); list.add(new Employee(104, "jerry master", 18, 25.3)); list.add(new Employee(105, "a master", 19, 77.3)); list.add(new Employee(106, "b master", 20, 82.3)); list.add(new Employee(107, "c master", 21, 92.3)); list.add(new Employee(108, "d master", 22, 12.3)); return list; } }
创建stream的三种方式:
(本文所有图片都来自https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV184411x7XA?p=13)



还有一个创建无限流,这里省略
案例:
public class StreamAPITest { @Test public void test1() { List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); // 1.通过集合返回一个流 Stream<Employee> stream1 = employees.stream(); // 1.通过集合返回一个并行流 Stream<Employee> stream2 = employees.parallelStream(); // 2.通过数组返回一个int流 int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5}; IntStream stream3 = Arrays.stream(arr); // 2.通过数组返回一个流 Employee e1 = new Employee(108, "yi master", 21, 12.3); Employee e2 = new Employee(109, "shi master", 22, 12.3); Employee e3 = new Employee(110, "a master", 23, 12.3); Employee[] emp = new Employee[] {e1, e2, e3}; Stream<Employee> stream4 = Arrays.stream(emp); // 3.通过stream的of方法 Stream<Integer> stream5 = Stream.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); } }
stream中间操作:

@Test public void testFirst() { List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); Stream<Employee> stream = employees.stream(); // 过滤age大于20的 System.out.println("过滤age大于20的:"); stream.filter(e-> e.getAge() > 20).forEach(System.out::println); //截断 System.out.println("截断前3个:"); employees.stream().limit(3).forEach(System.out::println); //跳过元素 System.out.println("跳过前2个:"); employees.stream().skip(2).forEach(System.out::println); // distinct去重 System.out.println("去重:"); employees.add(new Employee(108, "d master", 22, 12.3)); employees.add(new Employee(108, "d master", 22, 12.3)); employees.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println); }

public class StreamAPITest { @Test public void testSecond() { // 1. map demo1 System.out.println("map demo1:"); List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa", "bb", "cc"); list.stream().map(str -> str.toUpperCase()).forEach(System.out::println); // 1. map demo2 System.out.println("map demo2:"); List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); Stream<String> nameStream = employees.stream().map(e -> e.getName()); nameStream.forEach(System.out::println); // 2. map与flatmap对比之map System.out.println("map与flatmap对比之map:"); Stream<Stream<Character>> mapStream = list.stream().map(StreamAPITest::toCharacterSteam); mapStream.forEach(s->{ s.forEach(System.out::println); }); // 2. map与flatmap对比之flatmap System.out.println("map与flatmap对比之flatmap:"); Stream<Character> flatStream= list.stream().flatMap(StreamAPITest::toCharacterSteam); flatStream.forEach(System.out::println); } public static Stream<Character> toCharacterSteam(String s) { List<Character> charList = new ArrayList<>(); for (Character c : s.toCharArray()) { charList.add(c); } return charList.stream(); } }
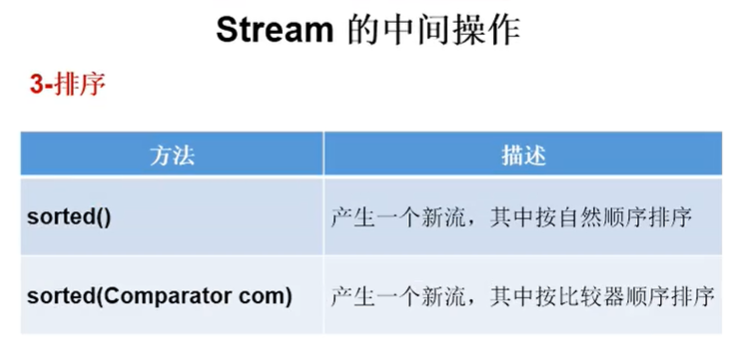
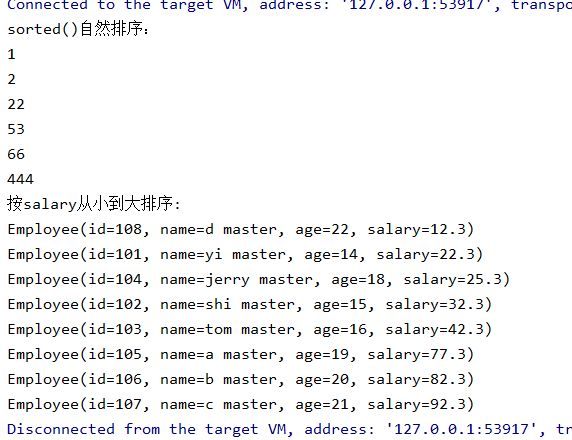
public class StreamAPITest2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 自然排序 System.out.println("sorted()自然排序:"); int[] arr = new int[]{1,2,444,53,66,22}; Arrays.stream(arr).sorted().forEach(System.out::println); // 选择器排序 // 按salary从小到大排序 System.out.println("按salary从小到大排序:"); Stream<Employee> stream = EmployeeData.getEmployees().stream(); stream.sorted((e1, e2) -> { return (int)(e1.getSalary() - e2.getSalary()); }).forEach(System.out::println); } }

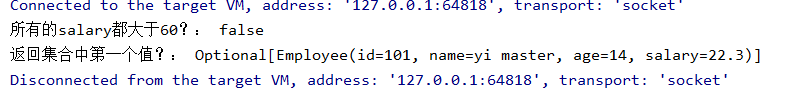
public class StreamAPITest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); boolean b = list.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getSalary() > 60); System.out.println("所有的salary都大于60?: " + b); Optional<Employee> first = list.stream().findFirst(); System.out.println("返回集合中第一个值?: " + first); } }
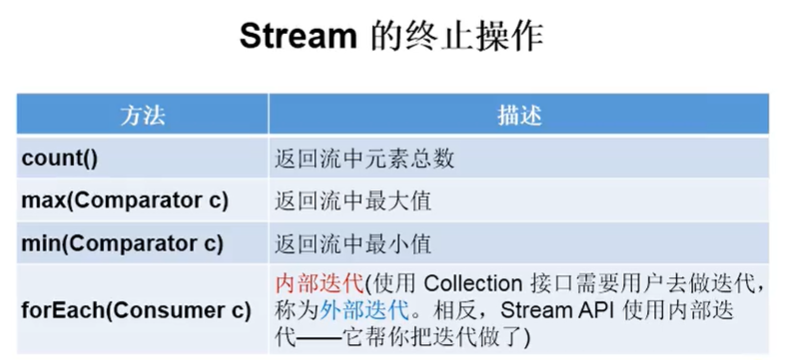
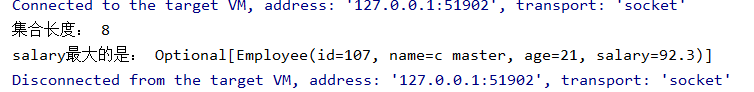
public class StreamAPITest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // count List<Employee> list = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); long count = list.stream().count(); System.out.println("集合长度: " +count); // max(), 返回salary最大的 Optional<Employee> max = list.stream().max((e1, e2) -> { return (int) (e1.getSalary() - e2.getSalary()); }); System.out.println("salary最大的是: " + max); } }
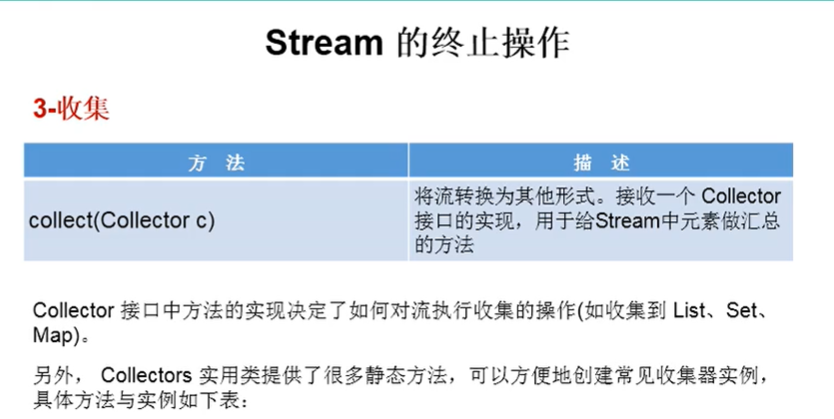
public class StreamAPITest3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 查找salary大于70的返回list List<Employee> employees = EmployeeData.getEmployees(); List<Employee> collect = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary() > 70).collect(Collectors.toList()); collect.forEach(System.out::println); } }