Angular SPA基于Ocelot API网关与IdentityServer4的身份认证与授权(一)
好吧,这个题目我也想了很久,不知道如何用最简单的几个字来概括这篇文章,原本打算取名《Angular单页面应用基于Ocelot API网关与IdentityServer4+ASP.NET Identity实现身份认证与授权》,然而如你所见,这样的名字实在是太长了。所以,我不得不缩写“单页面应用”几个字,然后去掉ASP.NET Identity的描述,最后形成目前的标题。
不过,这也就意味着这篇文章会涵盖很多内容和技术,我会利用这些技术来走通一个完整的流程,这个流程也代表着在微服务架构中单点登录的一种实现模式。在此过程中,我们会使用到如下技术或框架:
- Angular 8
- Ocelot API Gateway
- IdentityServer4
- ASP.NET Identity
- Entity Framework Core
- SQL Server
本文假设读者具有上述技术框架的基础知识。由于内容比较多,我还是将这篇文章分几个部分进行讲解和讨论。
场景描述
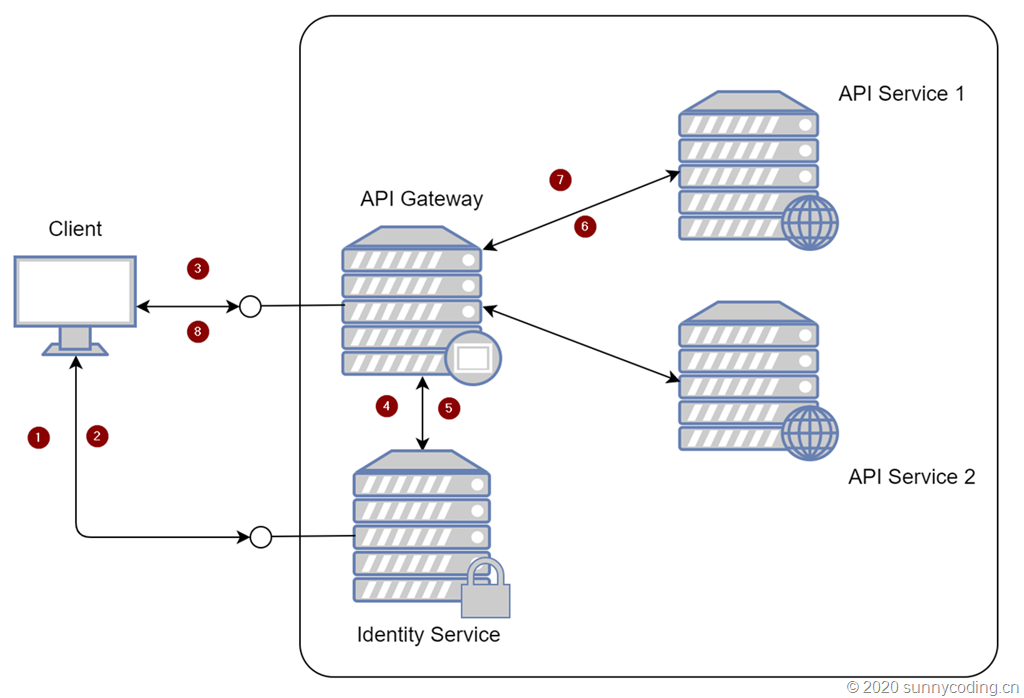
在微服务架构下的一种比较流行的设计,就是基于前后端分离,前端只做呈现和用户操作流的管理,后端服务由API网关同一协调,以从业务层面为前端提供各种服务。大致可以用下图表示:
在这个结构中,我没有将Identity Service放在API Gateway后端,因为考虑到Identity Service本身并没有承担任何业务功能。从它所能提供的端点(Endpoint)的角度,它也需要做负载均衡、熔断等保护,但我们暂时不讨论这些内容。
流程上其实也比较简单,在上图的数字标识中:
- Client向Identity Service发送认证请求,通常可以是用户名密码
- 如果验证通过,Identity Service会向Client返回认证的Token
- Client使用Token向API Gateway发送API调用请求
- API Gateway将Client发送过来的Token发送给Identity Service,以验证Token的有效性
- 如果验证成功,Identity Service会告知API Gateway认证成功
- API Gateway转发Client的请求到后端API Service
- API Service将结果返回给API Gateway
- API Gateway将API Service返回的结果转发到Client
只是在这些步骤中,我们有很多技术选择,比如Identity Service的实现方式、认证方式等等。接下来,我就在ASP.NET Core的基础上使用IdentityServer4、Entity Framework Core和Ocelot来完成这一流程。在完成整个流程的演练之前,需要确保机器满足以下条件:
- 安装Visual Studio 2019 Community Edition。使用Visual Studio Code也是可以的,根据自己的需要选择
- 安装Visual Studio Code
- 安装Angular 8
IdentityServer4结合ASP.NET Identity实现Identity Service
创建新项目
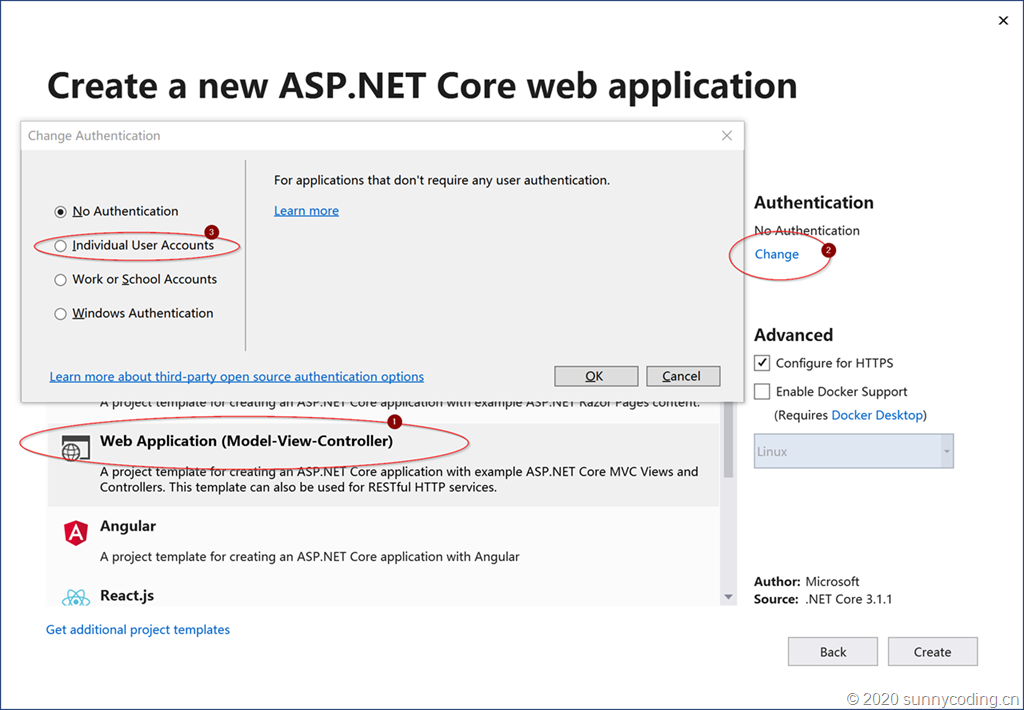
首先第一步就是实现Identity Service。在Visual Studio 2019 Community Edition中,新建一个ASP.NET Core Web Application,模板选择Web Application (Model-View-Controller),然后点击Authentication下的Change按钮,再选择Individual User Accounts选项,以便将ASP.NET Identity的依赖包都加入项目,并且自动完成基础代码的搭建。
然后,通过NuGet添加IdentityServer4.AspNetIdentity以及IdentityServer4.EntityFramework的引用,IdentityServer4也随之会被添加进来。接下来,在该项目的目录下,执行以下命令安装IdentityServer4的模板,并将IdentityServer4的GUI加入到当前项目:
dotnet new -i identityserver4.templates dotnet new is4ui --force
然后调整一下项目结构,将原本的Controllers目录删除,同时删除Models目录下的ErrorViewModel类,然后将Quickstart目录重命名为Controllers,编译代码,代码应该可以编译通过,接下来就是实现我们自己的Identity。
定制Identity Service
为了能够展现一个标准的应用场景,我自己定义了User和Role对象,它们分别继承于IdentityUser和IdentityRole类:
public class AppUser : IdentityUser
{
public string DisplayName { get; set; }
}
public class AppRole : IdentityRole
{
public string Description { get; set; }
}
当然,Data目录下的ApplicationDbContext也要做相应调整,它应该继承于IdentityDbContext<AppUser, AppRole, string>类,这是因为我们使用了自定义的IdentityUser和IdentityRole的实现:
public class ApplicationDbContext : IdentityDbContext<AppUser, AppRole, string>
{
public ApplicationDbContext(DbContextOptions<ApplicationDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
}
之后修改Startup.cs里的ConfigureServices方法,通过调用AddIdentity、AddIdentityServer以及AddDbContext,将ASP.NET Identity、IdentityServer4以及存储认证数据所使用的Entity Framework Core的依赖全部注册进来。为了测试方便,目前我们还是使用Developer Signing Credential,对于Identity Resource、API Resource以及Clients,我们也是暂时先写死(hard code):
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext<ApplicationDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(
Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection")));
services.AddIdentity<AppUser, AppRole>()
.AddEntityFrameworkStores<ApplicationDbContext>()
.AddDefaultTokenProviders();
services.AddIdentityServer().AddDeveloperSigningCredential()
.AddOperationalStore(options =>
{
options.ConfigureDbContext = builder => builder.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DefaultConnection"),
sqlServerDbContextOptionsBuilder =>
sqlServerDbContextOptionsBuilder.MigrationsAssembly(typeof(Startup).Assembly.GetName().Name));
options.EnableTokenCleanup = true;
options.TokenCleanupInterval = 30; // interval in seconds
})
.AddInMemoryIdentityResources(Config.GetIdentityResources())
.AddInMemoryApiResources(Config.GetApiResources())
.AddInMemoryClients(Config.GetClients())
.AddAspNetIdentity<AppUser>();
services.AddCors(options => options.AddPolicy("AllowAll", p => p.AllowAnyOrigin()
.AllowAnyMethod()
.AllowAnyHeader()));
services.AddControllersWithViews();
services.AddRazorPages();
services.AddControllers();
}
然后,调整Configure方法的实现,将IdentityServer加入进来,同时配置CORS使得站点能够被跨域访问:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseDatabaseErrorPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseCors("AllowAll");
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseIdentityServer();
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapControllerRoute(
name: "default",
pattern: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
endpoints.MapRazorPages();
});
}
完成这部分代码调整后,编译是通不过的,因为我们还没有定义IdentityServer4的IdentityResource、API Resource和Clients。在项目中新建一个Config类,代码如下:
public static class Config
{
public static IEnumerable<IdentityResource> GetIdentityResources() =>
new IdentityResource[]
{
new IdentityResources.OpenId(),
new IdentityResources.Email(),
new IdentityResources.Profile()
};
public static IEnumerable<ApiResource> GetApiResources() =>
new[]
{
new ApiResource("api.weather", "Weather API")
{
Scopes =
{
new Scope("api.weather.full_access", "Full access to Weather API")
},
UserClaims =
{
ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier,
ClaimTypes.Name,
ClaimTypes.Email,
ClaimTypes.Role
}
}
};
public static IEnumerable<Client> GetClients() =>
new[]
{
new Client
{
RequireConsent = false,
ClientId = "angular",
ClientName = "Angular SPA",
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.Implicit,
AllowedScopes = { "openid", "profile", "email", "api.weather.full_access" },
RedirectUris = {"http://localhost:4200/auth-callback"},
PostLogoutRedirectUris = {"http://localhost:4200/"},
AllowedCorsOrigins = {"http://localhost:4200"},
AllowAccessTokensViaBrowser = true,
AccessTokenLifetime = 3600
},
new Client
{
ClientId = "webapi",
AllowedGrantTypes = GrantTypes.ResourceOwnerPassword,
ClientSecrets =
{
new Secret("mysecret".Sha256())
},
AlwaysSendClientClaims = true,
AllowedScopes = { "api.weather.full_access" }
}
};
}
大致说明一下上面的代码。通俗地讲,IdentityResource是指允许应用程序访问用户的哪些身份认证资源,比如,用户的电子邮件或者其它用户账户信息,在Open ID Connect规范中,这些信息会被转换成Claims,保存在User Identity的对象里;ApiResource用来指定被IdentityServer4所保护的资源,比如这里新建了一个ApiResource,用来保护Weather API,它定义了自己的Scope和UserClaims。Scope其实是一种关联关系,它关联着Client与ApiResource,用来表示什么样的Client对于什么样的ApiResource具有怎样的访问权限,比如在这里,我定义了两个Client:angular和webapi,它们对Weather API都可以访问;UserClaims定义了当认证通过之后,IdentityServer4应该向请求方返回哪些Claim。至于Client,就比较容易理解了,它定义了客户端能够以哪几种方式来向IdentityServer4提交请求。
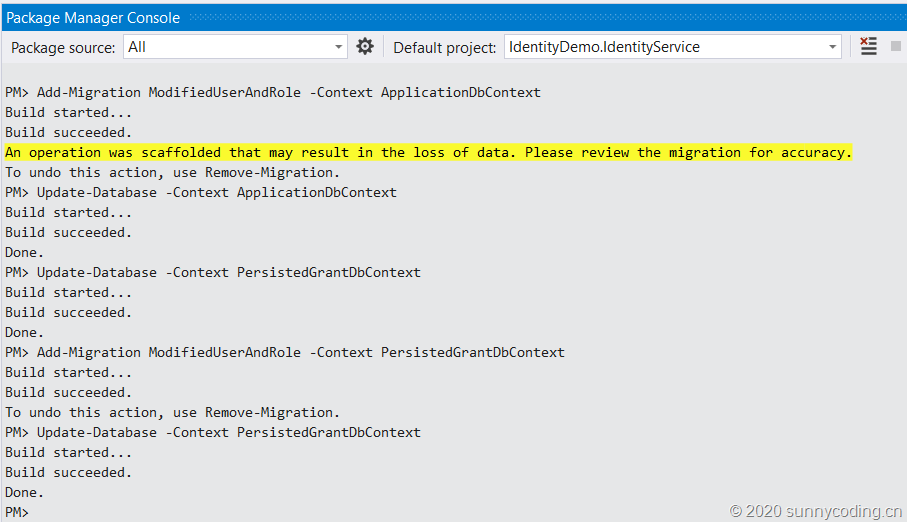
至此,我们的源代码就可以编译通过了,成功编译之后,还需要使用Entity Framework Core所提供的命令行工具或者Powershell Cmdlet来初始化数据库。我这里选择使用Visual Studio 2019 Community中的Package Manager Console,在执行数据库更新之前,确保appsettings.json文件里设置了正确的SQL Server连接字符串。当然,你也可以选择使用其它类型的数据库,只要对ConfigureServices方法做些相应的修改即可。在Package Manager Console中,依次执行下面的命令:
Add-Migration ModifiedUserAndRole -Context ApplicationDbContext Add-Migration ModifiedUserAndRole –Context PersistedGrantDbContext Update-Database -Context ApplicationDbContext Update-Database -Context PersistedGrantDbContext
效果如下:
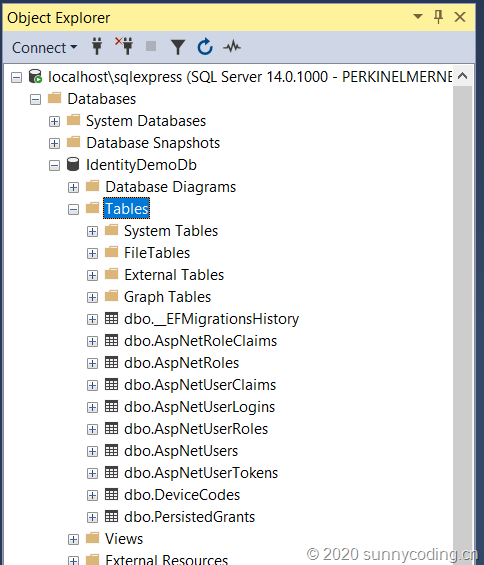
打开SQL Server Management Studio,看到数据表都已成功创建:
由于IdentityServer4的模板所产生的代码使用的是mock user,也就是IdentityServer4里默认的TestUser,因此,相关部分的代码需要被替换掉,最主要的部分就是AccountController的Login方法,将该方法中的相关代码替换为:
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
var user = await _userManager.FindByNameAsync(model.Username);
if (user != null && await _userManager.CheckPasswordAsync(user, model.Password))
{
await _events.RaiseAsync(new UserLoginSuccessEvent(user.UserName, user.Id, user.DisplayName));
// only set explicit expiration here if user chooses "remember me".
// otherwise we rely upon expiration configured in cookie middleware.
AuthenticationProperties props = null;
if (AccountOptions.AllowRememberLogin && model.RememberLogin)
{
props = new AuthenticationProperties
{
IsPersistent = true,
ExpiresUtc = DateTimeOffset.UtcNow.Add(AccountOptions.RememberMeLoginDuration)
};
};
// issue authentication cookie with subject ID and username
await HttpContext.SignInAsync(user.Id, user.UserName, props);
if (context != null)
{
if (await _clientStore.IsPkceClientAsync(context.ClientId))
{
// if the client is PKCE then we assume it's native, so this change in how to
// return the response is for better UX for the end user.
return View("Redirect", new RedirectViewModel { RedirectUrl = model.ReturnUrl });
}
// we can trust model.ReturnUrl since GetAuthorizationContextAsync returned non-null
return Redirect(model.ReturnUrl);
}
// request for a local page
if (Url.IsLocalUrl(model.ReturnUrl))
{
return Redirect(model.ReturnUrl);
}
else if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(model.ReturnUrl))
{
return Redirect("~/");
}
else
{
// user might have clicked on a malicious link - should be logged
throw new Exception("invalid return URL");
}
}
await _events.RaiseAsync(new UserLoginFailureEvent(model.Username, "invalid credentials", clientId: context?.ClientId));
ModelState.AddModelError(string.Empty, AccountOptions.InvalidCredentialsErrorMessage);
}
这样才能通过注入的userManager和EntityFramework Core来访问SQL Server,以完成登录逻辑。
新用户注册API
由IdentityServer4所提供的默认UI模板中没有包括新用户注册的页面,开发者可以根据自己的需要向Identity Service中增加View来提供注册界面。不过为了快速演示,我打算先增加两个API,然后使用curl来新建一些用于测试的角色(Role)和用户(User)。下面的代码为客户端提供了注册角色和注册用户的API:
public class RegisterRoleRequestViewModel
{
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
}
public class RegisterRoleResponseViewModel
{
public RegisterRoleResponseViewModel(AppRole role)
{
Id = role.Id;
Name = role.Name;
Description = role.Description;
}
public string Id { get; }
public string Name { get; }
public string Description { get; }
}
public class RegisterUserRequestViewModel
{
[Required]
[StringLength(50, ErrorMessage = "The {0} must be at least {2} and at max {1} characters long.", MinimumLength = 2)]
[Display(Name = "DisplayName")]
public string DisplayName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(100, ErrorMessage = "The {0} must be at least {2} and at max {1} characters long.", MinimumLength = 6)]
[DataType(DataType.Password)]
[Display(Name = "Password")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[Required]
[StringLength(20)]
[Display(Name = "UserName")]
public string UserName { get; set; }
public List<string> RoleNames { get; set; }
}
public class RegisterUserResponseViewModel
{
public string Id { get; set; }
public string UserName { get; set; }
public string DisplayName { get; set; }
public string Email { get; set; }
public RegisterUserResponseViewModel(AppUser user)
{
Id = user.Id;
UserName = user.UserName;
DisplayName = user.DisplayName;
Email = user.Email;
}
}
// Controllers\Account\AccountController.cs
[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/register-account")]
public async Task<IActionResult> RegisterAccount([FromBody] RegisterUserRequestViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
var user = new AppUser { UserName = model.UserName, DisplayName = model.DisplayName, Email = model.Email };
var result = await _userManager.CreateAsync(user, model.Password);
if (!result.Succeeded) return BadRequest(result.Errors);
await _userManager.AddClaimAsync(user, new Claim(ClaimTypes.NameIdentifier, user.UserName));
await _userManager.AddClaimAsync(user, new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, user.DisplayName));
await _userManager.AddClaimAsync(user, new Claim(ClaimTypes.Email, user.Email));
if (model.RoleNames?.Count > 0)
{
var validRoleNames = new List<string>();
foreach(var roleName in model.RoleNames)
{
var trimmedRoleName = roleName.Trim();
if (await _roleManager.RoleExistsAsync(trimmedRoleName))
{
validRoleNames.Add(trimmedRoleName);
await _userManager.AddToRoleAsync(user, trimmedRoleName);
}
}
await _userManager.AddClaimAsync(user, new Claim(ClaimTypes.Role, string.Join(',', validRoleNames)));
}
return Ok(new RegisterUserResponseViewModel(user));
}
// Controllers\Account\AccountController.cs
[HttpPost]
[Route("api/[controller]/register-role")]
public async Task<IActionResult> RegisterRole([FromBody] RegisterRoleRequestViewModel model)
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return BadRequest(ModelState);
}
var appRole = new AppRole { Name = model.Name, Description = model.Description };
var result = await _roleManager.CreateAsync(appRole);
if (!result.Succeeded) return BadRequest(result.Errors);
return Ok(new RegisterRoleResponseViewModel(appRole));
}
在上面的代码中,值得关注的就是register-account API中的几行AddClaimAsync调用,我们将一些用户信息数据加入到User Identity的Claims中,比如,将用户的角色信息,通过逗号分隔的字符串保存为Claim,在后续进行用户授权的时候,会用到这些数据。
创建一些基础数据
运行我们已经搭建好的Identity Service,然后使用下面的curl命令创建一些基础数据:
curl -X POST https://localhost:7890/api/account/register-role \
-d '{"name":"admin","description":"Administrator"}' \
-H 'Content-Type:application/json' --insecure
curl -X POST https://localhost:7890/api/account/register-account \
-d '{"userName":"daxnet","password":"P@ssw0rd123","displayName":"Sunny Chen","email":"daxnet@163.com","roleNames":["admin"]}' \
-H 'Content-Type:application/json' --insecure
curl -X POST https://localhost:7890/api/account/register-account \
-d '{"userName":"acqy","password":"P@ssw0rd123","displayName":"Qingyang Chen","email":"qychen@163.com"}' \
-H 'Content-Type:application/json' --insecure
完成这些命令后,系统中会创建一个admin的角色,并且会创建daxnet和acqy两个用户,daxnet具有admin角色,而acqy则没有该角色。
使用浏览器访问https://localhost:7890,点击主页的链接进入登录界面,用已创建的用户名和密码登录,可以看到如下的界面,表示Identity Service的开发基本完成:
小结
一篇文章实在是写不完,今天就暂且告一段落吧,下一讲我将介绍Weather API和基于Ocelot的API网关,整合Identity Service进行身份认证。
源代码
访问以下Github地址以获取源代码: