最小二乘法应用:用直线或曲线模型拟合散点
记录下用最小二乘法拟合线性模型的代码实现:
1、应用正规方程(Normal Equation)求解最小二乘法举例:
最简单的y关于x的线性方程\(y=\beta_0+\beta_1x\)
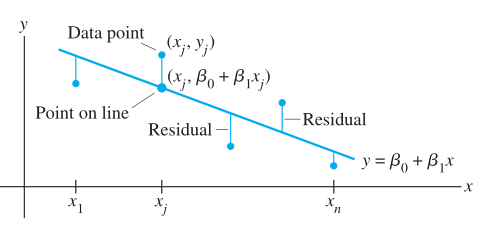
预测值和观察值:

写成矩阵形式:
\(X\beta=y\),其中\(X=\begin{bmatrix} 1& x_1\\ 1& x_2\\ ...&...\\ 1& x_n\\ \end{bmatrix}\) , \(\beta=\begin{bmatrix} \beta_0\\ \beta_1\\ \end{bmatrix}\) , \(y=\begin{bmatrix} y_1\\ y_2\\ ...\\ y_n\\ \end{bmatrix}\)
最小二乘法的解\(\beta\)可以通过解正规方程获得: \(X^TX\beta=X^Ty\)
python代码实现如下:
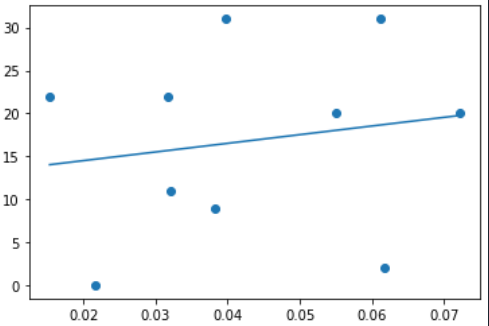
import numpy as np from numpy.linalg import inv x=[0.015348106072082663,0.021715879765738008,0.0316253067336889, 0.03212431406271639,0.03828189026158509,0.03965578961513808, 0.05502733389871053,0.06116957740576664,0.06170785924013203, 0.07206404835977503] y=[22, 0, 22, 11, 9, 31, 20, 31, 2, 20] def plotLinearRegression1(): X = np.array(x).reshape(len(x),1) reg=linear_model.LinearRegression(fit_intercept=True,normalize=False) reg.fit(X,y) k=reg.coef_#获取斜率w1,w2,w3,...,wn b=reg.intercept_#获取截距w0 #x0=np.arange(0,10,0.2) x0 = np.array(x).reshape(len(x),) y0=k*x0+b plt.scatter(x,y) plt.plot(x0, y0) print('k',k); print('b',b) ''' 用least squares ''' def plotLinearRegression2(): X = np.vstack([np.ones((1,len(x))),x]).T print('X:\n',X) Xt = X.T Z = Xt.dot(X) invZ = inv(Z) print('invZ:\n',invZ) W = (invZ.dot(Xt)).dot(y) print('W:\n',W) #plot plt.scatter(x,y) x0 = np.array(x).reshape(len(x),) # x0=np.arange(0,10,0.2) plt.plot(x0, W[1]*x0+W[0]) def plotLinearRegression3(): A = np.vstack([x, np.ones(len(x))]).T print('A:\n',A) m, c = np.linalg.lstsq(A, y, rcond=None)[0] print('m: ',m,' c:',c) x0 = np.array(x).reshape(len(x),) plt.plot(x, y, 'o', label='Original data', markersize=10) plt.plot(x0, m*x0 + c, 'r', label='Fitted line') plt.legend() plt.show() if __name__ == '__main__': plotLinearRegression2()
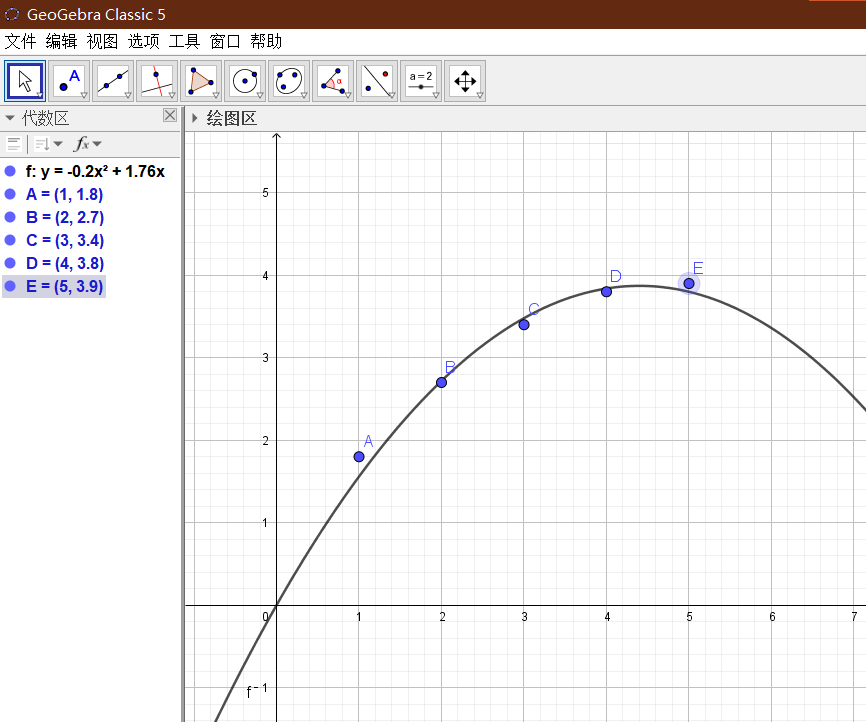
2、记录用最小二乘法拟合曲线模型
题目:(来源于书本《Linear Algebra And Its Applications Fifth Edition - David C.Lay · Steven R.Lay · Judi J. McDonald》)

解:
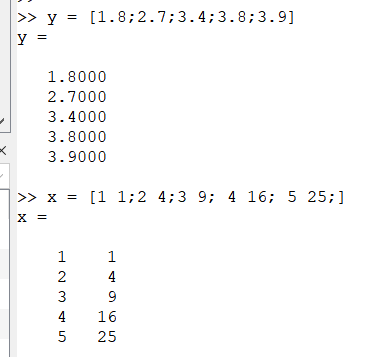
\(\bold{y}=\bold{x}\beta+\boldsymbol{\varepsilon}\),\(\bold{y}\) = \(\begin{bmatrix}
1.8
\\ 2.7
\\ 3.4
\\ 3.8
\\3.9
\end{bmatrix}\),\(\bold{x} = \begin{bmatrix}
1 & 1\\
2 & 4\\
3 & 9\\
4 & 16\\
5 & 25
\end{bmatrix}\), \(\boldsymbol{\beta } = \begin{bmatrix}
\beta _{1}\\
\beta _{2}
\end{bmatrix}\), \(\boldsymbol{\varepsilon } = \begin{bmatrix}
\varepsilon _{1}\\
\varepsilon _{2}\\
\varepsilon _{3}\\
\varepsilon _{4}\\
\varepsilon _{5}
\end{bmatrix}\)
由\(\bold{x}^T\bold{x}\boldsymbol{\beta}=\bold{x}^T\bold{y}\) 得 \(\boldsymbol{\beta} = (\bold{x^{T}x})^{-1}\bold{x^{T}}\bold{y}\)
octave计算结果如下:
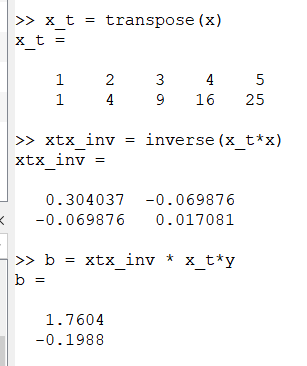
得\(\beta_{1} = 1.76,\beta_{2} = -0.20\)
曲线方程为:\(y = 1.76x - 0.20x^2\)
拟合效果如下图: