整个spring mvc的架构如下图所示:
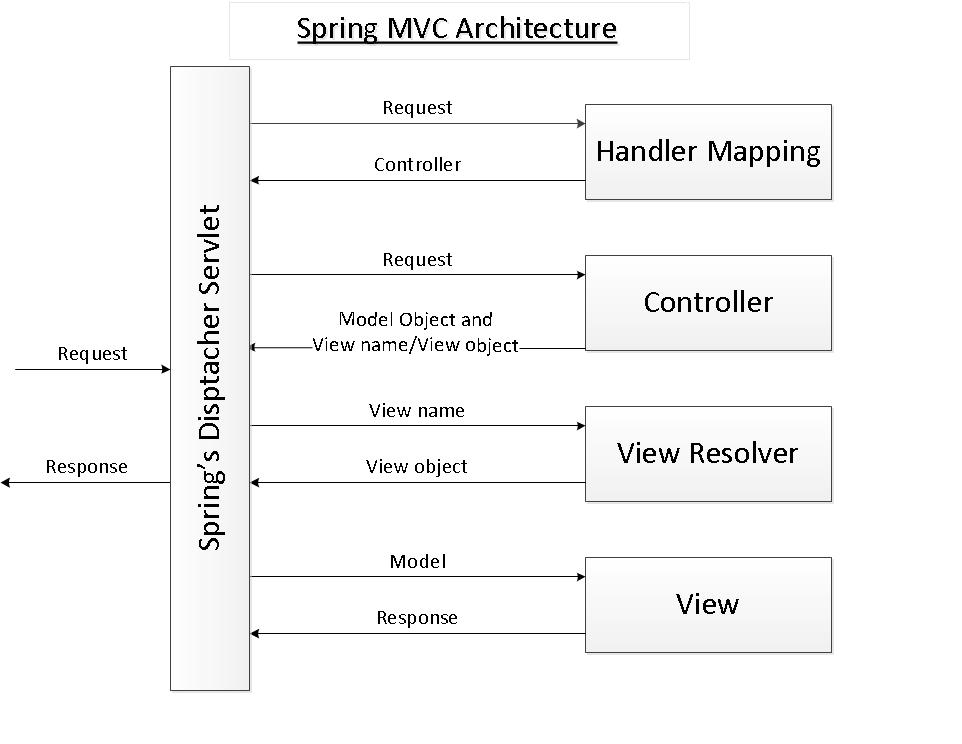
上篇文件讲解了DispatcherServlet第二步:通过request从Controller获取ModelAndView。现在来讲解第三步:request 从ModelAndView中获取view对象。
获取view对象一般是通过viewResolver来解析view name来完成的。若ModelAndView中view 不存在或者ModelAndView本身为null则填充默认值。代码如下:
ModelAndView中view 不存在或者ModelAndView本身为null
DispatcherServlet doService--->doDispatcher-->applyDefaultViewName(request, mv);
/** * Do we need view name translation? */ private void applyDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request, ModelAndView mv) throws Exception { if (mv != null && !mv.hasView()) { mv.setViewName(getDefaultViewName(request)); } }
从request中解析出默认view name
/** * Translate the supplied request into a default view name. * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the view name (or {@code null} if no default found) * @throws Exception if view name translation failed */ protected String getDefaultViewName(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { return this.viewNameTranslator.getViewName(request); }
我们先了解一下这个viewNameTranslator是怎么得到的吧?从容器中获取bean,bean 名称为:DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
/** * Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses. * <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects. */ protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) { initMultipartResolver(context); initLocaleResolver(context); initThemeResolver(context); initHandlerMappings(context); initHandlerAdapters(context); initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context); initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context); initViewResolvers(context); initFlashMapManager(context); } * Initialize the RequestToViewNameTranslator used by this servlet instance. * <p>If no implementation is configured then we default to DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator. */ private void initRequestToViewNameTranslator(ApplicationContext context) { try { this.viewNameTranslator = context.getBean(REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using RequestToViewNameTranslator [" + this.viewNameTranslator + "]"); } } catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) { // We need to use the default. this.viewNameTranslator = getDefaultStrategy(context, RequestToViewNameTranslator.class); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Unable to locate RequestToViewNameTranslator with name '" + REQUEST_TO_VIEW_NAME_TRANSLATOR_BEAN_NAME + "': using default [" + this.viewNameTranslator + "]"); } } }
获取默认view name的真正实现方法如下:
/** * Translates the request URI of the incoming {@link HttpServletRequest} * into the view name based on the configured parameters. * @see org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper#getLookupPathForRequest * @see #transformPath */ @Override public String getViewName(HttpServletRequest request) { String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request); return (this.prefix + transformPath(lookupPath) + this.suffix); } /** * Transform the request URI (in the context of the webapp) stripping * slashes and extensions, and replacing the separator as required. * @param lookupPath the lookup path for the current request, * as determined by the UrlPathHelper * @return the transformed path, with slashes and extensions stripped * if desired */ protected String transformPath(String lookupPath) { String path = lookupPath; if (this.stripLeadingSlash && path.startsWith(SLASH)) { path = path.substring(1); } if (this.stripTrailingSlash && path.endsWith(SLASH)) { path = path.substring(0, path.length() - 1); } if (this.stripExtension) { path = StringUtils.stripFilenameExtension(path); } if (!SLASH.equals(this.separator)) { path = StringUtils.replace(path, SLASH, this.separator); } return path; }
完整实现如下:
/** * Return the mapping lookup path for the given request, within the current * servlet mapping if applicable, else within the web application. * <p>Detects include request URL if called within a RequestDispatcher include. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the lookup path * @see #getPathWithinApplication * @see #getPathWithinServletMapping */ public String getLookupPathForRequest(HttpServletRequest request) { // Always use full path within current servlet context? if (this.alwaysUseFullPath) { return getPathWithinApplication(request); } // Else, use path within current servlet mapping if applicable String rest = getPathWithinServletMapping(request); if (!"".equals(rest)) { return rest; } else { return getPathWithinApplication(request); } } /** * Return the path within the servlet mapping for the given request, * i.e. the part of the request's URL beyond the part that called the servlet, * or "" if the whole URL has been used to identify the servlet. * <p>Detects include request URL if called within a RequestDispatcher include. * <p>E.g.: servlet mapping = "/test/*"; request URI = "/test/a" -> "/a". * <p>E.g.: servlet mapping = "/test"; request URI = "/test" -> "". * <p>E.g.: servlet mapping = "/*.test"; request URI = "/a.test" -> "". * @param request current HTTP request * @return the path within the servlet mapping, or "" */ public String getPathWithinServletMapping(HttpServletRequest request) { String pathWithinApp = getPathWithinApplication(request); String servletPath = getServletPath(request); String path = getRemainingPath(pathWithinApp, servletPath, false); if (path != null) { // Normal case: URI contains servlet path. return path; } else { // Special case: URI is different from servlet path. String pathInfo = request.getPathInfo(); if (pathInfo != null) { // Use path info if available. Indicates index page within a servlet mapping? // e.g. with index page: URI="/", servletPath="/index.html" return pathInfo; } if (!this.urlDecode) { // No path info... (not mapped by prefix, nor by extension, nor "/*") // For the default servlet mapping (i.e. "/"), urlDecode=false can // cause issues since getServletPath() returns a decoded path. // If decoding pathWithinApp yields a match just use pathWithinApp. path = getRemainingPath(decodeInternal(request, pathWithinApp), servletPath, false); if (path != null) { return pathWithinApp; } } // Otherwise, use the full servlet path. return servletPath; } } /** * Return the path within the web application for the given request. * <p>Detects include request URL if called within a RequestDispatcher include. * @param request current HTTP request * @return the path within the web application */ public String getPathWithinApplication(HttpServletRequest request) { String contextPath = getContextPath(request); String requestUri = getRequestUri(request); String path = getRemainingPath(requestUri, contextPath, true); if (path != null) { // Normal case: URI contains context path. return (StringUtils.hasText(path) ? path : "/"); } else { return requestUri; } } /** * Match the given "mapping" to the start of the "requestUri" and if there * is a match return the extra part. This method is needed because the * context path and the servlet path returned by the HttpServletRequest are * stripped of semicolon content unlike the requesUri. */ private String getRemainingPath(String requestUri, String mapping, boolean ignoreCase) { int index1 = 0; int index2 = 0; for (; (index1 < requestUri.length()) && (index2 < mapping.length()); index1++, index2++) { char c1 = requestUri.charAt(index1); char c2 = mapping.charAt(index2); if (c1 == ';') { index1 = requestUri.indexOf('/', index1); if (index1 == -1) { return null; } c1 = requestUri.charAt(index1); } if (c1 == c2) { continue; } if (ignoreCase && (Character.toLowerCase(c1) == Character.toLowerCase(c2))) { continue; } return null; } if (index2 != mapping.length()) { return null; } if (index1 == requestUri.length()) { return ""; } else if (requestUri.charAt(index1) == ';') { index1 = requestUri.indexOf('/', index1); } return (index1 != -1 ? requestUri.substring(index1) : ""); }
ModelAndView中view 定义为view name,解析为view实例。
DispatcherServlet doService--->doDispatcher-->processDispatchResult--->render--->resolveViewName
/** * Resolve the given view name into a View object (to be rendered). * <p>The default implementations asks all ViewResolvers of this dispatcher. * Can be overridden for custom resolution strategies, potentially based on * specific model attributes or request parameters. * @param viewName the name of the view to resolve * @param model the model to be passed to the view * @param locale the current locale * @param request current HTTP servlet request * @return the View object, or {@code null} if none found * @throws Exception if the view cannot be resolved * (typically in case of problems creating an actual View object) * @see ViewResolver#resolveViewName */ protected View resolveViewName(String viewName, Map<String, Object> model, Locale locale, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) { View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale); if (view != null) { return view; } } return null; }
InternalResourceViewResolver是具体实现:
@Override protected AbstractUrlBasedView buildView(String viewName) throws Exception { InternalResourceView view = (InternalResourceView) super.buildView(viewName); if (this.alwaysInclude != null) { view.setAlwaysInclude(this.alwaysInclude); } if (this.exposeContextBeansAsAttributes != null) { view.setExposeContextBeansAsAttributes(this.exposeContextBeansAsAttributes); } if (this.exposedContextBeanNames != null) { view.setExposedContextBeanNames(this.exposedContextBeanNames); } view.setPreventDispatchLoop(true); return view; }
/**
* Creates a new View instance of the specified view class and configures it.
* Does <i>not</i> perform any lookup for pre-defined View instances.
* <p>Spring lifecycle methods as defined by the bean container do not have to
* be called here; those will be applied by the {@code loadView} method
* after this method returns.
* <p>Subclasses will typically call {@code super.buildView(viewName)}
* first, before setting further properties themselves. {@code loadView}
* will then apply Spring lifecycle methods at the end of this process.
* @param viewName the name of the view to build
* @return the View instance
* @throws Exception if the view couldn't be resolved
* @see #loadView(String, java.util.Locale)
*/
protected AbstractUrlBasedView buildView(String viewName) throws Exception {
AbstractUrlBasedView view = (AbstractUrlBasedView) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(getViewClass());
view.setUrl(getPrefix() + viewName + getSuffix());
String contentType = getContentType();
if (contentType != null) {
view.setContentType(contentType);
}
view.setRequestContextAttribute(getRequestContextAttribute());
view.setAttributesMap(getAttributesMap());
Boolean exposePathVariables = getExposePathVariables();
if (exposePathVariables != null) {
view.setExposePathVariables(exposePathVariables);
}
return view;
}
ModelAndView 本身存在view实例
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object. view = mv.getView();
不需要查询,使用getView方法即可获取到。
小结:
本文主要讲解request怎么从ModelAndView中获取view实例的,分三种情况:mv本身为空或者mv中view为空时,使用默认的view name;mv本身中view 为string 表示viewname而非view实例,那么根据view name使用viewResolver转换成view实例;mv本身有view实例则使用getview方法获取。

微信公众号: 架构师日常笔记 欢迎关注!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号