springboot-webservice
文档摘要:
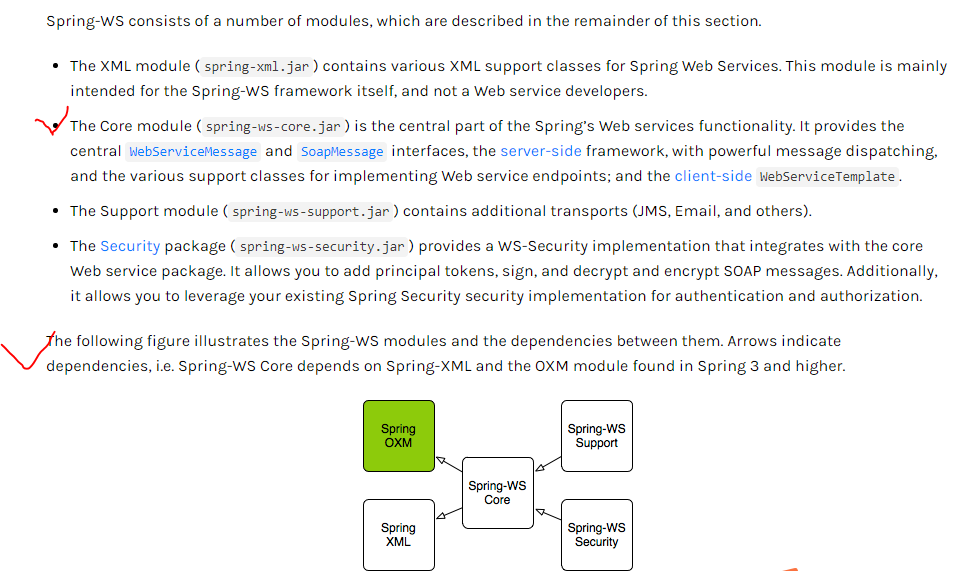
Why Contract First?
When creating Web services, there are two development styles: Contract Last and Contract First. When using a contract-last approach, you start with the Java code, and let the Web service contract (WSDL, see sidebar) be generated from that. When using contract-first, you start with the WSDL contract, and use Java to implement said contract.
Spring-WS only supports the contract-first development style
why contract-first? 主要是讲了Object/XML mapping的问题.就不详细摘录了。
When using contract-first, you explicitly describe what XML is sent where, thus making sure that it is exactly what you want.
Writing Contract-First Web Services
contract-first Web services, that is, developing web services that start with the XML Schema/WSDL contract first followed by the Java code second.
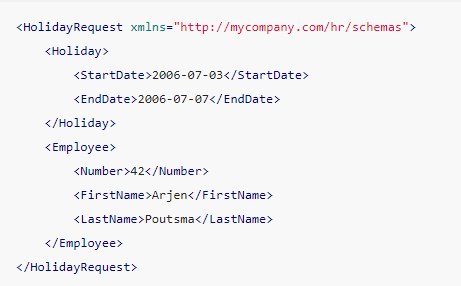
xml message:
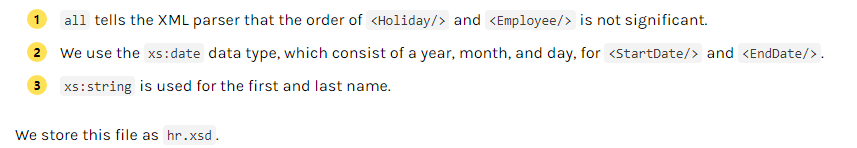
使用约束:XML Schema(XSD)



<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ws</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ws-core</artifactId>
<version></version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jdom</groupId>
<artifactId>jdom</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>jaxen</groupId>
<artifactId>jaxen</artifactId>
<version>1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
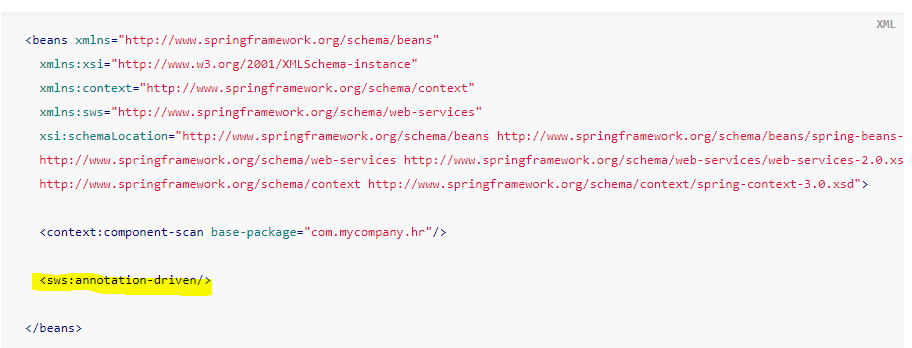
We also instruct Spring-WS to use annotation-driven endpoints, with the <sws:annotation-driven>element.
package com.mycompany.hr.ws; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.Endpoint; import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.PayloadRoot; import org.springframework.ws.server.endpoint.annotation.RequestPayload; import com.mycompany.hr.service.HumanResourceService; import org.jdom2.Element; import org.jdom2.JDOMException; import org.jdom2.Namespace; import org.jdom2.filter.Filters; import org.jdom2.xpath.XPathExpression; import org.jdom2.xpath.XPathFactory; @Endpoint public class HolidayEndpoint { private static final String NAMESPACE_URI = "http://mycompany.com/hr/schemas"; private XPathExpression<Element> startDateExpression; private XPathExpression<Element> endDateExpression; private XPathExpression<Element> firstNameExpression; private XPathExpression<Element> lastNameExpression; private HumanResourceService humanResourceService; @Autowired public HolidayEndpoint(HumanResourceService humanResourceService) throws JDOMException { this.humanResourceService = humanResourceService; Namespace namespace = Namespace.getNamespace("hr", NAMESPACE_URI); XPathFactory xPathFactory = XPathFactory.instance(); startDateExpression = xPathFactory.compile("//hr:StartDate", Filters.element(), null, namespace); endDateExpression = xPathFactory.compile("//hr:EndDate", Filters.element(), null, namespace); firstNameExpression = xPathFactory.compile("//hr:FirstName", Filters.element(), null, namespace); lastNameExpression = xPathFactory.compile("//hr:LastName", Filters.element(), null, namespace); } @PayloadRoot(namespace = NAMESPACE_URI, localPart = "HolidayRequest") public void handleHolidayRequest(@RequestPayload Element holidayRequest) throws Exception { Date startDate = parseDate(startDateExpression, holidayRequest); Date endDate = parseDate(endDateExpression, holidayRequest); String name = firstNameExpression.evaluateFirst(holidayRequest).getText() + " " + lastNameExpression.evaluateFirst(holidayRequest).getText(); humanResourceService.bookHoliday(startDate, endDate, name); } private Date parseDate(XPathExpression<Element> expression, Element element) throws ParseException { Element result = expression.evaluateFirst(element); if (result != null) { SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); return dateFormat.parse(result.getText()); } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not evaluate [" + expression + "] on [" + element + "]"); } } }
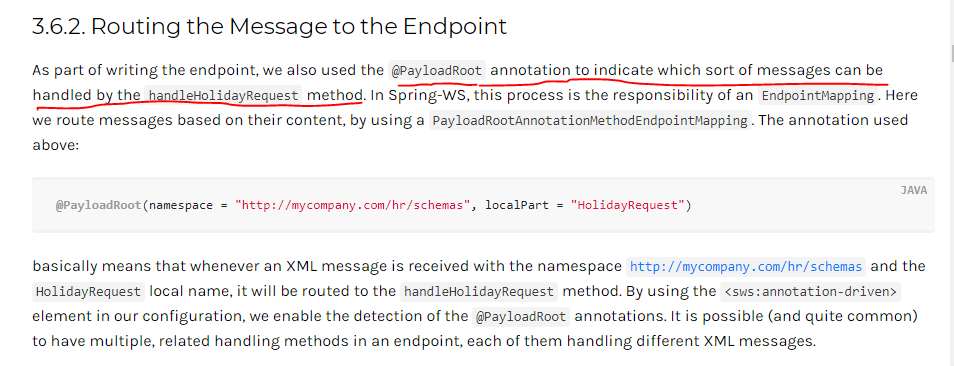
重点来了,接口和它的实现:
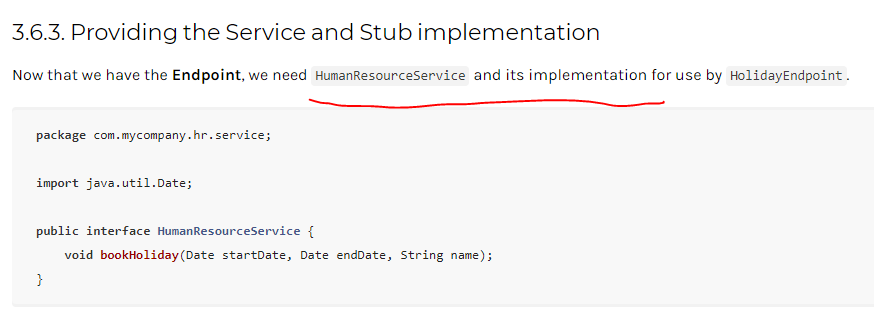
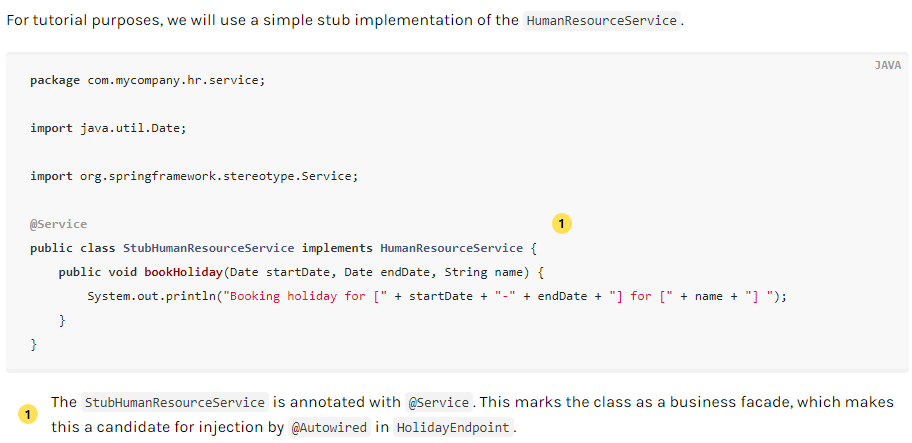
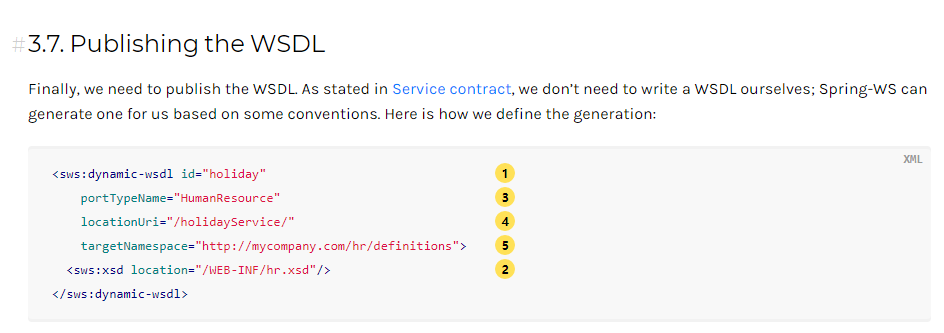
发布接口